SENSITIVE RF VOLTMETER
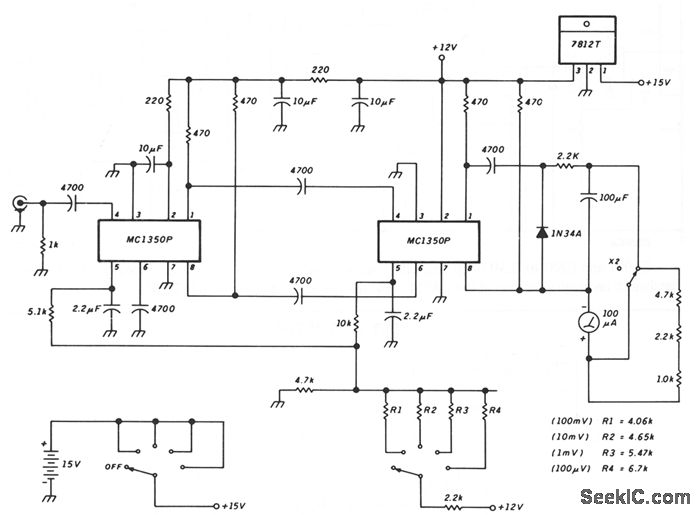
This schematic illustrates a peak-reading diode voltmeter that is powered by two amplification stages. A 100 µF capacitor is utilized to create a substantial time constant, which ensures effective damping of the meter. The restricted differential output voltage, combined with an overdamped meter, minimizes the risk of needle pinning when an incorrect range is selected or when other errors occur. An SPST toggle switch is employed to add extra series resistance. This X2 function enhances the overlap of the sensitivity ranges. The resistance values specified are appropriate for use with a 100 µA meter that has a 1500 Ω internal resistance.
The described circuit comprises several critical components that work together to deliver accurate voltage readings while maintaining meter stability. The peak-reading diode voltmeter operates by first amplifying the input signal through two stages of amplification, which enhances the sensitivity of the measurement. The use of a 100 µF capacitor is crucial as it determines the time constant of the circuit, allowing for a smooth response to voltage changes while avoiding excessive oscillations or overshoot. This is particularly important in applications where transient voltages may be present.
The design incorporates an overdamped meter mechanism, which is essential for preventing the needle from sticking at maximum deflection when there is a sudden change in the input voltage or when the user mistakenly selects an inappropriate measurement range. This feature significantly improves the usability of the voltmeter, especially in field applications where quick adjustments may be necessary.
The inclusion of an SPST toggle switch for additional series resistance allows the user to extend the measurement range of the voltmeter. This X2 function effectively doubles the sensitivity range, providing more flexibility in measuring varying voltage levels without compromising accuracy. The resistance values indicated in the schematic are tailored for a specific configuration that utilizes a 100 µA meter with a 1500 Ω internal resistance, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
Overall, this peak-reading diode voltmeter schematic is designed to provide reliable and accurate voltage measurements across a range of conditions, making it a valuable tool in electronic testing and diagnostics.This schematic shows a peak-reading diode voltmeter driven by two stages of amplification. A 100- F capacitor provides a fairly large time constant, which results in satisfactory meter damping. The limited differential output voltage coupled with an overdamped meter prevents most needle pinning when you select an incorrect range position, or make
other errors. An SPST toggle switch selects additional series resistance. This X2 function gives some more overlap of the sensitivity ranges. The resistance values shown are correct for use with a 100- A meter with 1500- © internal resistance. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit comprises several critical components that work together to deliver accurate voltage readings while maintaining meter stability. The peak-reading diode voltmeter operates by first amplifying the input signal through two stages of amplification, which enhances the sensitivity of the measurement. The use of a 100 µF capacitor is crucial as it determines the time constant of the circuit, allowing for a smooth response to voltage changes while avoiding excessive oscillations or overshoot. This is particularly important in applications where transient voltages may be present.
The design incorporates an overdamped meter mechanism, which is essential for preventing the needle from sticking at maximum deflection when there is a sudden change in the input voltage or when the user mistakenly selects an inappropriate measurement range. This feature significantly improves the usability of the voltmeter, especially in field applications where quick adjustments may be necessary.
The inclusion of an SPST toggle switch for additional series resistance allows the user to extend the measurement range of the voltmeter. This X2 function effectively doubles the sensitivity range, providing more flexibility in measuring varying voltage levels without compromising accuracy. The resistance values indicated in the schematic are tailored for a specific configuration that utilizes a 100 µA meter with a 1500 Ω internal resistance, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
Overall, this peak-reading diode voltmeter schematic is designed to provide reliable and accurate voltage measurements across a range of conditions, making it a valuable tool in electronic testing and diagnostics.This schematic shows a peak-reading diode voltmeter driven by two stages of amplification. A 100- F capacitor provides a fairly large time constant, which results in satisfactory meter damping. The limited differential output voltage coupled with an overdamped meter prevents most needle pinning when you select an incorrect range position, or make
other errors. An SPST toggle switch selects additional series resistance. This X2 function gives some more overlap of the sensitivity ranges. The resistance values shown are correct for use with a 100- A meter with 1500- © internal resistance. 🔗 External reference