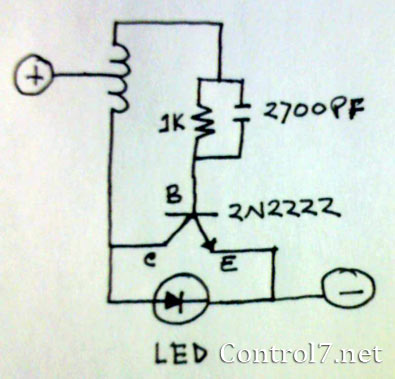
Simple Rf Test Oscillator Circuit
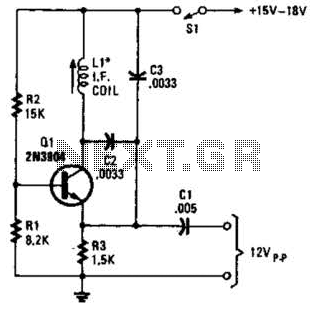
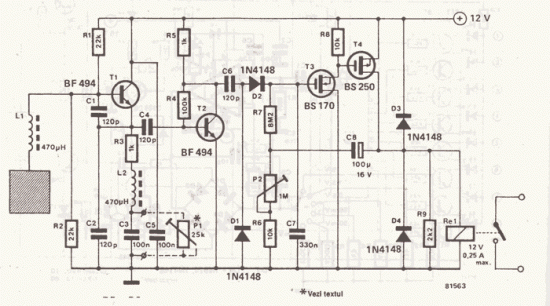
A simple oscillator for intermediate frequency (IF) alignment at 455 kHz can be useful in field testing or in scenarios where a standard signal generator is available. The inductor (L1) should resonate at the desired output frequency with the series combination of capacitors (C2 and C3).
The oscillator circuit is designed to generate a stable sine wave signal at 455 kHz, commonly used in radio frequency applications, particularly for IF alignment in superheterodyne receivers. The circuit typically consists of an inductor (L1) and two capacitors (C2 and C3) configured in a tank circuit that determines the resonant frequency.
The resonant frequency (f) of the LC circuit can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π√(L * C))
where L is the inductance in henries and C is the total capacitance in farads. In this case, the total capacitance (C) is the series combination of C2 and C3, which can be calculated as:
1/C = 1/C2 + 1/C3
This configuration allows for fine-tuning the output frequency by adjusting the values of the capacitors. The oscillator can be powered by a low-voltage DC source, and it may include additional components such as resistors for biasing or feedback to stabilize the oscillation.
The output can be taken directly across the inductor or through a buffer stage to prevent loading effects that could alter the frequency. This oscillator can be employed in various applications, including signal generation for testing receivers, frequency calibration, and alignment procedures, making it a valuable tool for engineers and technicians in the field of electronics. A simple oscillator for IF alignment (455 kHz) can prove useful in field testing or where a standard signal generator is available. LI should resonate at the desired output frequency with the series combination of C2 and C3. 🔗 External reference
The oscillator circuit is designed to generate a stable sine wave signal at 455 kHz, commonly used in radio frequency applications, particularly for IF alignment in superheterodyne receivers. The circuit typically consists of an inductor (L1) and two capacitors (C2 and C3) configured in a tank circuit that determines the resonant frequency.
The resonant frequency (f) of the LC circuit can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π√(L * C))
where L is the inductance in henries and C is the total capacitance in farads. In this case, the total capacitance (C) is the series combination of C2 and C3, which can be calculated as:
1/C = 1/C2 + 1/C3
This configuration allows for fine-tuning the output frequency by adjusting the values of the capacitors. The oscillator can be powered by a low-voltage DC source, and it may include additional components such as resistors for biasing or feedback to stabilize the oscillation.
The output can be taken directly across the inductor or through a buffer stage to prevent loading effects that could alter the frequency. This oscillator can be employed in various applications, including signal generation for testing receivers, frequency calibration, and alignment procedures, making it a valuable tool for engineers and technicians in the field of electronics. A simple oscillator for IF alignment (455 kHz) can prove useful in field testing or where a standard signal generator is available. LI should resonate at the desired output frequency with the series combination of C2 and C3. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713