simple 15v powered led flasher circuit
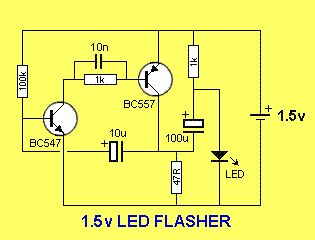
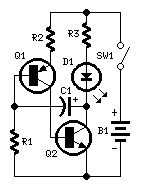
This is a simple 1.5V powered LED flasher circuit diagram. This circuit can flash 1.7V or 2.3V LEDs (depending on the color) using a 1.5V DC input. The LED will turn on when the 100µF capacitor is charged by the collector of a BC557 transistor. The circuit employs a charge-pump design, where an electrolytic capacitor charges and then discharges into a load, allowing the load to experience a voltage higher than the supply voltage.
The circuit operates at a nominal input voltage of 1.5V, which is suitable for battery-powered applications. The core component, the BC557 transistor, is used in a switching configuration. When the circuit is powered, the transistor is activated, allowing current to flow through the 100µF capacitor. The capacitor stores energy and, once charged to a sufficient voltage level, discharges through the LED, causing it to illuminate.
The choice of LED voltage ratings (1.7V or 2.3V) is significant, as it determines the brightness and color of the emitted light. Different colors of LEDs have varying forward voltage requirements; hence, the circuit's ability to flash these LEDs demonstrates its versatility. The charge-pump mechanism is particularly effective in this design, as it allows the circuit to boost the voltage from the 1.5V supply to a level sufficient to drive the LED.
In terms of component selection, the electrolytic capacitor must be rated for a voltage higher than the expected peak voltage during discharge to ensure reliability and safety. Additionally, the use of a resistor in series with the LED may be necessary to limit the current and protect the LED from excessive current, which could lead to failure.
The overall simplicity of the circuit makes it an excellent choice for educational purposes, as well as for hobbyist projects. It effectively demonstrates principles of charge storage, voltage boosting, and basic transistor switching, providing a practical application for these fundamental concepts in electronics.This is a simple 1. 5V powered LED Flasher circuit diagram. This circuit can flash 1. 7V or 2. 3V LED (depend on the color) using 1. 5Vdc input. The LED will turn on when the 100u capacitor jacked up by the collector of BC557. The circuit is a charge-pump design. This is where a capacitor (electrolytic) is allowed to charge and is then raised highe r and allowed to discharge into a load. The load sees a voltage that can be higher than the supply. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates at a nominal input voltage of 1.5V, which is suitable for battery-powered applications. The core component, the BC557 transistor, is used in a switching configuration. When the circuit is powered, the transistor is activated, allowing current to flow through the 100µF capacitor. The capacitor stores energy and, once charged to a sufficient voltage level, discharges through the LED, causing it to illuminate.
The choice of LED voltage ratings (1.7V or 2.3V) is significant, as it determines the brightness and color of the emitted light. Different colors of LEDs have varying forward voltage requirements; hence, the circuit's ability to flash these LEDs demonstrates its versatility. The charge-pump mechanism is particularly effective in this design, as it allows the circuit to boost the voltage from the 1.5V supply to a level sufficient to drive the LED.
In terms of component selection, the electrolytic capacitor must be rated for a voltage higher than the expected peak voltage during discharge to ensure reliability and safety. Additionally, the use of a resistor in series with the LED may be necessary to limit the current and protect the LED from excessive current, which could lead to failure.
The overall simplicity of the circuit makes it an excellent choice for educational purposes, as well as for hobbyist projects. It effectively demonstrates principles of charge storage, voltage boosting, and basic transistor switching, providing a practical application for these fundamental concepts in electronics.This is a simple 1. 5V powered LED Flasher circuit diagram. This circuit can flash 1. 7V or 2. 3V LED (depend on the color) using 1. 5Vdc input. The LED will turn on when the 100u capacitor jacked up by the collector of BC557. The circuit is a charge-pump design. This is where a capacitor (electrolytic) is allowed to charge and is then raised highe r and allowed to discharge into a load. The load sees a voltage that can be higher than the supply. 🔗 External reference