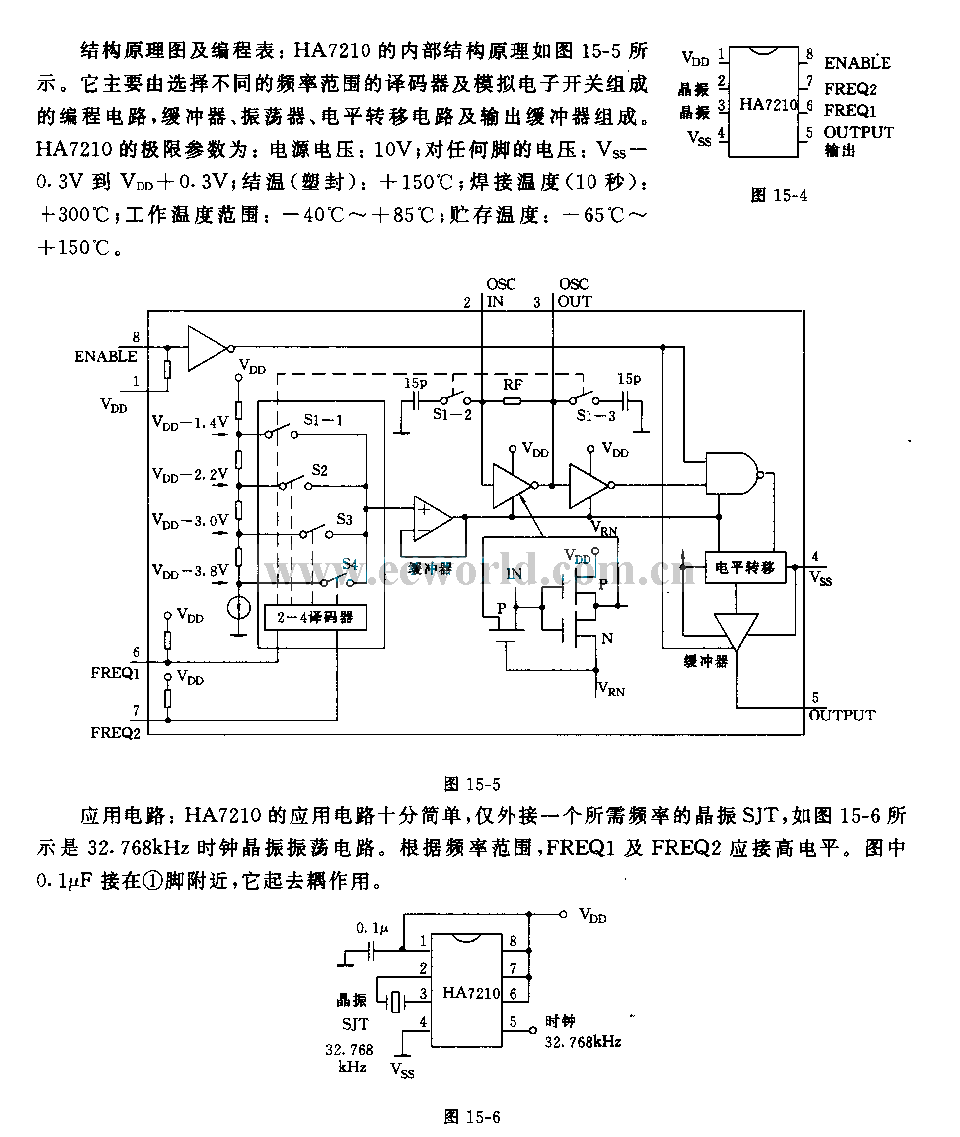
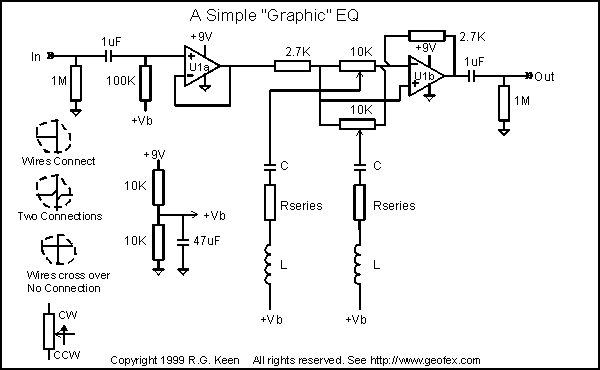
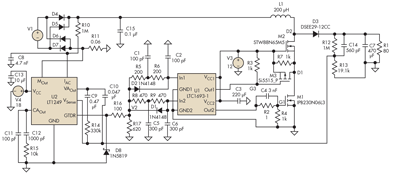
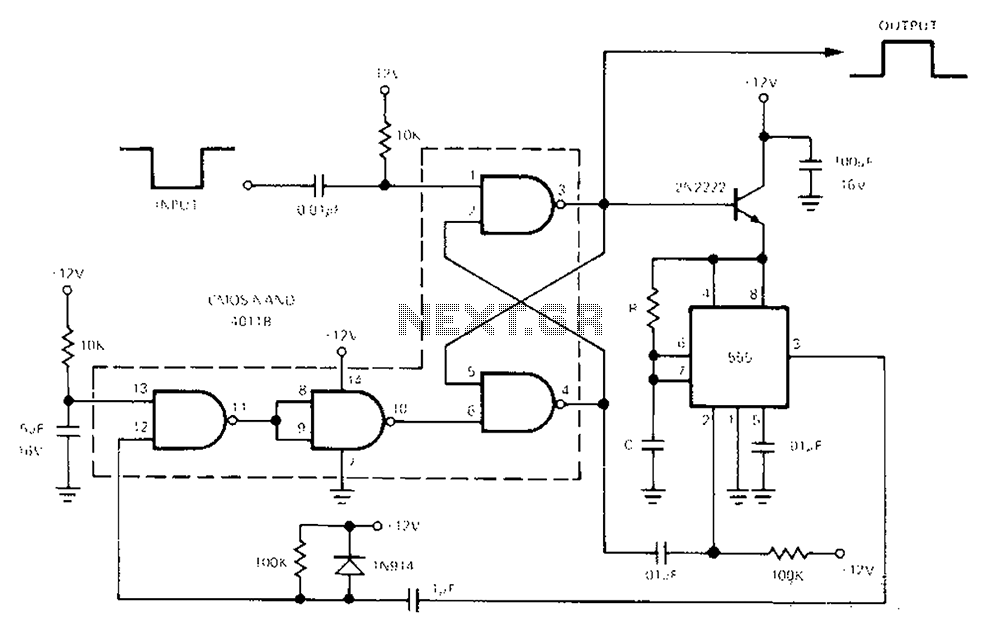
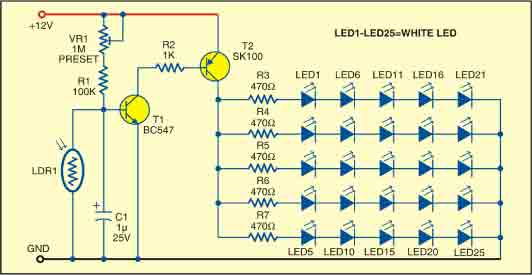
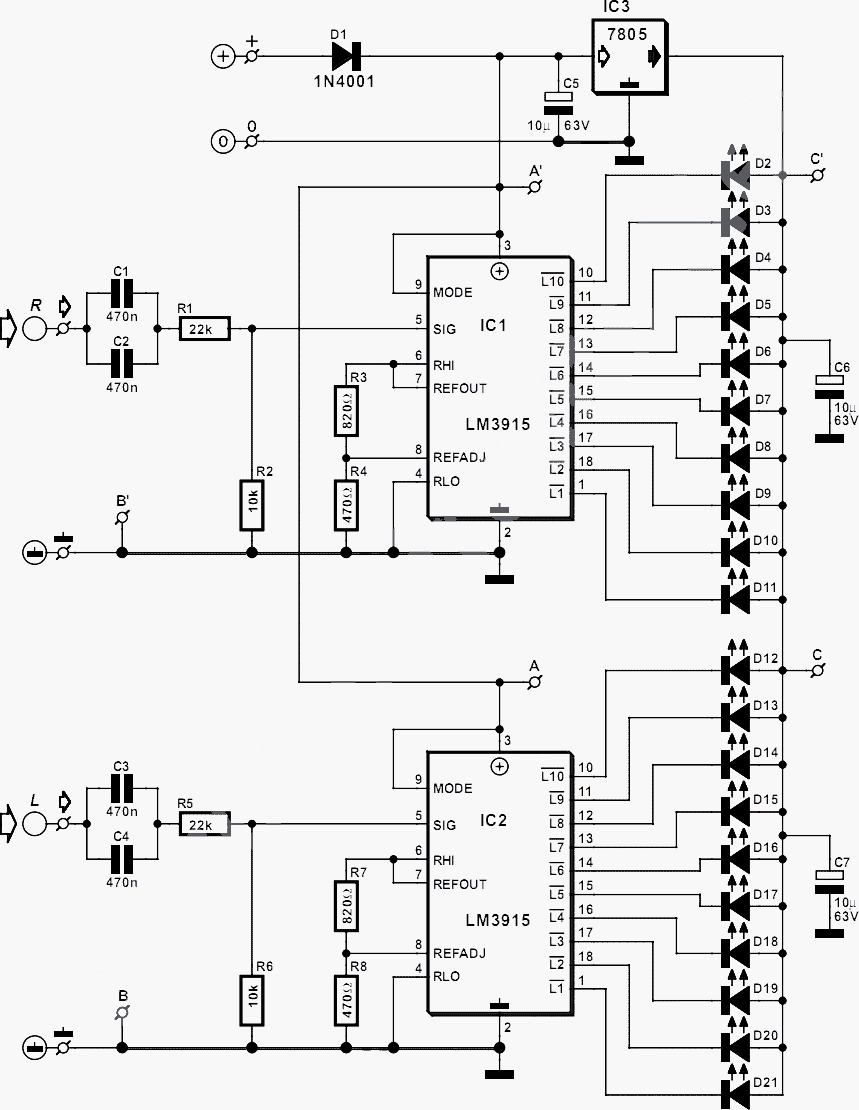
Simple split power supply
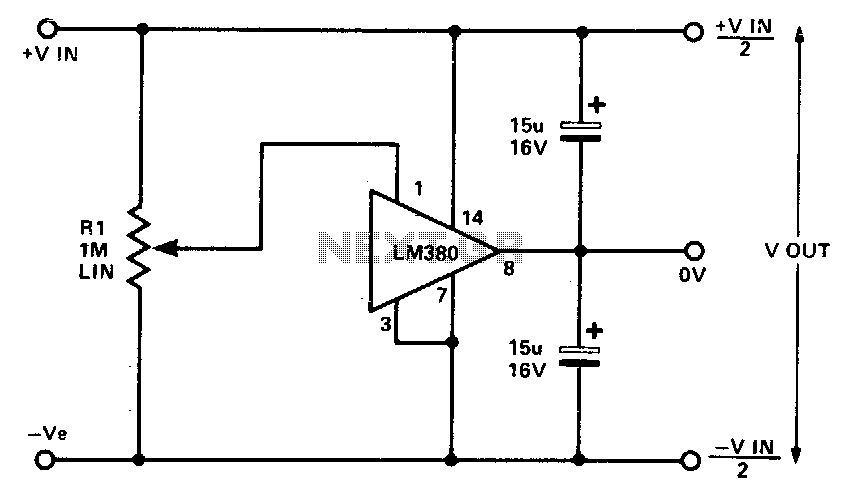
This circuit employs the quasi-complementary output stage of the well-known LM380 audio power integrated circuit (IC). The IC is internally biased to maintain the output at a midpoint between the supply rails when there is no input signal. A resistor labeled Rl is initially set to mid-travel to compensate for any output imbalance. The regulation of the output voltage (Vout) is contingent upon the circuitry supplying the LM380; however, both positive and negative outputs will accurately track regardless of input regulation and unbalanced loads. Additionally, the free-air dissipation is slightly over 1 watt, necessitating potential extra cooling. The device features full protection mechanisms, entering thermal shutdown if the rated dissipation limit is surpassed. Current limiting is activated if the output current exceeds 1 A, and the input voltage must not exceed 20 V.
The circuit design leveraging the LM380 audio power IC is notable for its efficiency in audio amplification applications. The quasi-complementary output stage configuration allows for a more linear response and reduces distortion, which is critical in high-fidelity audio systems. The internal biasing of the LM380 ensures that the output remains stable at half the supply voltage when idle, preventing unwanted noise and allowing for seamless transitions when audio signals are present.
The resistor Rl plays a crucial role in maintaining output balance. By adjusting this resistor to mid-travel, any inherent imbalances in the output stage can be corrected, ensuring that both the positive and negative outputs remain symmetrical. This is particularly important in applications where audio clarity and fidelity are paramount, as any imbalance can lead to distortion and a decrease in sound quality.
In terms of power management, the LM380's ability to handle a free-air dissipation of slightly over 1 watt highlights the importance of thermal management. In scenarios where the power dissipation approaches the limits, additional cooling solutions, such as heat sinks or active cooling methods, may be necessary to prevent thermal shutdown. The built-in thermal protection feature is a significant advantage, as it safeguards the device from damage due to overheating, ensuring reliability and longevity in operation.
Current limiting at 1 A output current is another protective feature that prevents damage to the circuit during overload conditions. This ensures that the circuit can handle transient spikes in demand without compromising its integrity. Furthermore, adhering to the input voltage specification of not exceeding 20 V is critical, as exceeding this limit could lead to irreversible damage to the IC.
Overall, the design considerations surrounding the LM380 audio power IC and its associated circuitry provide a robust framework for high-performance audio amplification, ensuring both reliability and audio fidelity in various applications.This circuit utilizes the quasi-complementary output stage of the popular LM380 audio power IC. The device is internally biased so that with no input the output is held midway between the supply rails Rl, which should be initially set to mid-travel, is used to nullify any inbalance in the output. Regulation of Vout depends upon the circuit feeding the LM380, but positive and negative outputs will track accurately irrespective of input regulation and unbalanced loads
The free-air dissipation is a little over 1 watt, and so extra cooling: may be required. The device is fully protected and will go into thermal shutdown if its rated dissipation is exceeded. Current limiting occurs if the output current exceeds 1 A. The input voltage should not exceed 20 V.
The circuit design leveraging the LM380 audio power IC is notable for its efficiency in audio amplification applications. The quasi-complementary output stage configuration allows for a more linear response and reduces distortion, which is critical in high-fidelity audio systems. The internal biasing of the LM380 ensures that the output remains stable at half the supply voltage when idle, preventing unwanted noise and allowing for seamless transitions when audio signals are present.
The resistor Rl plays a crucial role in maintaining output balance. By adjusting this resistor to mid-travel, any inherent imbalances in the output stage can be corrected, ensuring that both the positive and negative outputs remain symmetrical. This is particularly important in applications where audio clarity and fidelity are paramount, as any imbalance can lead to distortion and a decrease in sound quality.
In terms of power management, the LM380's ability to handle a free-air dissipation of slightly over 1 watt highlights the importance of thermal management. In scenarios where the power dissipation approaches the limits, additional cooling solutions, such as heat sinks or active cooling methods, may be necessary to prevent thermal shutdown. The built-in thermal protection feature is a significant advantage, as it safeguards the device from damage due to overheating, ensuring reliability and longevity in operation.
Current limiting at 1 A output current is another protective feature that prevents damage to the circuit during overload conditions. This ensures that the circuit can handle transient spikes in demand without compromising its integrity. Furthermore, adhering to the input voltage specification of not exceeding 20 V is critical, as exceeding this limit could lead to irreversible damage to the IC.
Overall, the design considerations surrounding the LM380 audio power IC and its associated circuitry provide a robust framework for high-performance audio amplification, ensuring both reliability and audio fidelity in various applications.This circuit utilizes the quasi-complementary output stage of the popular LM380 audio power IC. The device is internally biased so that with no input the output is held midway between the supply rails Rl, which should be initially set to mid-travel, is used to nullify any inbalance in the output. Regulation of Vout depends upon the circuit feeding the LM380, but positive and negative outputs will track accurately irrespective of input regulation and unbalanced loads
The free-air dissipation is a little over 1 watt, and so extra cooling: may be required. The device is fully protected and will go into thermal shutdown if its rated dissipation is exceeded. Current limiting occurs if the output current exceeds 1 A. The input voltage should not exceed 20 V.