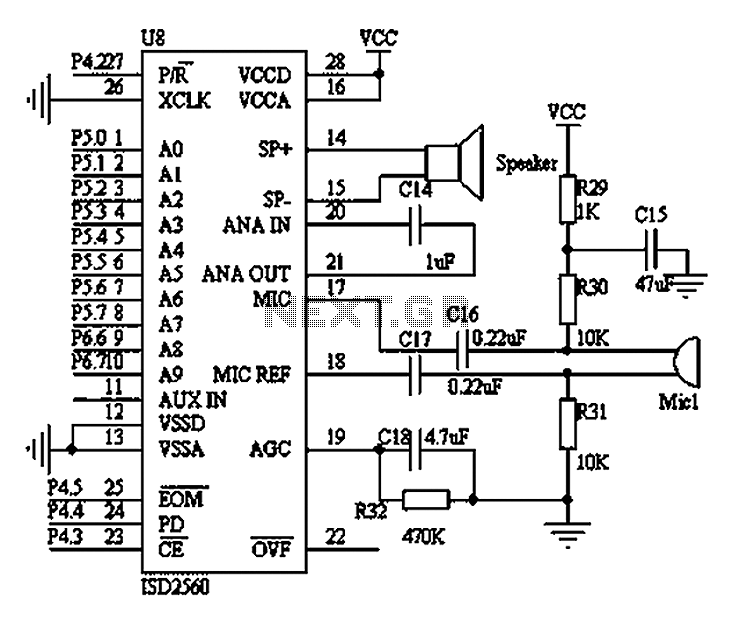
Selective Preamplifier For Infrared Photodiode Circuit
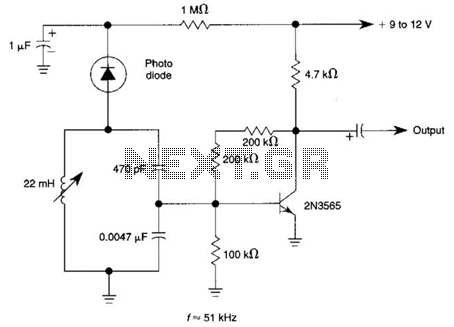
The circuit utilizes a tuned circuit for frequency selection, designed to operate at approximately 51 kHz. The 2N3565 transistor amplifies the output generated by the tuned circuit.
The described circuit operates on the principle of resonance, where the tuned circuit is typically composed of an inductor and a capacitor. At the specified frequency of 51 kHz, the circuit is designed to selectively amplify signals that match this frequency while attenuating others. The choice of components, including the inductor and capacitor values, is critical to achieving the desired resonant frequency.
The 2N3565 is a high-frequency NPN transistor that is well-suited for this application due to its ability to operate effectively in the RF range. It is commonly used in amplification stages of radio frequency circuits. When the tuned circuit receives an input signal at or near 51 kHz, it resonates, producing a voltage that is fed into the base of the 2N3565.
The transistor then amplifies this voltage, providing a higher power output that can be utilized for further processing or transmission. Proper biasing of the transistor is essential to ensure it operates in the active region, allowing for linear amplification of the input signal. Additionally, the circuit may include resistors and capacitors for stability and to set the gain of the amplifier.
Overall, this circuit configuration is typical in applications such as radio receivers, where selective frequency amplification is required to isolate desired signals from a range of frequencies. The circuit uses a tuned circuit to achieve frequency selection. Values are for operation at about 51 kHz. The 2N3565 amplifies the output developed by the tuned circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates on the principle of resonance, where the tuned circuit is typically composed of an inductor and a capacitor. At the specified frequency of 51 kHz, the circuit is designed to selectively amplify signals that match this frequency while attenuating others. The choice of components, including the inductor and capacitor values, is critical to achieving the desired resonant frequency.
The 2N3565 is a high-frequency NPN transistor that is well-suited for this application due to its ability to operate effectively in the RF range. It is commonly used in amplification stages of radio frequency circuits. When the tuned circuit receives an input signal at or near 51 kHz, it resonates, producing a voltage that is fed into the base of the 2N3565.
The transistor then amplifies this voltage, providing a higher power output that can be utilized for further processing or transmission. Proper biasing of the transistor is essential to ensure it operates in the active region, allowing for linear amplification of the input signal. Additionally, the circuit may include resistors and capacitors for stability and to set the gain of the amplifier.
Overall, this circuit configuration is typical in applications such as radio receivers, where selective frequency amplification is required to isolate desired signals from a range of frequencies. The circuit uses a tuned circuit to achieve frequency selection. Values are for operation at about 51 kHz. The 2N3565 amplifies the output developed by the tuned circuit. 🔗 External reference