
room noise detector
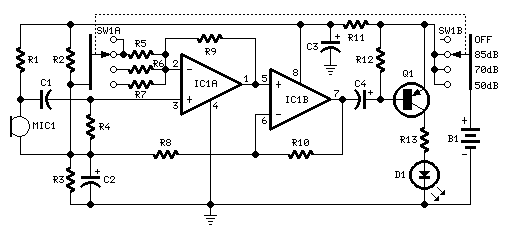
This circuit is designed to indicate, via a flashing LED, when room noise exceeds a predetermined threshold, which can be set to one of three fixed levels: 50, 70, or 85 dB. Two operational amplifiers (op-amps) are utilized to amplify sounds detected by a miniature electret microphone, enabling the LED to be driven appropriately. The circuit can be powered on or off using switch SW1, which has four positions. The first position turns the circuit off, while the second, third, and fourth positions activate the circuit and adjust the input sensitivity threshold to 85, 70, and 50 dB, respectively. The 50 dB setting is specifically intended for monitoring noise levels in a bedroom during nighttime. If the LED remains steadily illuminated or frequently flashes brightly, it indicates that the noise level in the bedroom is excessive and may disrupt sleep.
This noise threshold monitoring circuit employs a miniature electret microphone to capture ambient sound. The microphone's output is fed into two operational amplifiers configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration to increase the signal strength. The gain of the op-amps can be adjusted based on the selected threshold level, allowing for sensitivity tuning to accommodate different environments.
The circuit's design incorporates a potentiometer connected to the op-amps, enabling fine-tuning of the gain to achieve the desired sensitivity level. The output from the op-amps is then connected to a comparator circuit, which compares the amplified microphone signal against reference voltages corresponding to the fixed dB thresholds. When the microphone signal exceeds the set threshold, the comparator activates the LED driver circuit, causing the LED to flash or illuminate steadily.
The use of a switch (SW1) allows the user to select between the various sensitivity settings. In the first position, the circuit is completely powered down to conserve energy. The second through fourth positions activate the circuit and set the sensitivity to the respective thresholds of 85, 70, and 50 dB. The 50 dB threshold is particularly useful for monitoring nighttime noise levels in a bedroom, providing a practical application for improving sleep quality.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective noise monitoring solution, utilizing simple yet reliable components to provide visual feedback on ambient noise levels. The flashing LED acts as an alert to indicate when noise levels may be too high, promoting a quieter and more conducive sleeping environment.This circuit is intended to signal, through a flashing LED, the exceeding of a fixed threshold in room noise, chosen from three fixed levels, namely 50, 70 & 85 dB. Two Op-amps provide the necessary circuit gain for sounds picked-up by a miniature electret microphone to drive a LED.
With SW1 in the first position the circuit is off. Second, third and fourth positions power the circuit and set the input sensitivity threshold to 85, 70 & 50 dB respectively. The 50 dB setting is provided to monitor the noise in the bedroom at night. If the LED is steady on, or flashes bright often, then your bedroom is inadequate and too noisy for sleep.
🔗 External reference
This noise threshold monitoring circuit employs a miniature electret microphone to capture ambient sound. The microphone's output is fed into two operational amplifiers configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration to increase the signal strength. The gain of the op-amps can be adjusted based on the selected threshold level, allowing for sensitivity tuning to accommodate different environments.
The circuit's design incorporates a potentiometer connected to the op-amps, enabling fine-tuning of the gain to achieve the desired sensitivity level. The output from the op-amps is then connected to a comparator circuit, which compares the amplified microphone signal against reference voltages corresponding to the fixed dB thresholds. When the microphone signal exceeds the set threshold, the comparator activates the LED driver circuit, causing the LED to flash or illuminate steadily.
The use of a switch (SW1) allows the user to select between the various sensitivity settings. In the first position, the circuit is completely powered down to conserve energy. The second through fourth positions activate the circuit and set the sensitivity to the respective thresholds of 85, 70, and 50 dB. The 50 dB threshold is particularly useful for monitoring nighttime noise levels in a bedroom, providing a practical application for improving sleep quality.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective noise monitoring solution, utilizing simple yet reliable components to provide visual feedback on ambient noise levels. The flashing LED acts as an alert to indicate when noise levels may be too high, promoting a quieter and more conducive sleeping environment.This circuit is intended to signal, through a flashing LED, the exceeding of a fixed threshold in room noise, chosen from three fixed levels, namely 50, 70 & 85 dB. Two Op-amps provide the necessary circuit gain for sounds picked-up by a miniature electret microphone to drive a LED.
With SW1 in the first position the circuit is off. Second, third and fourth positions power the circuit and set the input sensitivity threshold to 85, 70 & 50 dB respectively. The 50 dB setting is provided to monitor the noise in the bedroom at night. If the LED is steady on, or flashes bright often, then your bedroom is inadequate and too noisy for sleep.
🔗 External reference
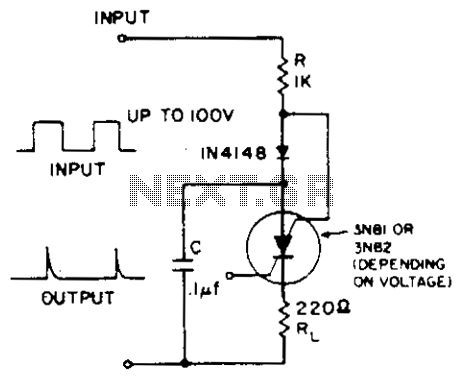
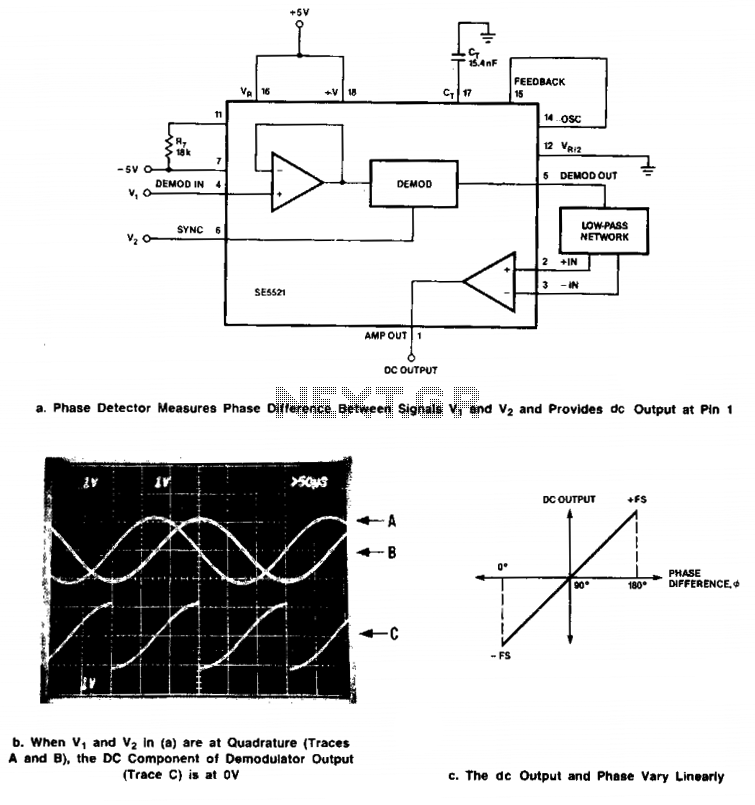
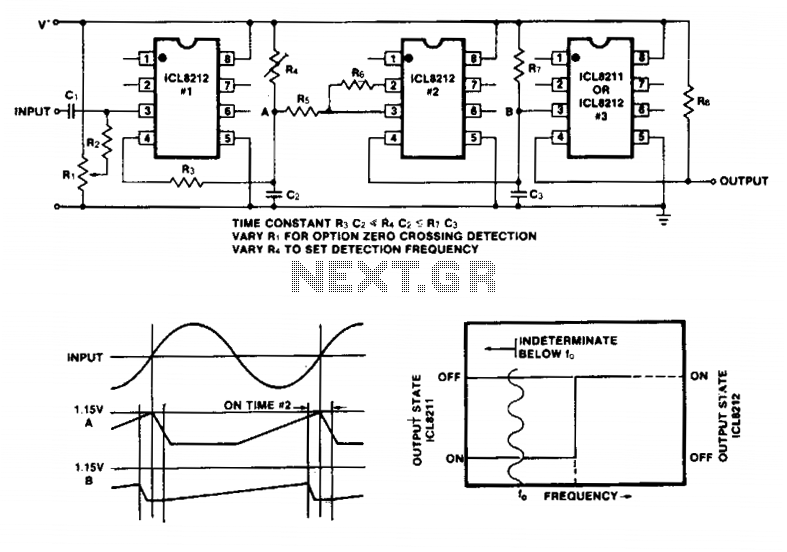
.png)