Radio remote control circuit
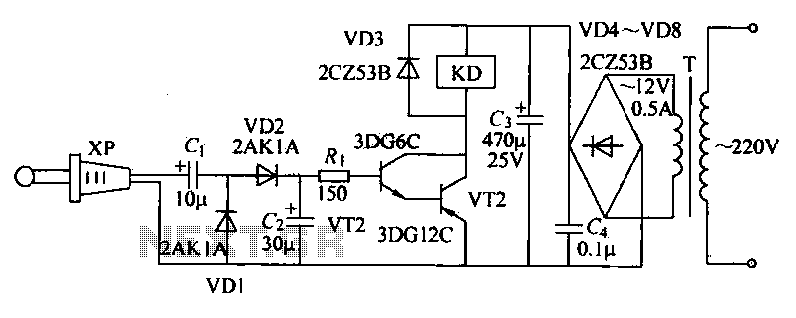
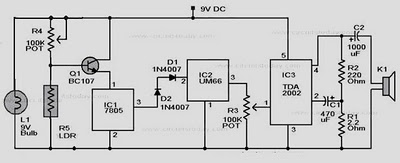
The receiver circuit depicted in the figure requires the insertion of a plug into the radio headphone jack. When the radio receiver detects a signal from the transmitter, an audio signal is output from the jack. This signal is then rectified and filtered by diodes VD1, VD2, and capacitor C2, resulting in a direct current (DC) signal. This DC signal is fed to transistors VT1 and VT2, which are configured as a composite transistor arrangement. When activated, these transistors energize relay KD. The relay's normally open and normally closed contacts can be utilized to connect to any load circuit, enabling wireless remote control for turning devices on or off.
The receiver circuit operates by receiving an audio signal from a transmitter, which is input through a radio headphone jack (XP). The process begins with the detection of the transmitted audio signal, which is then sent to the rectification stage. Diodes VD1 and VD2 serve as rectifiers, converting the alternating current (AC) audio signal into a pulsating DC signal. This pulsating signal is smoothed out by capacitor C2, which acts as a filter, providing a steady DC output that is suitable for further processing.
The output from the filter is connected to the base terminals of transistors VT1 and VT2. These transistors are arranged in a composite configuration, allowing them to amplify the DC signal effectively. When the transistors are turned on, they complete the circuit for relay KD, causing it to activate. The relay is a crucial component in this circuit, as it allows for control over a larger load circuit without the need for direct electrical connection to the control circuit.
Relay KD features both normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contacts. The NO contacts close when the relay is energized, allowing current to flow through the connected load circuit. Conversely, the NC contacts open, interrupting the current flow. This dual functionality enables the circuit to be used for various applications, including remote control of lights, fans, or other electronic devices. The design of this receiver circuit provides a simple yet effective solution for wireless control, making it suitable for a range of practical applications in home automation and remote device management.The receiver circuit shown in FIG. Insert the plug XP radio headphone jack xs, when the radio receiver to the hair after the transmitter signal, the audio signal output from xs by VD1, VD2, c2 rectifier filter, the resulting DC signal is applied by the VT1, VT2 constituting the composite tube base, turning it on, so the relay KD pull. KD pull, can use its normally open and normally closed contacts connected to any load circuit, realize the wireless remote control to turn on or off.
The receiver circuit operates by receiving an audio signal from a transmitter, which is input through a radio headphone jack (XP). The process begins with the detection of the transmitted audio signal, which is then sent to the rectification stage. Diodes VD1 and VD2 serve as rectifiers, converting the alternating current (AC) audio signal into a pulsating DC signal. This pulsating signal is smoothed out by capacitor C2, which acts as a filter, providing a steady DC output that is suitable for further processing.
The output from the filter is connected to the base terminals of transistors VT1 and VT2. These transistors are arranged in a composite configuration, allowing them to amplify the DC signal effectively. When the transistors are turned on, they complete the circuit for relay KD, causing it to activate. The relay is a crucial component in this circuit, as it allows for control over a larger load circuit without the need for direct electrical connection to the control circuit.
Relay KD features both normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contacts. The NO contacts close when the relay is energized, allowing current to flow through the connected load circuit. Conversely, the NC contacts open, interrupting the current flow. This dual functionality enables the circuit to be used for various applications, including remote control of lights, fans, or other electronic devices. The design of this receiver circuit provides a simple yet effective solution for wireless control, making it suitable for a range of practical applications in home automation and remote device management.The receiver circuit shown in FIG. Insert the plug XP radio headphone jack xs, when the radio receiver to the hair after the transmitter signal, the audio signal output from xs by VD1, VD2, c2 rectifier filter, the resulting DC signal is applied by the VT1, VT2 constituting the composite tube base, turning it on, so the relay KD pull. KD pull, can use its normally open and normally closed contacts connected to any load circuit, realize the wireless remote control to turn on or off.