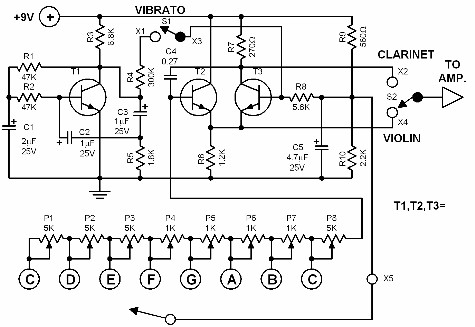
simple analog comparator
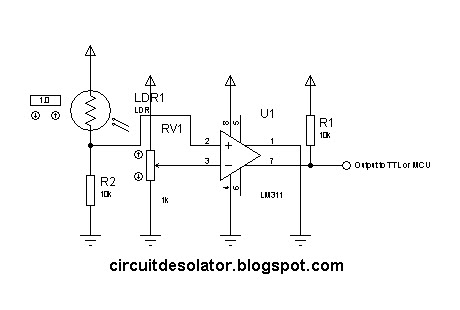
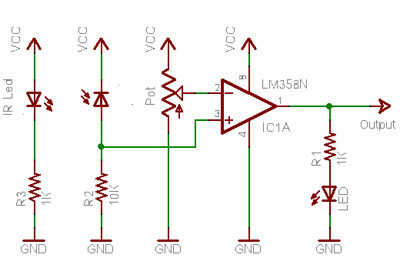
This is a common circuit block utilized in both digital and analog electronics. Its output depends on the relationship between its two input pins. One input is designated to provide the reference voltage, while the other is typically connected to various sensors. If the input connected to the sensor exceeds the reference voltage, the output of the comparator changes. The advantage of a comparator integrated circuit (IC) over an operational amplifier (op-amp) used as a comparator lies in the open collector output property of IC comparators. This feature allows the output of the comparator to be set beyond its biased voltage.
A comparator circuit is essential in various applications, including signal conditioning, level detection, and control systems. The fundamental operation of a comparator involves comparing two input voltages: the inverting input (often labeled as V-) and the non-inverting input (labeled as V+). The comparator outputs a high or low signal based on which input voltage is greater. When V+ exceeds V-, the output transitions to a high state, while if V- is greater, the output transitions to a low state.
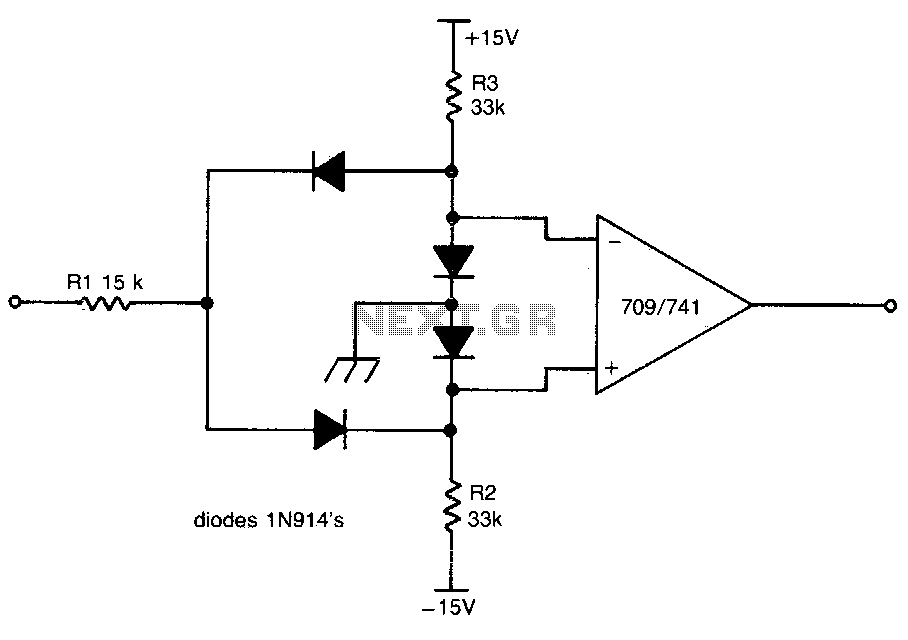
The open collector output configuration of comparator ICs allows for greater flexibility in interfacing with other components. This configuration means that the output stage of the comparator can pull the output to ground but cannot drive it high. Instead, an external pull-up resistor is employed to pull the output to a high state when the comparator output is inactive. This arrangement enables multiple comparators to share a common output line, facilitating wired-AND logic in applications such as multi-sensor systems.
In practical applications, the reference voltage can be set using a voltage divider network or a precision voltage reference IC, ensuring accurate comparisons with sensor outputs. The choice of sensors connected to the comparator can vary widely, including temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and light sensors, depending on the specific application requirements.
Additionally, the response time of the comparator is a crucial factor in high-speed applications. Comparators designed for fast switching can be utilized in applications requiring rapid changes in output states, such as pulse width modulation (PWM) control or zero-crossing detection in AC signals.
Overall, the comparator circuit is a versatile and essential building block in electronic design, providing critical functionality in a wide range of applications.This is one of the common circuit blocks being used both in digital and analog electronics. Its output is dependent on the relationship of its two input pins. One of the inputs is set to give the reference voltage while the other one is commonly connected to different sensors. If the reference voltage was overcome by the input connected to the sen sor, the output of the comparator changes. The advantage of a comparator IC than an opamp used as an comparator is the property of IC comparators to be open collector output. Having this feature, we can set the output of the comparator beyond its biased voltage. 🔗 External reference
A comparator circuit is essential in various applications, including signal conditioning, level detection, and control systems. The fundamental operation of a comparator involves comparing two input voltages: the inverting input (often labeled as V-) and the non-inverting input (labeled as V+). The comparator outputs a high or low signal based on which input voltage is greater. When V+ exceeds V-, the output transitions to a high state, while if V- is greater, the output transitions to a low state.
The open collector output configuration of comparator ICs allows for greater flexibility in interfacing with other components. This configuration means that the output stage of the comparator can pull the output to ground but cannot drive it high. Instead, an external pull-up resistor is employed to pull the output to a high state when the comparator output is inactive. This arrangement enables multiple comparators to share a common output line, facilitating wired-AND logic in applications such as multi-sensor systems.
In practical applications, the reference voltage can be set using a voltage divider network or a precision voltage reference IC, ensuring accurate comparisons with sensor outputs. The choice of sensors connected to the comparator can vary widely, including temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and light sensors, depending on the specific application requirements.
Additionally, the response time of the comparator is a crucial factor in high-speed applications. Comparators designed for fast switching can be utilized in applications requiring rapid changes in output states, such as pulse width modulation (PWM) control or zero-crossing detection in AC signals.
Overall, the comparator circuit is a versatile and essential building block in electronic design, providing critical functionality in a wide range of applications.This is one of the common circuit blocks being used both in digital and analog electronics. Its output is dependent on the relationship of its two input pins. One of the inputs is set to give the reference voltage while the other one is commonly connected to different sensors. If the reference voltage was overcome by the input connected to the sen sor, the output of the comparator changes. The advantage of a comparator IC than an opamp used as an comparator is the property of IC comparators to be open collector output. Having this feature, we can set the output of the comparator beyond its biased voltage. 🔗 External reference