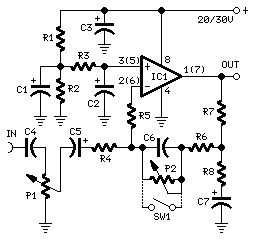
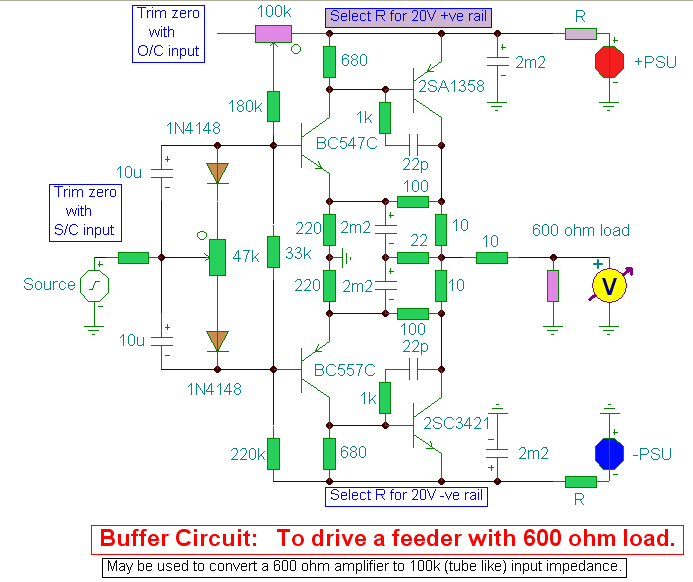
Simple LM386 amplifier
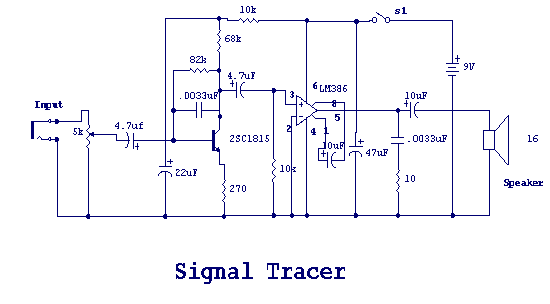
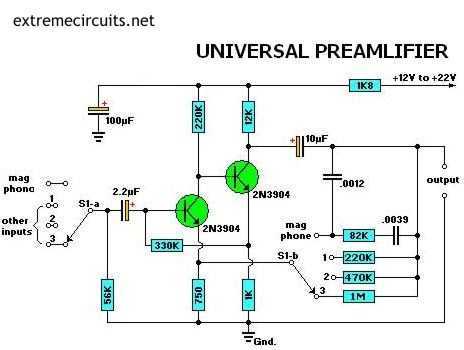
The main part of this circuit is the LM386 amplifier chip. It also uses a transistor input to buffer the input signal and provide extra gain for the LM386. The little unit has helped me out on numerous occasions when troubleshooting any amplifier circuit like a stereo receiver, TV/VCR audio section, radios, CD players, and car stereos.
The circuit primarily revolves around the LM386, a low-voltage audio power amplifier capable of delivering substantial output power, typically around 0.5 watts. It is designed to operate with a single supply voltage, ranging from 4 to 12 volts, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The LM386 is favored for its simple design and minimal external components, which contribute to its compactness and efficiency.
In this configuration, a transistor is utilized at the input stage to buffer the incoming audio signal. This transistor acts as a preamplifier, ensuring that the signal fed into the LM386 is sufficiently amplified for optimal performance. The use of a transistor allows for higher input impedance, reducing the loading effect on the previous stage of the circuit, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity.
The circuit design typically includes bypass capacitors connected to the power supply pins of the LM386 to filter out noise and provide stability during operation. Additionally, a gain-setting resistor and capacitor can be connected to the gain pin of the LM386 to adjust the amplification level, allowing for customization based on the application requirements.
The output from the LM386 can be connected directly to a small speaker or further processed through additional amplification stages, depending on the desired output power and application. The versatility of this circuit makes it applicable in various audio devices, including portable speakers, intercom systems, and other audio amplification needs.
Furthermore, the circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an excellent choice for troubleshooting audio-related issues in various devices, such as stereo receivers, televisions, VCRs, radios, CD players, and car stereos. By understanding and implementing this circuit, one can effectively diagnose and resolve audio amplification problems in a range of consumer electronics.The main part of this circuit is the LM386 amplifier chip. It also uses a transistor input to buffer the input signal and provide extra gain for the LM386. The little unit has helped me out on numerous occasions when trouble shooting any amplifier circuit like a stereo receiver, tv / vcr audio section, radios, cd players and car stereos. 🔗 External reference
The circuit primarily revolves around the LM386, a low-voltage audio power amplifier capable of delivering substantial output power, typically around 0.5 watts. It is designed to operate with a single supply voltage, ranging from 4 to 12 volts, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The LM386 is favored for its simple design and minimal external components, which contribute to its compactness and efficiency.
In this configuration, a transistor is utilized at the input stage to buffer the incoming audio signal. This transistor acts as a preamplifier, ensuring that the signal fed into the LM386 is sufficiently amplified for optimal performance. The use of a transistor allows for higher input impedance, reducing the loading effect on the previous stage of the circuit, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity.
The circuit design typically includes bypass capacitors connected to the power supply pins of the LM386 to filter out noise and provide stability during operation. Additionally, a gain-setting resistor and capacitor can be connected to the gain pin of the LM386 to adjust the amplification level, allowing for customization based on the application requirements.
The output from the LM386 can be connected directly to a small speaker or further processed through additional amplification stages, depending on the desired output power and application. The versatility of this circuit makes it applicable in various audio devices, including portable speakers, intercom systems, and other audio amplification needs.
Furthermore, the circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an excellent choice for troubleshooting audio-related issues in various devices, such as stereo receivers, televisions, VCRs, radios, CD players, and car stereos. By understanding and implementing this circuit, one can effectively diagnose and resolve audio amplification problems in a range of consumer electronics.The main part of this circuit is the LM386 amplifier chip. It also uses a transistor input to buffer the input signal and provide extra gain for the LM386. The little unit has helped me out on numerous occasions when trouble shooting any amplifier circuit like a stereo receiver, tv / vcr audio section, radios, cd players and car stereos. 🔗 External reference