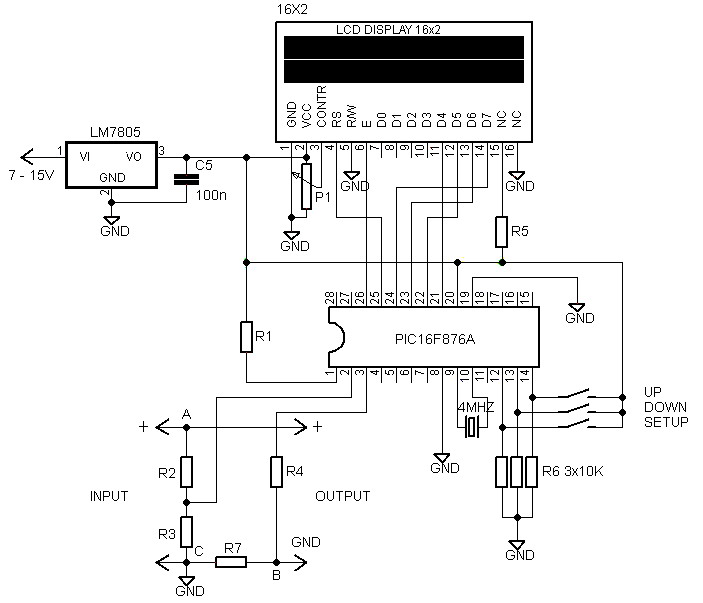
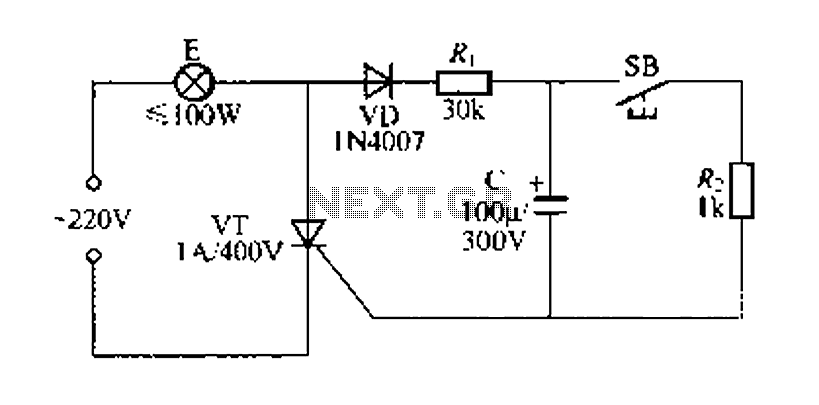
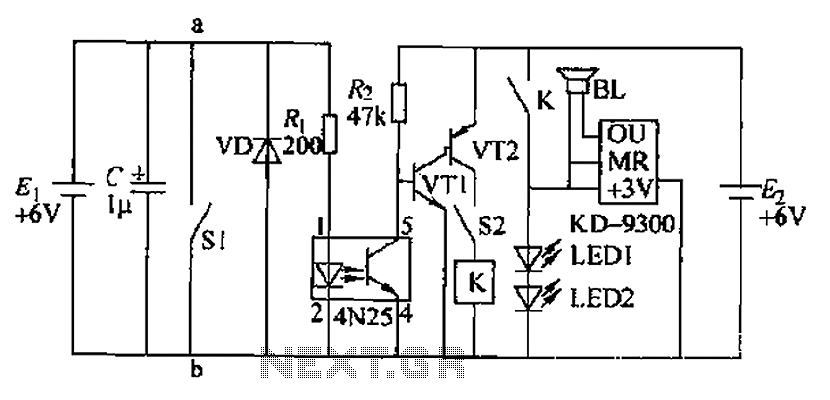
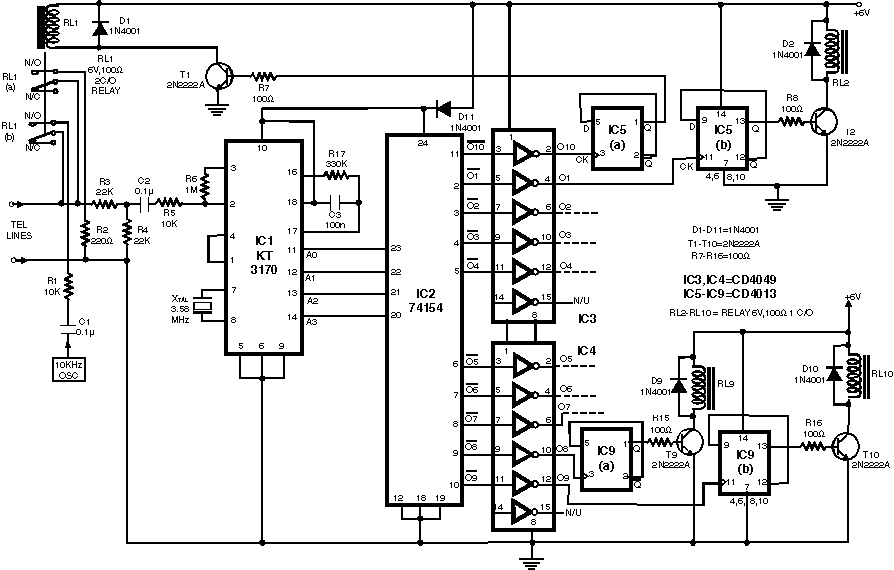
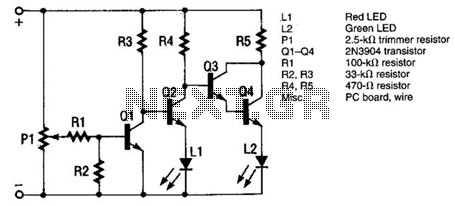
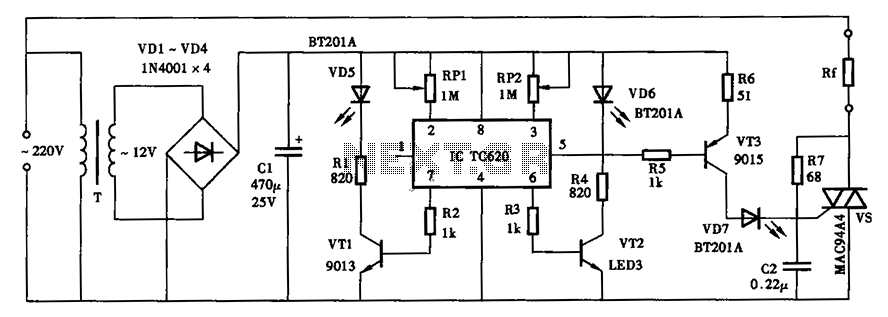
Sensor Alarm using thyristor circuit
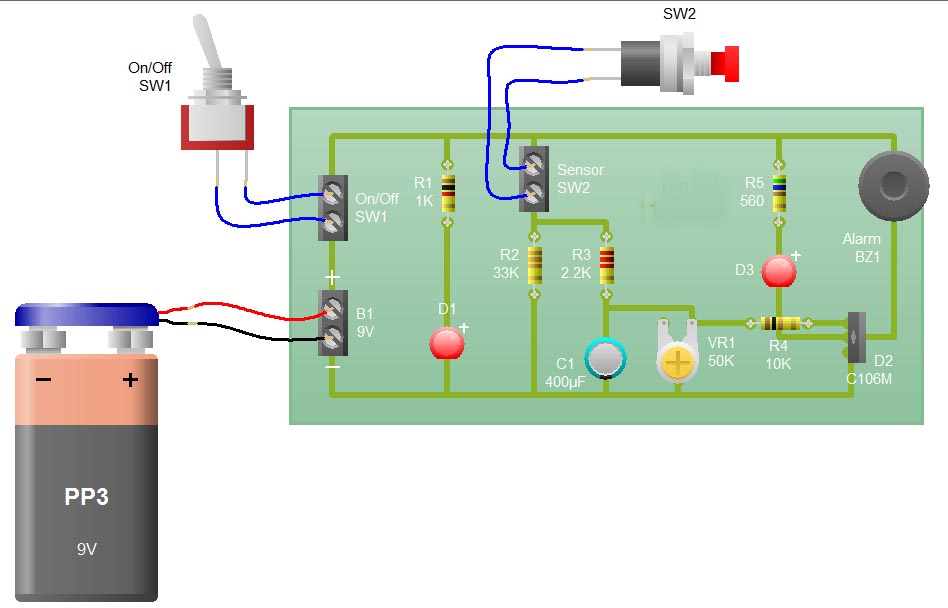
When the sensor switch SW2 is pressed, the LED D3 and the alarm are activated for a certain duration. The timing of the circuit is determined by the resistor R3 and capacitor C1. Additional details regarding the RC circuit can be found in the provided links. The schematic indicates that the circuit utilizes a C106M Thyristor. A data sheet for the C106M Thyristor is available for download.
The described circuit functions as a simple timing alarm system, utilizing a sensor switch (SW2) to initiate the activation of an LED (D3) and an alarm. The operation begins when SW2 is pressed, which closes the circuit and allows current to flow. The LED serves as a visual indicator, while the alarm provides an audible signal, enhancing the alertness of the system.
The timing mechanism is established through the combination of resistor R3 and capacitor C1, forming an RC timing circuit. The time constant of this circuit, defined as τ (tau), is calculated using the formula τ = R3 * C1. This time constant determines how long the LED and alarm remain active after the switch is pressed. The discharge of capacitor C1 through resistor R3 controls the timing interval, allowing for adjustable delay periods by varying the values of R3 and C1.
In addition to the timing function, the circuit incorporates a C106M Thyristor, which is a type of semiconductor device that can control power. The Thyristor is used to switch the load (in this case, the alarm) on and off. Upon pressing SW2, a small gate current is applied to the Thyristor, allowing it to conduct and energize the load. Once triggered, the Thyristor remains in the conducting state until the current through it drops below a certain threshold, which is influenced by the timing circuit.
For further understanding of the C106M Thyristor's specifications and operational characteristics, referring to its data sheet is recommended. This document provides essential information regarding voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, and other critical parameters necessary for proper integration into the circuit.When you press sensor switch SW2, the LED D3 and the alarm switches ON for a while. The timing of the circuit is dependent upon R3 and C1. You can get all the details of the RC circuit from the links given above. You can see on the schematic that the circuit is based on C106M Thyristor. Download data sheet of C106M Thyristor 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a simple timing alarm system, utilizing a sensor switch (SW2) to initiate the activation of an LED (D3) and an alarm. The operation begins when SW2 is pressed, which closes the circuit and allows current to flow. The LED serves as a visual indicator, while the alarm provides an audible signal, enhancing the alertness of the system.
The timing mechanism is established through the combination of resistor R3 and capacitor C1, forming an RC timing circuit. The time constant of this circuit, defined as τ (tau), is calculated using the formula τ = R3 * C1. This time constant determines how long the LED and alarm remain active after the switch is pressed. The discharge of capacitor C1 through resistor R3 controls the timing interval, allowing for adjustable delay periods by varying the values of R3 and C1.
In addition to the timing function, the circuit incorporates a C106M Thyristor, which is a type of semiconductor device that can control power. The Thyristor is used to switch the load (in this case, the alarm) on and off. Upon pressing SW2, a small gate current is applied to the Thyristor, allowing it to conduct and energize the load. Once triggered, the Thyristor remains in the conducting state until the current through it drops below a certain threshold, which is influenced by the timing circuit.
For further understanding of the C106M Thyristor's specifications and operational characteristics, referring to its data sheet is recommended. This document provides essential information regarding voltage ratings, current handling capabilities, and other critical parameters necessary for proper integration into the circuit.When you press sensor switch SW2, the LED D3 and the alarm switches ON for a while. The timing of the circuit is dependent upon R3 and C1. You can get all the details of the RC circuit from the links given above. You can see on the schematic that the circuit is based on C106M Thyristor. Download data sheet of C106M Thyristor 🔗 External reference