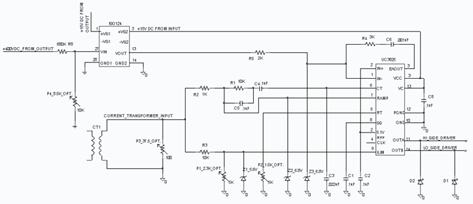
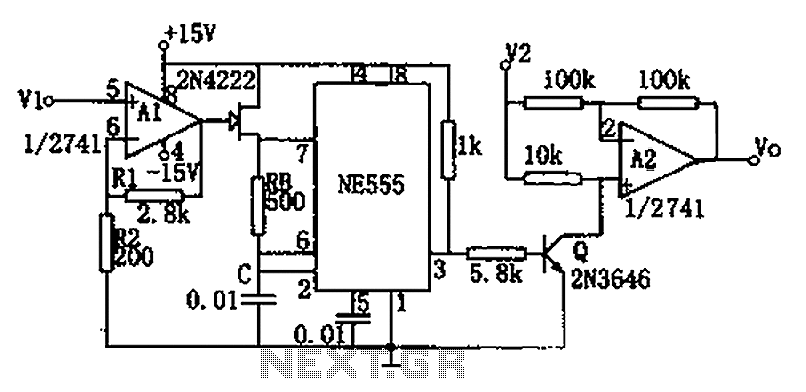
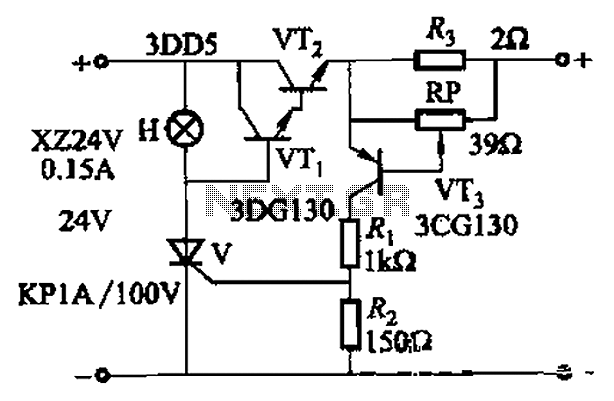
Rf-Type Battery Charger Circuit

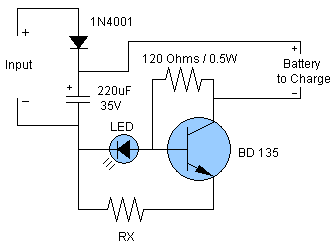
This type of charger transfers RF energy from an inductor (L2) to an external pickup coil. The pickup coil is connected to a rectifier and a battery that requires charging. This design is advantageous as it eliminates the need for wires or contacts. L2 consists of 10 turns of #24 wire, while L3 is made of 10 turns of #30 wire. Both coils are mounted on a 1V ferrite rod.
The described RF charger operates on the principle of inductive coupling, where an alternating magnetic field produced by L2 induces a voltage in the external pickup coil. The use of RF energy is particularly beneficial in applications where contact-based charging methods are impractical or undesirable. The design's reliance on ferrite material enhances the efficiency of energy transfer by providing a high magnetic permeability, which concentrates the magnetic field and reduces losses.
In this configuration, L2 acts as the primary coil, generating an RF field when energized. The external pickup coil, acting as the secondary, captures this energy and converts it into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. The rectifier connected to the pickup coil is crucial for converting the induced AC voltage into a usable DC voltage suitable for charging the battery.
The choice of wire gauge for the coils is significant; #24 wire for L2 and #30 wire for L3 indicates a balance between resistance and inductance. Thicker wire (like #24) for the primary coil allows for lower resistance and better current handling, while the thinner wire (like #30) for the secondary coil may be sufficient for the lower currents expected during the charging process.
The 1V ferrite rod serves as a structural support for the coils while also enhancing the magnetic coupling between them. The dimensions and material properties of the ferrite rod are critical in optimizing the performance of the charger, as they affect the inductance values and the efficiency of energy transfer.
This wireless charging system can be utilized in various applications, including medical implants, consumer electronics, and other devices where traditional charging methods may be impractical. The absence of physical connectors minimizes wear and tear, reduces maintenance, and enhances the overall reliability of the charging solution. This type of charger couples RF from L2 to an external pickup coil. The pickup coil connects to a rectifier and battery to be charged. This idea is handy because no wire or contacts are required. L2 is 10T #24 wire and L3 is 10T #30 wire. Both coils are mounted on a 1 V ferrite rod. 🔗 External reference
The described RF charger operates on the principle of inductive coupling, where an alternating magnetic field produced by L2 induces a voltage in the external pickup coil. The use of RF energy is particularly beneficial in applications where contact-based charging methods are impractical or undesirable. The design's reliance on ferrite material enhances the efficiency of energy transfer by providing a high magnetic permeability, which concentrates the magnetic field and reduces losses.
In this configuration, L2 acts as the primary coil, generating an RF field when energized. The external pickup coil, acting as the secondary, captures this energy and converts it into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. The rectifier connected to the pickup coil is crucial for converting the induced AC voltage into a usable DC voltage suitable for charging the battery.
The choice of wire gauge for the coils is significant; #24 wire for L2 and #30 wire for L3 indicates a balance between resistance and inductance. Thicker wire (like #24) for the primary coil allows for lower resistance and better current handling, while the thinner wire (like #30) for the secondary coil may be sufficient for the lower currents expected during the charging process.
The 1V ferrite rod serves as a structural support for the coils while also enhancing the magnetic coupling between them. The dimensions and material properties of the ferrite rod are critical in optimizing the performance of the charger, as they affect the inductance values and the efficiency of energy transfer.
This wireless charging system can be utilized in various applications, including medical implants, consumer electronics, and other devices where traditional charging methods may be impractical. The absence of physical connectors minimizes wear and tear, reduces maintenance, and enhances the overall reliability of the charging solution. This type of charger couples RF from L2 to an external pickup coil. The pickup coil connects to a rectifier and battery to be charged. This idea is handy because no wire or contacts are required. L2 is 10T #24 wire and L3 is 10T #30 wire. Both coils are mounted on a 1 V ferrite rod. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713