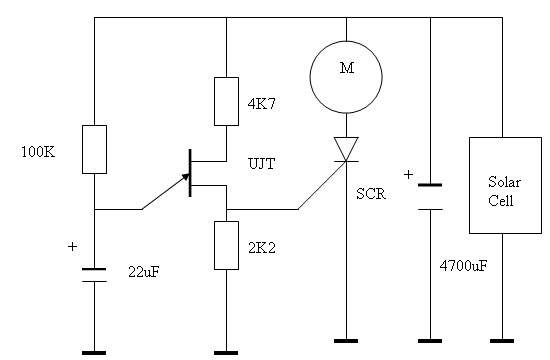
Shunt Regulator for Solar Cells
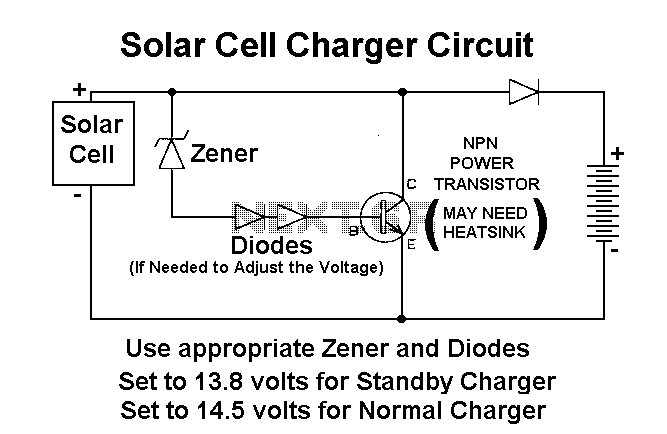
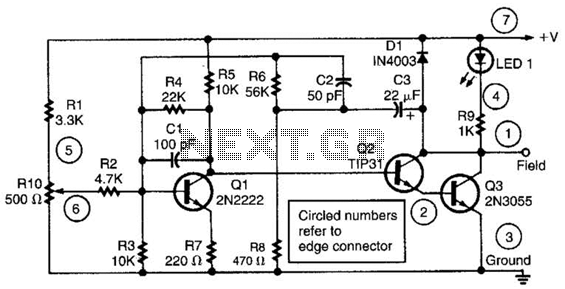
One application is where you need a Higher Power Zener, possibly even a 100 watt rating. Another useful application is as a Shunt Regulator for Solar Cells that are used to charge lead acid batteries. Simply place it in parallel with the Solar Cell and use diode de-coupling between it and the battery. A 13 volt Zener diode will work well for charging a 12 volt battery on standby use. Or use a 14 volt Zener diode for a standard 14.6 volt charge. The output voltage of this amplified Zener is the Zener voltage plus the emitter to base voltage drop.
The application of a higher power Zener diode, particularly rated at 100 watts, serves multiple functions in electronic circuits, primarily in voltage regulation and protection. In scenarios where solar cells are employed to charge lead-acid batteries, the Zener diode can be configured as a shunt regulator. This configuration ensures that the output voltage remains stable, preventing overcharging of the battery.
The Zener diode should be connected in parallel with the solar cell, effectively clamping the voltage to a predetermined level. A diode must be included in series with the battery to prevent reverse current flow, which could otherwise discharge the battery when solar input is low. The choice of a 13-volt Zener diode is suitable for maintaining a stable charge on a 12-volt battery, while a 14-volt Zener diode can be utilized for applications requiring a higher charging voltage, such as maintaining a 14.6-volt charge.
When designing the circuit, it is crucial to consider the additional voltage drop across the transistor's emitter-base junction in configurations where the Zener diode is amplified. The output voltage will thus be the Zener voltage plus this voltage drop, which typically ranges around 0.7 volts for silicon-based transistors.
In summary, the integration of a higher power Zener diode in solar charging applications not only facilitates efficient voltage regulation but also enhances the longevity and performance of lead-acid batteries by preventing overvoltage conditions. Proper circuit design, including the use of appropriate diodes and consideration of voltage drops, will ensure optimal functionality and reliability.One application is where you need a Higher Power Zener, Possibly even a 100 watt rating. Another useful application is as a Shunt Regulator for Solar Cells that are used to charge "Lead Acid Batteries". Simply Place it in parallel with the Solar Cell and use Diode De-coupling between it and the battery.
A 13 volt Zener diode will work well for charging a 12 volt battery on Standby use. Or use a 14 volt zener a diode for a Standard 14.6 volt charge. The Output voltage of this Amplified Zener is the "Zener Voltage" PLUS the "Emitter to Ba 🔗 External reference
The application of a higher power Zener diode, particularly rated at 100 watts, serves multiple functions in electronic circuits, primarily in voltage regulation and protection. In scenarios where solar cells are employed to charge lead-acid batteries, the Zener diode can be configured as a shunt regulator. This configuration ensures that the output voltage remains stable, preventing overcharging of the battery.
The Zener diode should be connected in parallel with the solar cell, effectively clamping the voltage to a predetermined level. A diode must be included in series with the battery to prevent reverse current flow, which could otherwise discharge the battery when solar input is low. The choice of a 13-volt Zener diode is suitable for maintaining a stable charge on a 12-volt battery, while a 14-volt Zener diode can be utilized for applications requiring a higher charging voltage, such as maintaining a 14.6-volt charge.
When designing the circuit, it is crucial to consider the additional voltage drop across the transistor's emitter-base junction in configurations where the Zener diode is amplified. The output voltage will thus be the Zener voltage plus this voltage drop, which typically ranges around 0.7 volts for silicon-based transistors.
In summary, the integration of a higher power Zener diode in solar charging applications not only facilitates efficient voltage regulation but also enhances the longevity and performance of lead-acid batteries by preventing overvoltage conditions. Proper circuit design, including the use of appropriate diodes and consideration of voltage drops, will ensure optimal functionality and reliability.One application is where you need a Higher Power Zener, Possibly even a 100 watt rating. Another useful application is as a Shunt Regulator for Solar Cells that are used to charge "Lead Acid Batteries". Simply Place it in parallel with the Solar Cell and use Diode De-coupling between it and the battery.
A 13 volt Zener diode will work well for charging a 12 volt battery on Standby use. Or use a 14 volt zener a diode for a Standard 14.6 volt charge. The Output voltage of this Amplified Zener is the "Zener Voltage" PLUS the "Emitter to Ba 🔗 External reference