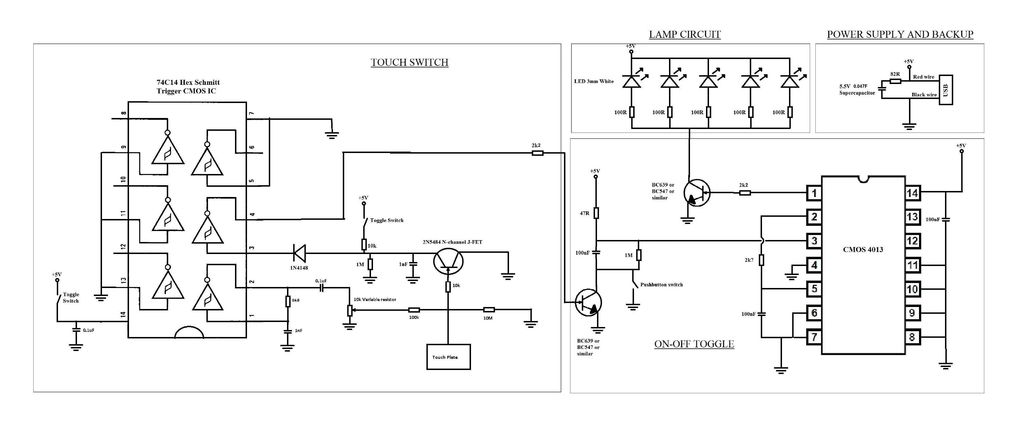
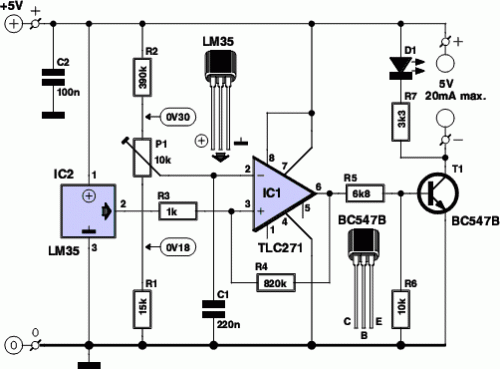
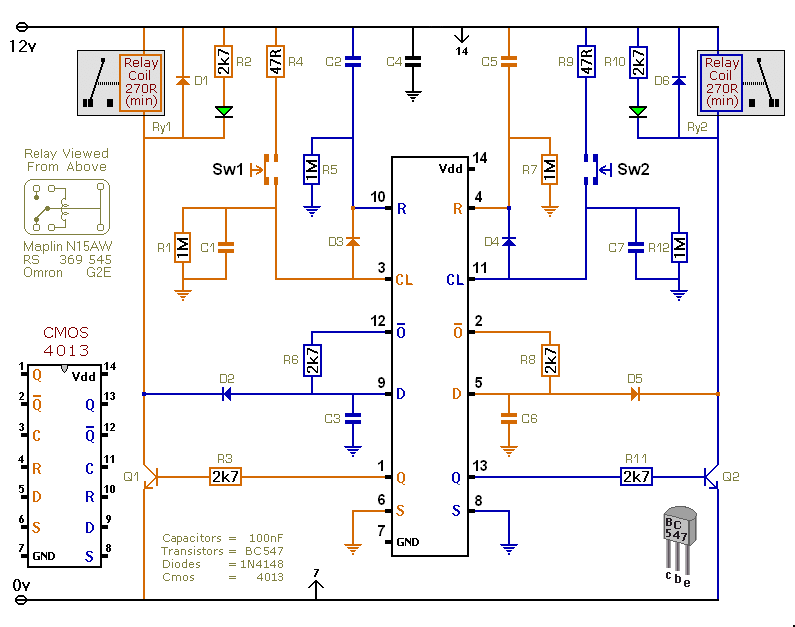
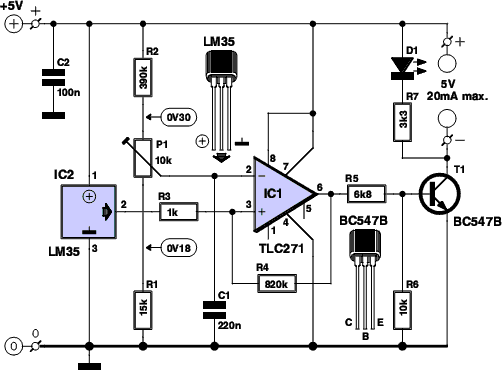
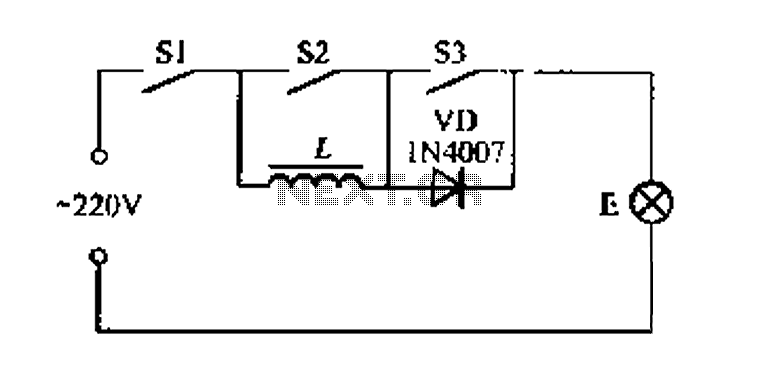
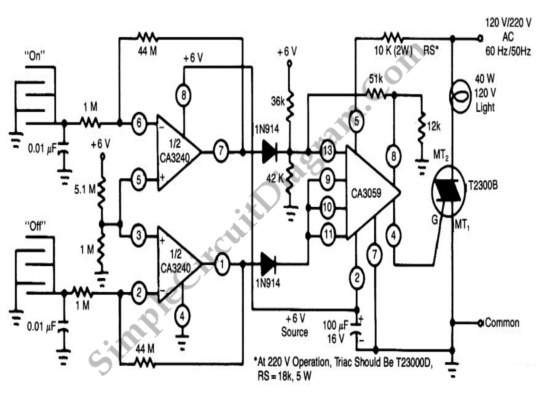
ROTARY SWITCH DEBOUNCE
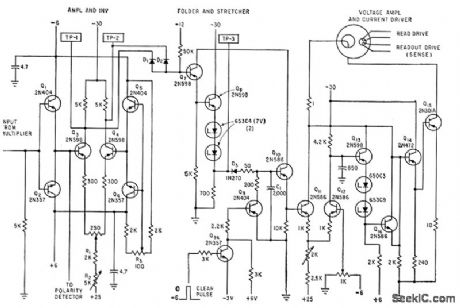
A three-stage active Butterworth bandpass input filter is utilized in a radioteletype demodulator to differentiate RTTY tones from one another and from noise. The filter is centered at 2200 Hz and has a bandwidth of approximately 260 Hz, allowing for the reception of some audio sidebands generated by keying and accommodating minor frequency drift. Five potentiometers are employed to adjust the center frequency and the Q factor of the end stages. The article provides step-by-step design and alignment procedures. Two 10K resistors are used between the voltage supply and ground to achieve a bias voltage of V/2 when operating from a single supply. Triggering is achieved by turning transistors on, in contrast to most similar circuits where transistors are turned off. The trigger pulse must only lower the voltage below ground for a fraction of a microsecond. Any diode and transistor can be utilized, with operational speeds reaching up to 10 MHz when using high-speed transistors. The output fall time is rapid. A simple circuit employing the Signetics NE565 phase-locked loop (PLL) locks onto the input frequency and tracks it between two specified values to produce a corresponding DC shift at the output. The specified values pertain to 1070-Hz and 1270-Hz FSK signals. A three-stage RC ladder filter eliminates the sum frequency component, with the band edge of the filter selected to be approximately midway between the maximum keying rate (150 Hz) and twice the input frequency (approximately 2200 Hz). The output is made logic-compatible by connecting a voltage comparator to pin 6. Cross-coupling two basic inverters results in a low-cost flip-flop using 2N711 germanium PNP mesa switching transistors. The flip-flop can be set and subsequently reset, or operated as a counter using a combined input. Close regulation is necessary for the -4 V supply. A circuit is employed to protect sensitive equipment from prolonged high AC line voltage by disconnecting the supply when it exceeds a preset level determined by resistor R16. When the base-emitter voltage of transistor Tr2 exceeds 7.5 V, the optocoupler activates transistor Tr1 to enable rapid switching action. The output pulse is shaped by IC3 for triggering mono IC2. When the line voltage falls below the preset level, the mono reverts to a stable state, reconnecting the AC supply. Seven 567 PLLs detect the presence of selected tones from a common 100-200 VBBMS input line, while 8885 NOR gates perform the necessary decoding logic to generate decimal outputs. This circuit leverages the excellent frequency selectivity provided by the lock-and-capture ranges of the PLLs, which is essential for discriminating against multiple tones. The output of comparator A1 is high when the input signal exceeds zero and low when it is below zero, producing a square wave output in phase with the zero crossings of the input. When R1 is set to 22K, the input can handle amplitudes of up to ±10 V. A2 is a mono MVBR configured to trigger when output 1 of A1 goes high (at zero crossings), resulting in negative-going narrow pulses at output 2 that serve as useful time marks. This configuration is suitable for transferring data into storage systems with significant capacitive loads, such as long connecting wires. The complementary configuration, with the load situated in the emitter circuit of one transistor, ensures reliable triggering in a fraction of a microsecond. The circuit provides a full output of 60 V peak-to-peak up to 1 MHz, with a slew rate of 200 V/µs and a small-signal bandwidth of 5 MHz, utilizing a fast input operational amplifier, voltage buffer, and a straightforward compensation technique.Three-stage active Butterworth bandpass input filter is used in radioteletype demodulator to separate RTTY tones from each other and from noise. Filter is centered on 2200 Hz, and has bandpass of about 260 Hz to allow reception of some of audio sidebands produced by keying and allow for small drift.
Five pots serve for trimming center frequency of each stage andQ of end stages. Article gives step-by-step design and alignment procedures. Use two 10K resistors between V and ground to get V/2 for bias when operating from single supply. -P. A. Stark, Design an Active RTTY Filter, 73 Magazine, Sept. 1977, p 38-43. (View) Triggering is accomplished by turning transistors on, whereas in most similar circuits the transistors are turned off. Trigger pulse merely has to lower point o below ground for fraction of microsecond. Almost any diode and transistor can be used. Speed can be up to 10 Mc with high-speed transistors. Output fall time is fast. -Binary Flip-Flop Tums On, Electronic Circuit Design Handbook, Mactier Pub. Corp. , N. Y. , 1965, p 214. (View) Simple circuit for Signetics NE565 PLL locks to input frequency and tracks it between two values used, to produce corresponding DC shift at output.
Values shown are for 1070-Hz and 1270-Hz FSK signals. Three-stage RC ladder filter removes sum frequency component. Band edge of filter is chosen to be about halfway between maximum keying rate (150 Hz) and twice input frequency (about 2200 Hz). Output is made logic-compatible by connecting voltage comparator to pin 6. - Signetics Analog Data Manual, Signetics, Sunnyvale, CA, 1977, p 845. (View) Cross-coupling of two basic inverters gives low-cost lip-lop using 2N711 germanium pnp mesa switching transistors.
Flip-flop can be set and then reset, or run as Gaunter using combined input. Close regulation is required for -4 v supply. -P. A. Mclnnis, Low-Cost Computer Circuits, Motorola Application Note AN-130, Nov. 1965. (View) Used to protect delicate equipment from sustained high AC line voltage, by disconnecting supply when it exceeds preset level selected by R16. When base-emitter voltage of Tr2 exceeds 7. 5 V, optocoupler switches Tr1 on to provide fast switching action. Output pulse is shaped by IC3 for use in triggering mono IC2. When line falls below preset level, mono reverts to stable state and switches on AC supply again. -F. E. George, A. C. Line Sensor, Wireless World, March 1977, p 42. (View) Seven 567 PLLs sense presence of selected tones from common 100-200 VBMS input line, while 8885 NOR gates perform necessary decoding logic to generate decimal outputs.
Circuit takes advantage of good frequency selectivity provided by lock-and-capture ranges of PLLs, as required for discriminating against many tones. -E. Murthi, Monolithic Phase-Locked Loops-Analogs Do All the Work of Digitals, and Much More, EDN Magazine, Sept.
5, 1977, p 59-64. (View) Output 1 of 322 comparator A1 is high when input signal is above zero and low when input is below zero. Output of comparator A1 is thus square wave in phase with zero crossings of input. When R1, is 22K, input can be up to ±10 V amplitude. A2 is mono MVBR connected to fire when output 1 of A1 goes high (at zero crossings). Resulting negative-going narrow pulses at output 2 are useful for time marks. -W. G. Jung, IC Timer Cook-book, Howard W. Sams, Indianapolis, IN, 1977, p 152. (View) Used for transferring data into storage having heavy capacitive load, such as long connecting wires.
Complementary con figuration, with load in emitter circuit of one transistor, makes stage trigger reliably in fraction of microsecond. -Non-Stalling Flip-Flop for Capacitive Load, Electronic Circuit Design Handbook, Mactier Pub. Corp. , N. Y. , 1965, p 213. (View) Provides full output of 60 V P-P up to 1 MHz Slew rate is 200 V/ s, and small-signal bandwidth is 5 MHz.
Uses fastinput opamp, voltage buffer, and simple compensation technique. C2 is trimme 🔗 External reference
Five pots serve for trimming center frequency of each stage andQ of end stages. Article gives step-by-step design and alignment procedures. Use two 10K resistors between V and ground to get V/2 for bias when operating from single supply. -P. A. Stark, Design an Active RTTY Filter, 73 Magazine, Sept. 1977, p 38-43. (View) Triggering is accomplished by turning transistors on, whereas in most similar circuits the transistors are turned off. Trigger pulse merely has to lower point o below ground for fraction of microsecond. Almost any diode and transistor can be used. Speed can be up to 10 Mc with high-speed transistors. Output fall time is fast. -Binary Flip-Flop Tums On, Electronic Circuit Design Handbook, Mactier Pub. Corp. , N. Y. , 1965, p 214. (View) Simple circuit for Signetics NE565 PLL locks to input frequency and tracks it between two values used, to produce corresponding DC shift at output.
Values shown are for 1070-Hz and 1270-Hz FSK signals. Three-stage RC ladder filter removes sum frequency component. Band edge of filter is chosen to be about halfway between maximum keying rate (150 Hz) and twice input frequency (about 2200 Hz). Output is made logic-compatible by connecting voltage comparator to pin 6. - Signetics Analog Data Manual, Signetics, Sunnyvale, CA, 1977, p 845. (View) Cross-coupling of two basic inverters gives low-cost lip-lop using 2N711 germanium pnp mesa switching transistors.
Flip-flop can be set and then reset, or run as Gaunter using combined input. Close regulation is required for -4 v supply. -P. A. Mclnnis, Low-Cost Computer Circuits, Motorola Application Note AN-130, Nov. 1965. (View) Used to protect delicate equipment from sustained high AC line voltage, by disconnecting supply when it exceeds preset level selected by R16. When base-emitter voltage of Tr2 exceeds 7. 5 V, optocoupler switches Tr1 on to provide fast switching action. Output pulse is shaped by IC3 for use in triggering mono IC2. When line falls below preset level, mono reverts to stable state and switches on AC supply again. -F. E. George, A. C. Line Sensor, Wireless World, March 1977, p 42. (View) Seven 567 PLLs sense presence of selected tones from common 100-200 VBMS input line, while 8885 NOR gates perform necessary decoding logic to generate decimal outputs.
Circuit takes advantage of good frequency selectivity provided by lock-and-capture ranges of PLLs, as required for discriminating against many tones. -E. Murthi, Monolithic Phase-Locked Loops-Analogs Do All the Work of Digitals, and Much More, EDN Magazine, Sept.
5, 1977, p 59-64. (View) Output 1 of 322 comparator A1 is high when input signal is above zero and low when input is below zero. Output of comparator A1 is thus square wave in phase with zero crossings of input. When R1, is 22K, input can be up to ±10 V amplitude. A2 is mono MVBR connected to fire when output 1 of A1 goes high (at zero crossings). Resulting negative-going narrow pulses at output 2 are useful for time marks. -W. G. Jung, IC Timer Cook-book, Howard W. Sams, Indianapolis, IN, 1977, p 152. (View) Used for transferring data into storage having heavy capacitive load, such as long connecting wires.
Complementary con figuration, with load in emitter circuit of one transistor, makes stage trigger reliably in fraction of microsecond. -Non-Stalling Flip-Flop for Capacitive Load, Electronic Circuit Design Handbook, Mactier Pub. Corp. , N. Y. , 1965, p 213. (View) Provides full output of 60 V P-P up to 1 MHz Slew rate is 200 V/ s, and small-signal bandwidth is 5 MHz.
Uses fastinput opamp, voltage buffer, and simple compensation technique. C2 is trimme 🔗 External reference