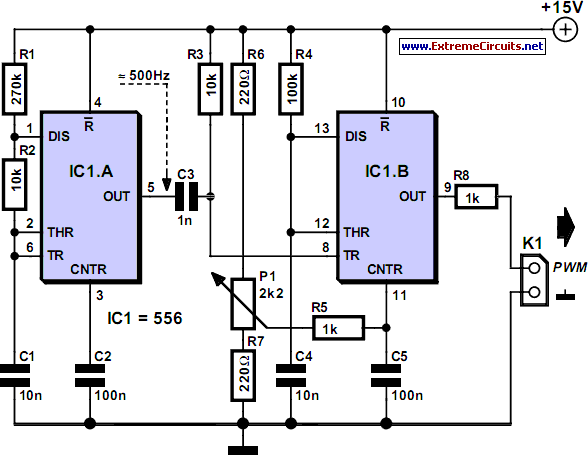
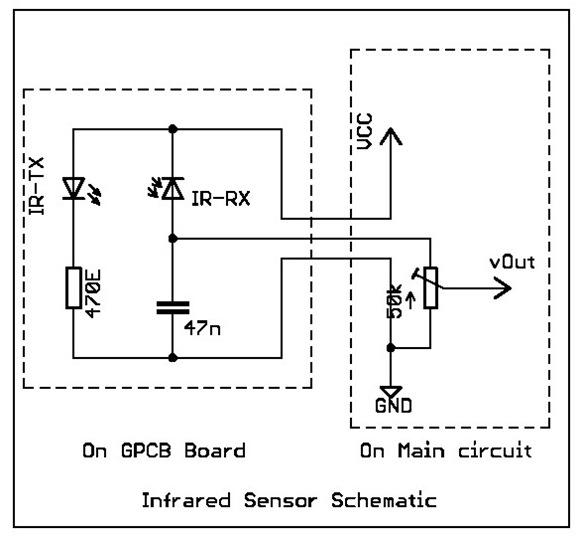
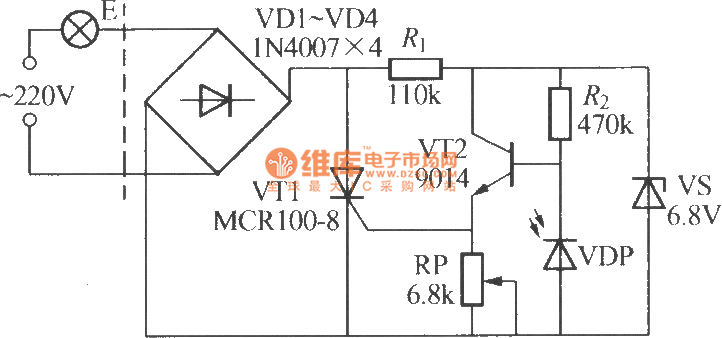
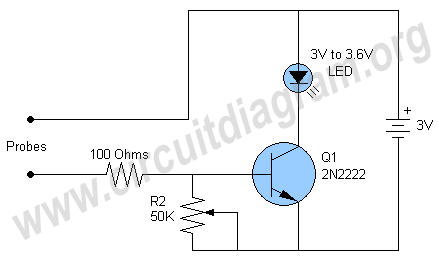
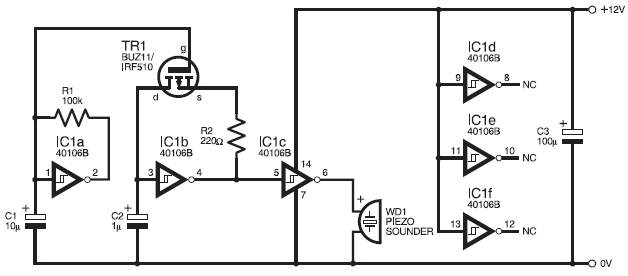
simple pwm boost converter io disconnect solves malfunctions
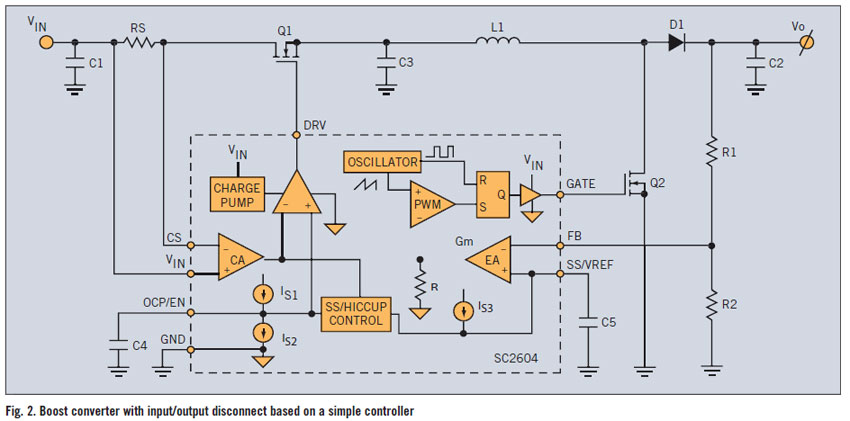
A PWM boost converter in a simple controller has a DC path from input VIN to VOUT, which is utilized for high-efficiency power conversion.
A PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) boost converter is an essential component in power electronics, designed to step up a lower input voltage (VIN) to a higher output voltage (VOUT) while maintaining high efficiency. The operation of this converter relies on the control of the duty cycle of the switching element, typically a transistor, to regulate the output voltage.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: an inductor, a switch (transistor), a diode, and a capacitor. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it to the output when the switch is open. The PWM controller adjusts the duty cycle of the switch to control the amount of energy transferred to the output, ensuring that VOUT remains stable despite variations in VIN or load conditions.
The DC path from VIN to VOUT implies that there is a direct electrical connection between the input and output, which is crucial for maintaining efficiency during the conversion process. This connection allows for minimal energy loss, as the converter can directly transfer the input voltage to the output when the switch is in the appropriate state.
In summary, a PWM boost converter is a vital circuit for applications requiring voltage step-up with high efficiency, leveraging a simple controller to manage the power conversion process effectively.A PWM boost converter in a simple controller has a DC path from input VIN to VOUT, which is utilized for high-efficiency power conversion.. 🔗 External reference
A PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) boost converter is an essential component in power electronics, designed to step up a lower input voltage (VIN) to a higher output voltage (VOUT) while maintaining high efficiency. The operation of this converter relies on the control of the duty cycle of the switching element, typically a transistor, to regulate the output voltage.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: an inductor, a switch (transistor), a diode, and a capacitor. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it to the output when the switch is open. The PWM controller adjusts the duty cycle of the switch to control the amount of energy transferred to the output, ensuring that VOUT remains stable despite variations in VIN or load conditions.
The DC path from VIN to VOUT implies that there is a direct electrical connection between the input and output, which is crucial for maintaining efficiency during the conversion process. This connection allows for minimal energy loss, as the converter can directly transfer the input voltage to the output when the switch is in the appropriate state.
In summary, a PWM boost converter is a vital circuit for applications requiring voltage step-up with high efficiency, leveraging a simple controller to manage the power conversion process effectively.A PWM boost converter in a simple controller has a DC path from input VIN to VOUT, which is utilized for high-efficiency power conversion.. 🔗 External reference