Simple Low-Frequency V/F Converter
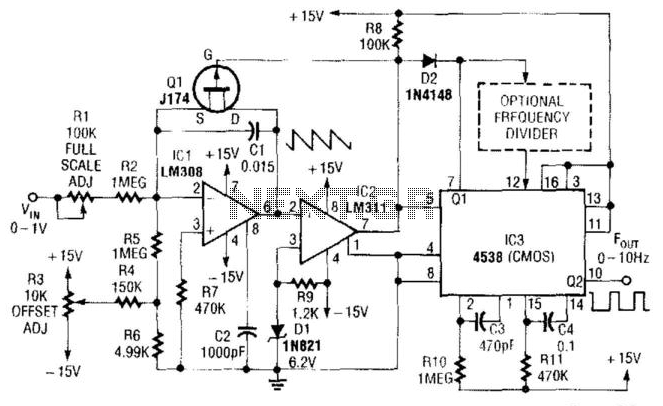
In this circuit, capacitor CI is charged to a fixed reference level and then discharged. The integrator IC1 charges CI until IC1 has a -6.2 V output, at which point comparator IC2 outputs a low signal. FET Q1 triggers one section of the monostable multivibrator IC3, pulling pin 3 low for 470 µs, ensuring that Q1 completely discharges CI. The other section of IC3 produces a longer pulse of about 47 ms. The full scale of this circuit is 10 Hz. For lower output pulse rates, a counter circuit can be inserted between the sections of IC3. It is important to note that since CI does not integrate while Q1 is biased on, this circuit has an error in the output period, which must be minimized. Consequently, the circuit's application is restricted to low frequencies.
This circuit operates as a timing mechanism utilizing an integrator, comparator, and monostable multivibrator. The primary component, capacitor CI, is charged through a defined pathway until it reaches a threshold voltage of -6.2 V, which is monitored by the comparator IC2. Upon detecting this voltage, IC2 outputs a low signal, which activates the FET Q1. This action triggers one section of the monostable multivibrator IC3, resulting in a brief low state on pin 3 for approximately 470 µs. This pulse duration is critical as it ensures that Q1 fully discharges CI, resetting the capacitor for the next cycle.
The second section of IC3 is configured to generate a longer output pulse, typically around 47 ms. This extended pulse duration allows for stable output signals necessary for applications requiring precise timing. The circuit is designed to operate effectively at a full scale of 10 Hz, which establishes a baseline frequency for the output pulse generation. For applications requiring lower pulse rates, a counter circuit can be integrated between the two sections of IC3, allowing for further manipulation of the output frequency.
However, it is essential to recognize a limitation inherent in the design: while Q1 is conducting, CI does not integrate, leading to potential inaccuracies in the output period. The circuit must be optimized to minimize this error to ensure reliable performance. As a result, the application of this circuit is best suited for low-frequency operations, where the timing accuracy can be maintained without significant deviations. Overall, the design encapsulates a straightforward yet effective approach to generating controlled timing pulses within specified frequency ranges. In this circuit, CI is charged to a fixed reference level, then discharged. Integrator ICl circuit charg es CI until ICl has -6.2-V output, when comparator IC2 outputs a low. FET Ql, triggers one-section monostable multivibrator IC3, pulls pin 3 low for 470, ensuring that Ql completely discharges CI. The other section of IC3 produces a longer pulse of about 47 ms. Full scale of this circuit is 10 Hz. For lower output pulse rates, a counter circuit can be inserted between the sections of IC3. Notice that because CI does not integrate while Ql is biased on, this circuit has an error in the output period, which must be as short as possible.
Therefore, the circuit"s use is limited to low frequencies. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates as a timing mechanism utilizing an integrator, comparator, and monostable multivibrator. The primary component, capacitor CI, is charged through a defined pathway until it reaches a threshold voltage of -6.2 V, which is monitored by the comparator IC2. Upon detecting this voltage, IC2 outputs a low signal, which activates the FET Q1. This action triggers one section of the monostable multivibrator IC3, resulting in a brief low state on pin 3 for approximately 470 µs. This pulse duration is critical as it ensures that Q1 fully discharges CI, resetting the capacitor for the next cycle.
The second section of IC3 is configured to generate a longer output pulse, typically around 47 ms. This extended pulse duration allows for stable output signals necessary for applications requiring precise timing. The circuit is designed to operate effectively at a full scale of 10 Hz, which establishes a baseline frequency for the output pulse generation. For applications requiring lower pulse rates, a counter circuit can be integrated between the two sections of IC3, allowing for further manipulation of the output frequency.
However, it is essential to recognize a limitation inherent in the design: while Q1 is conducting, CI does not integrate, leading to potential inaccuracies in the output period. The circuit must be optimized to minimize this error to ensure reliable performance. As a result, the application of this circuit is best suited for low-frequency operations, where the timing accuracy can be maintained without significant deviations. Overall, the design encapsulates a straightforward yet effective approach to generating controlled timing pulses within specified frequency ranges. In this circuit, CI is charged to a fixed reference level, then discharged. Integrator ICl circuit charg es CI until ICl has -6.2-V output, when comparator IC2 outputs a low. FET Ql, triggers one-section monostable multivibrator IC3, pulls pin 3 low for 470, ensuring that Ql completely discharges CI. The other section of IC3 produces a longer pulse of about 47 ms. Full scale of this circuit is 10 Hz. For lower output pulse rates, a counter circuit can be inserted between the sections of IC3. Notice that because CI does not integrate while Ql is biased on, this circuit has an error in the output period, which must be as short as possible.
Therefore, the circuit"s use is limited to low frequencies. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713