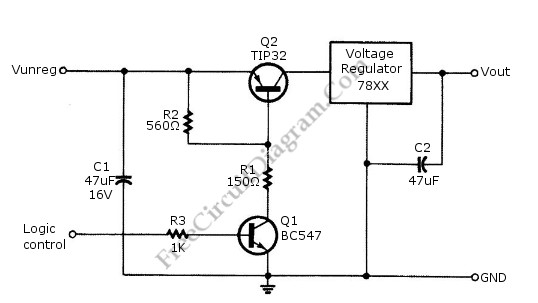
Scoring Game Circuit
This is a design for a scoring game circuit suitable for any occasion where dice are used. The circuit utilizes a NE555 timer, a 74LS192 counter, a 74LS247 decoder, and a seven-segment LED display. The timer IC1 generates a clock signal for the counter IC2, with the frequency determined by resistors R1 and capacitor C2. When switch S2 is activated, IC2 counts in an upward direction; conversely, when switch S3 is activated, IC2 counts downwards. The output from IC2 is decoded by IC3 to display the count on the seven-segment LED display. The circuit is designed with fundamental counter principles, making it an excellent project for beginners. To operate the game, the power must be switched on, and switch S1 should be pressed to reset the counter. Players can then press either S2 or S3 and release it to hold the last count. Pressing S4 will display the score. The second player follows the same procedure: pressing S1 to reset, then S2 or S3 to count, and S4 to view the score. The circuit can be powered using a 9V battery or a 9V regulated DC power supply.
The scoring game circuit serves as an educational tool for understanding basic digital electronics concepts, particularly in the use of timers and counters. The NE555 timer operates in astable mode, providing a continuous clock signal to the 74LS192 counter, which can count both up and down based on the switch inputs. The design incorporates debouncing techniques to ensure that switch presses are registered accurately without multiple counts from a single press.
The 74LS192 counter is a synchronous binary counter that provides a count output in binary format. This output is fed into the 74LS247 BCD to 7-segment decoder/driver, which converts the binary count into a format suitable for display on the seven-segment LED. This allows for clear and immediate visual feedback of the current score.
Power management is crucial in this design, with the option for a 9V battery or regulated power supply ensuring reliable operation. The choice of components allows for a compact design, suitable for portable applications. The circuit's simplicity and adherence to fundamental electronic principles make it an excellent project for beginners, providing hands-on experience with digital logic and component integration. Each interaction with the circuit reinforces learning about how timers and counters function in a practical context, making it an ideal educational tool.This is a design circuit for scoring game circuit that can be used for all occasions when a dice is needed. The circuit is based on a NE555 timer, a 74LS192 counter, a74LS247 decoder and a & segment LED display.
The timer IC1 will produce the clock for the counter IC(IC2) whose frequency is determined by R1 and C2. When S2 is pressed the IC2 will co unt in up mode and when S3 is pressed the IC2 will count in down mode. This is the figure of the circuit; The IC 3 will decode the count to display it on the seven segment LED display. That is about the working of the circuit. The circuit is designed strictly sticking on to the basics of counters and is a good one for beginners.
There is nothing big deal. To play the game switch the power ON and press S1 to reset the counter. Now press S2 or S3 and release. The IC2 will hold the last count. Now press S4 to see the score on display. That`s your score. Now the second person can try. Each time one tries, he should press the S1 to reset the count and then press S2 or S3 and then S4 to see the score. Circuit can be powered from a 9V radio cell or a 9V regulated DC power supply. 🔗 External reference
The scoring game circuit serves as an educational tool for understanding basic digital electronics concepts, particularly in the use of timers and counters. The NE555 timer operates in astable mode, providing a continuous clock signal to the 74LS192 counter, which can count both up and down based on the switch inputs. The design incorporates debouncing techniques to ensure that switch presses are registered accurately without multiple counts from a single press.
The 74LS192 counter is a synchronous binary counter that provides a count output in binary format. This output is fed into the 74LS247 BCD to 7-segment decoder/driver, which converts the binary count into a format suitable for display on the seven-segment LED. This allows for clear and immediate visual feedback of the current score.
Power management is crucial in this design, with the option for a 9V battery or regulated power supply ensuring reliable operation. The choice of components allows for a compact design, suitable for portable applications. The circuit's simplicity and adherence to fundamental electronic principles make it an excellent project for beginners, providing hands-on experience with digital logic and component integration. Each interaction with the circuit reinforces learning about how timers and counters function in a practical context, making it an ideal educational tool.This is a design circuit for scoring game circuit that can be used for all occasions when a dice is needed. The circuit is based on a NE555 timer, a 74LS192 counter, a74LS247 decoder and a & segment LED display.
The timer IC1 will produce the clock for the counter IC(IC2) whose frequency is determined by R1 and C2. When S2 is pressed the IC2 will co unt in up mode and when S3 is pressed the IC2 will count in down mode. This is the figure of the circuit; The IC 3 will decode the count to display it on the seven segment LED display. That is about the working of the circuit. The circuit is designed strictly sticking on to the basics of counters and is a good one for beginners.
There is nothing big deal. To play the game switch the power ON and press S1 to reset the counter. Now press S2 or S3 and release. The IC2 will hold the last count. Now press S4 to see the score on display. That`s your score. Now the second person can try. Each time one tries, he should press the S1 to reset the count and then press S2 or S3 and then S4 to see the score. Circuit can be powered from a 9V radio cell or a 9V regulated DC power supply. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713