simple supply voltage monitor
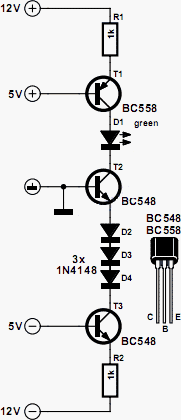
A circuit for monitoring supply voltages of ±5 V and ±12 V can be constructed as shown in the diagram. It is significantly simpler than the typical monitors that utilize comparators and AND gates. The circuit is not designed to indicate the level of the inputs. During normal operation, transistors T1 and T3 function as current sources. The voltage drop across resistors R1 and R2 is 6.3 V (12 - 5 - 0.7). This results in a current of 6.3 mA flowing through diode D1 when all four voltages are present. However, if the 5 V line fails, transistor T3 remains on, but the base-emitter junction of transistor T2 is no longer biased, causing T2 to turn off. Consequently, there is no current through D, which then becomes inactive.
The described voltage monitoring circuit employs a straightforward design that leverages the characteristics of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) to provide a reliable indication of supply voltage integrity. The circuit operates within a dual voltage range, monitoring both positive and negative supply lines, specifically ±5 V and ±12 V. The configuration includes two primary transistors, T1 and T3, which are configured as current sources, ensuring stable operation across varying load conditions.
Resistors R1 and R2 play a crucial role in setting the reference voltage drop across the circuit, calculated to be 6.3 V. This voltage drop is essential for maintaining the necessary biasing conditions for the transistors. The current flowing through these resistors is measured at 6.3 mA, which is adequate to activate diode D1 under normal operating conditions, indicating that all monitored voltages are present.
In the event of a failure in the 5 V supply line, the circuit is designed to respond effectively. Transistor T3 continues to conduct, maintaining its state; however, the failure impacts transistor T2's base-emitter junction, which loses its bias. As a result, T2 ceases to conduct, interrupting the current flow through diode D. This change serves as an indication of the fault condition, effectively signaling that one of the critical supply voltages is no longer available.
Overall, this voltage monitoring circuit provides a robust and efficient solution for ensuring the integrity of ±5 V and ±12 V supply lines, utilizing minimal components while maintaining clear operational functionality. The design's simplicity enhances reliability and reduces potential points of failure, making it suitable for various applications in electronic systems where voltage monitoring is essential.A circuit for monitoring supply voltages of ±5 V and ±12 V is readily constructed as shown in the diagram. It is appreciably simpler than the usual monitors that use comparators, and AND gates. The circuit is not intended to indicate the level of the inputs. In normal operation, transistors T1 and T3 must be seen as current sources. The drop acr oss resistors R1 and R2 is 6. 3 V (12 5 0. 7). This means that the current is 6. 3mA and this flows through diode D1 when all four voltages are present. However, if for instance, the 5 V line fails, transistor T3 remains on but the base-emitter junction of T2 is no longer biased, so that this transistor is cut off. When this happens, there is no current through D which then goes out. 🔗 External reference
The described voltage monitoring circuit employs a straightforward design that leverages the characteristics of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) to provide a reliable indication of supply voltage integrity. The circuit operates within a dual voltage range, monitoring both positive and negative supply lines, specifically ±5 V and ±12 V. The configuration includes two primary transistors, T1 and T3, which are configured as current sources, ensuring stable operation across varying load conditions.
Resistors R1 and R2 play a crucial role in setting the reference voltage drop across the circuit, calculated to be 6.3 V. This voltage drop is essential for maintaining the necessary biasing conditions for the transistors. The current flowing through these resistors is measured at 6.3 mA, which is adequate to activate diode D1 under normal operating conditions, indicating that all monitored voltages are present.
In the event of a failure in the 5 V supply line, the circuit is designed to respond effectively. Transistor T3 continues to conduct, maintaining its state; however, the failure impacts transistor T2's base-emitter junction, which loses its bias. As a result, T2 ceases to conduct, interrupting the current flow through diode D. This change serves as an indication of the fault condition, effectively signaling that one of the critical supply voltages is no longer available.
Overall, this voltage monitoring circuit provides a robust and efficient solution for ensuring the integrity of ±5 V and ±12 V supply lines, utilizing minimal components while maintaining clear operational functionality. The design's simplicity enhances reliability and reduces potential points of failure, making it suitable for various applications in electronic systems where voltage monitoring is essential.A circuit for monitoring supply voltages of ±5 V and ±12 V is readily constructed as shown in the diagram. It is appreciably simpler than the usual monitors that use comparators, and AND gates. The circuit is not intended to indicate the level of the inputs. In normal operation, transistors T1 and T3 must be seen as current sources. The drop acr oss resistors R1 and R2 is 6. 3 V (12 5 0. 7). This means that the current is 6. 3mA and this flows through diode D1 when all four voltages are present. However, if for instance, the 5 V line fails, transistor T3 remains on but the base-emitter junction of T2 is no longer biased, so that this transistor is cut off. When this happens, there is no current through D which then goes out. 🔗 External reference