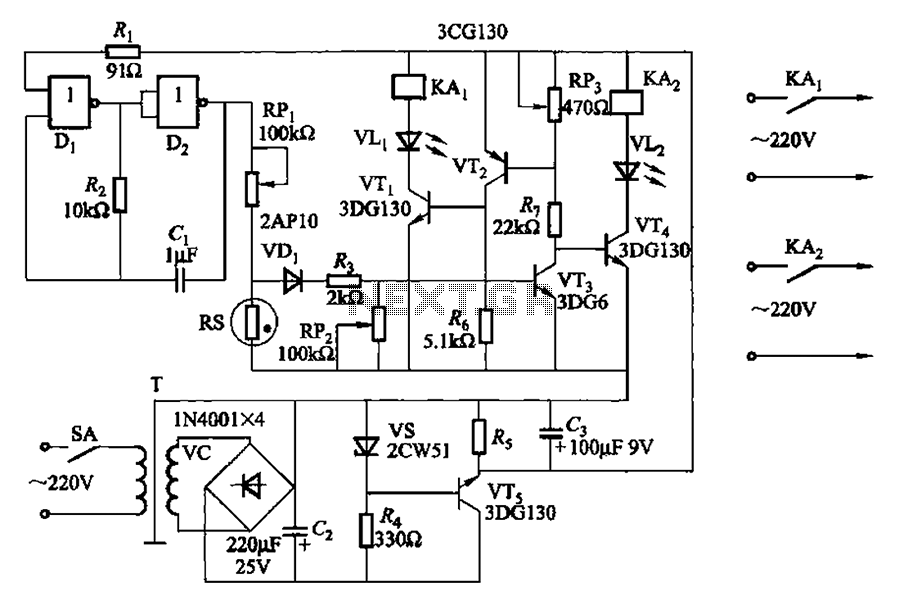
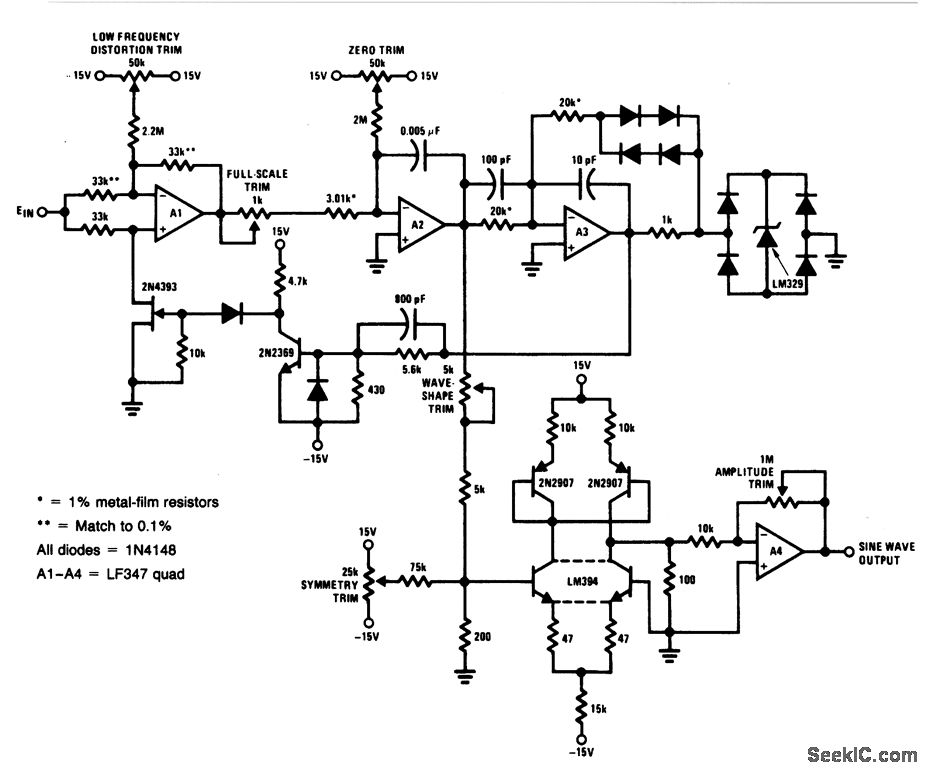
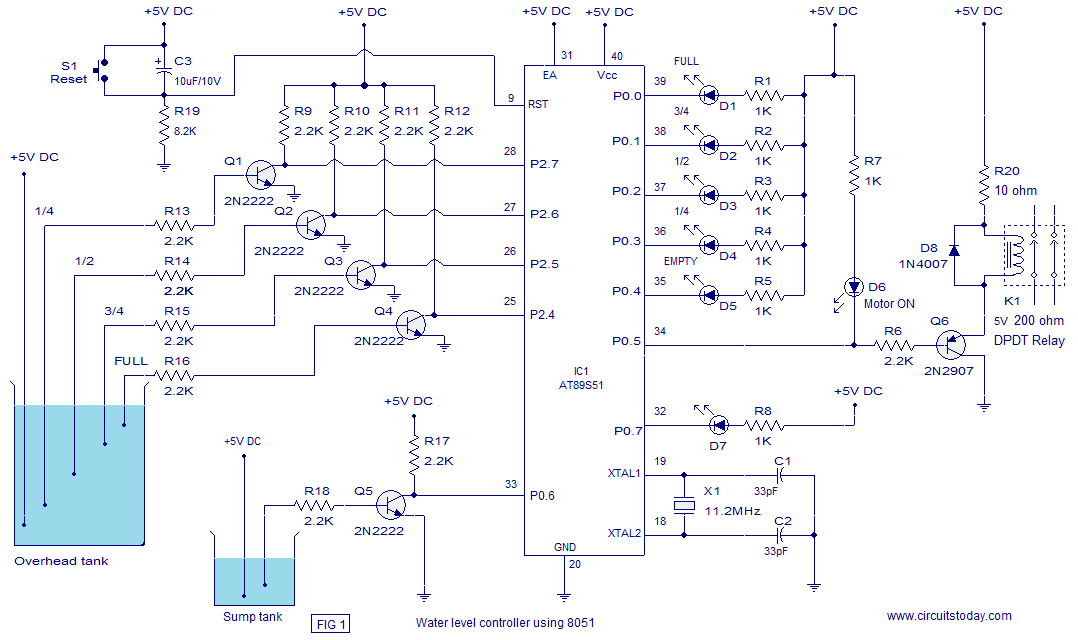
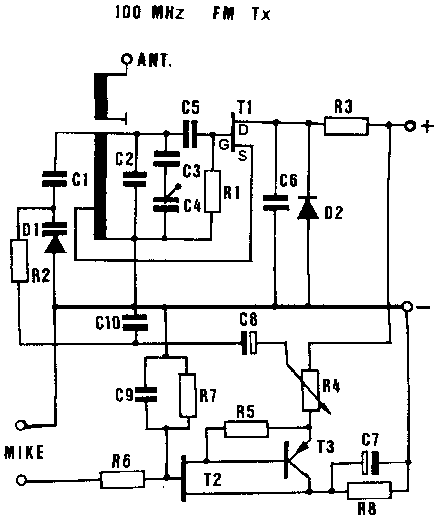
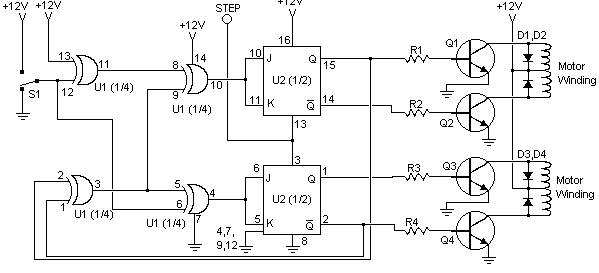
Radio frequency Of Remote Control
This is a remote control circuit that uses radio frequency electrical signals to control a variety of applications. Component: Transistor.
The remote control circuit operates by transmitting radio frequency (RF) signals to communicate with various devices. At its core, the circuit typically comprises a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter generates RF signals, which are modulated to convey specific commands, while the receiver interprets these signals to execute the desired actions on the controlled device.
Key components of the circuit include a transistor, which functions as a switch or amplifier, allowing for the modulation of the RF signal. The circuit may also incorporate resistors, capacitors, and inductors to form oscillators and filters that ensure the RF signal is stable and operates within the desired frequency range.
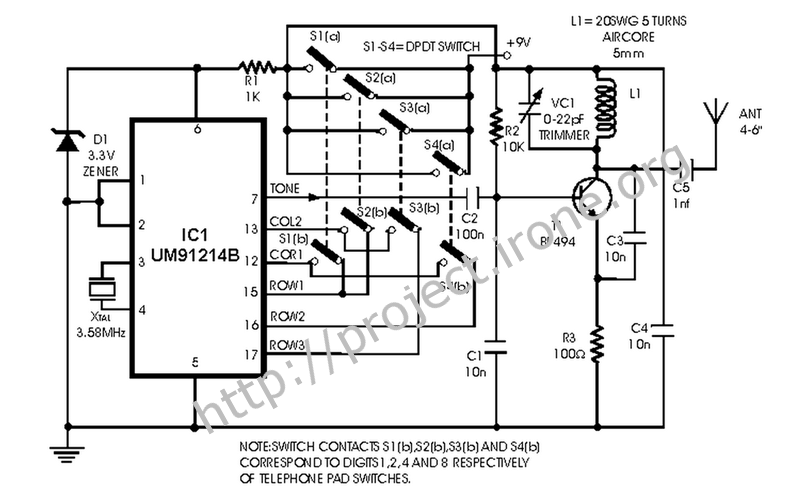
The transmitter section usually consists of an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency signal. This signal is then modulated using a method such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM) to encode the control commands. The modulated signal is amplified by the transistor before being sent out through an antenna.
On the receiving end, the receiver circuit captures the RF signals using an antenna and demodulates them to extract the control commands. This is typically achieved using another transistor configured as a demodulator, along with additional components to filter and amplify the received signal. The output of the receiver can then be connected to a microcontroller or relay, which executes the commands by controlling various devices, such as motors, lights, or other electronic systems.
Overall, this remote control circuit provides a versatile solution for wireless control applications, enabling users to operate devices from a distance with ease and convenience.This is a remote control Circuit that uses radio frequency electrical signal to control a variety of applications. Component: Transistor, .. 🔗 External reference
The remote control circuit operates by transmitting radio frequency (RF) signals to communicate with various devices. At its core, the circuit typically comprises a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter generates RF signals, which are modulated to convey specific commands, while the receiver interprets these signals to execute the desired actions on the controlled device.
Key components of the circuit include a transistor, which functions as a switch or amplifier, allowing for the modulation of the RF signal. The circuit may also incorporate resistors, capacitors, and inductors to form oscillators and filters that ensure the RF signal is stable and operates within the desired frequency range.
The transmitter section usually consists of an oscillator circuit that generates a high-frequency signal. This signal is then modulated using a method such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM) to encode the control commands. The modulated signal is amplified by the transistor before being sent out through an antenna.
On the receiving end, the receiver circuit captures the RF signals using an antenna and demodulates them to extract the control commands. This is typically achieved using another transistor configured as a demodulator, along with additional components to filter and amplify the received signal. The output of the receiver can then be connected to a microcontroller or relay, which executes the commands by controlling various devices, such as motors, lights, or other electronic systems.
Overall, this remote control circuit provides a versatile solution for wireless control applications, enabling users to operate devices from a distance with ease and convenience.This is a remote control Circuit that uses radio frequency electrical signal to control a variety of applications. Component: Transistor, .. 🔗 External reference