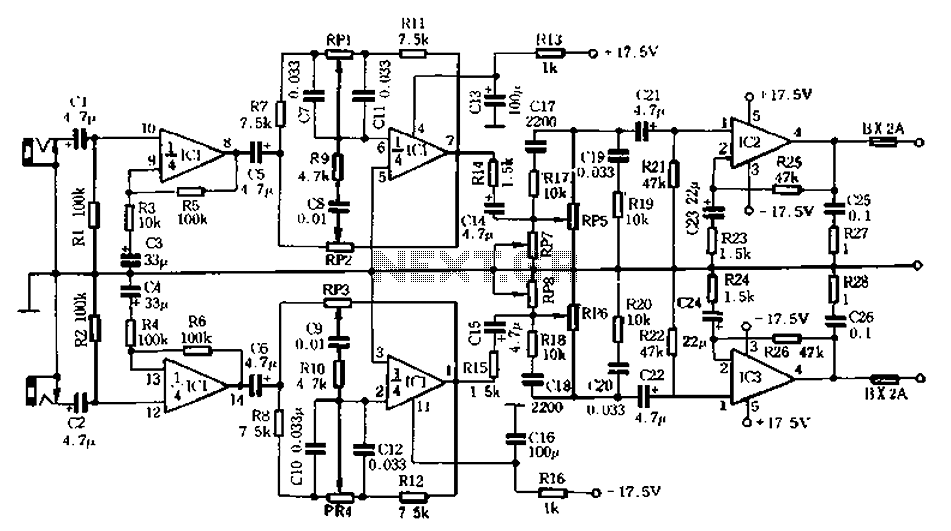
simple thermocouple amplifier
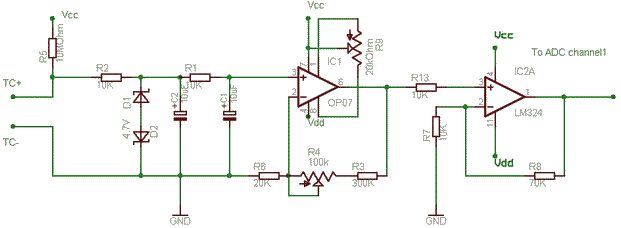
The OP07 operates as a non-inverting amplifier to avoid loading the millivolt signal from the thermocouple. Zener diodes are included to protect the circuit in the event of a failure in the junction contacts, heaters, or ground. A resistor-capacitor (RC) filter is employed to eliminate 50Hz noise that may be induced in the thermocouple wires when they are near heater wiring, and it also minimizes reading fluctuations caused by the operation of high-current three-phase contactors. A 10M pull-up resistor is utilized to ensure proper output behavior. In the case of a thermocouple failure, the circuit output will reach its maximum value, which serves as an open sensor protection mechanism. This feature is particularly important in industrial temperature controllers, as it will produce an output of 3.5V, prompting the software to shut off the heater. An additional operational amplifier is used for further amplification, with the OP07 set to a gain of approximately 30. The offset must be fine-tuned using resistor R9. If the OP07 is configured with a gain greater than 100, adjusting the offset to 75µV may become challenging. For applications requiring very high gain in the first stage, it is advisable to consider using an instrumentation amplifier or a chopper-stabilized amplifier.
The circuit comprises several key components that work together to ensure accurate temperature measurement and control. The OP07 operational amplifier is chosen for its low offset voltage and high precision, making it suitable for amplifying the low-level signals from thermocouples. The non-inverting configuration allows the amplifier to provide a high input impedance, which is essential to avoid loading the thermocouple and altering its output voltage.
The inclusion of Zener diodes serves as a protective measure against voltage spikes that could occur due to faults in the system. These diodes clamp the voltage to a safe level, preventing damage to the sensitive components of the circuit. The RC filter is strategically placed to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) from surrounding AC power sources, particularly in environments where heaters are present. This filtering ensures that the output signal remains stable and reliable, even in the presence of noise.
The pull-up resistor plays a crucial role in defining the output state during a thermocouple failure. By pulling the output to a defined high level, the circuit can trigger safety mechanisms in the control software, thus preventing potential overheating or damage to the system.
The second operational amplifier in the configuration allows for additional gain, enhancing the overall sensitivity of the temperature measurement system. Careful adjustment of the gain and offset is necessary to maintain accuracy, particularly when working with high gains. If higher gains are required, alternative amplifier types, such as instrumentation amplifiers, can provide better performance without the complications associated with offset adjustments.
Overall, this circuit design is tailored for industrial temperature control applications, where precision, reliability, and safety are paramount. The combination of operational amplifiers, filtering, and protective components creates a robust system capable of handling the challenges presented by thermocouple measurements in demanding environments.The OP07 is in a non inverting amplifier so as not load the mV of thermocouple, the zeners are to protect circuit if junction contacts heaters or the earth gets broken. The RC is to filter out 50Hz pick up in thermocouple wires if near heater wiring and also reduces reading jumps when high current three phase contacter operates.
The Pull-up 10M is when a Thermocouple breaks the output of circuit will be max. This is open sensor protection, in case Thermocouple breaks, Required only in industrial temperature controllers for protection. This means it will be 3. 5V which should make you turn off the heater in software. The other opamp is for further amplification as OP07 is set to around 30 gain and offset has to be adjusted with R9.
If OP07 is kept in > 100 gain it may be difficult to adjust offset of 75uV. If you need very high gain in the first stage use some instrumentation amplifier or chopper stabilized amplifier. I am not very sure. 🔗 External reference
The circuit comprises several key components that work together to ensure accurate temperature measurement and control. The OP07 operational amplifier is chosen for its low offset voltage and high precision, making it suitable for amplifying the low-level signals from thermocouples. The non-inverting configuration allows the amplifier to provide a high input impedance, which is essential to avoid loading the thermocouple and altering its output voltage.
The inclusion of Zener diodes serves as a protective measure against voltage spikes that could occur due to faults in the system. These diodes clamp the voltage to a safe level, preventing damage to the sensitive components of the circuit. The RC filter is strategically placed to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) from surrounding AC power sources, particularly in environments where heaters are present. This filtering ensures that the output signal remains stable and reliable, even in the presence of noise.
The pull-up resistor plays a crucial role in defining the output state during a thermocouple failure. By pulling the output to a defined high level, the circuit can trigger safety mechanisms in the control software, thus preventing potential overheating or damage to the system.
The second operational amplifier in the configuration allows for additional gain, enhancing the overall sensitivity of the temperature measurement system. Careful adjustment of the gain and offset is necessary to maintain accuracy, particularly when working with high gains. If higher gains are required, alternative amplifier types, such as instrumentation amplifiers, can provide better performance without the complications associated with offset adjustments.
Overall, this circuit design is tailored for industrial temperature control applications, where precision, reliability, and safety are paramount. The combination of operational amplifiers, filtering, and protective components creates a robust system capable of handling the challenges presented by thermocouple measurements in demanding environments.The OP07 is in a non inverting amplifier so as not load the mV of thermocouple, the zeners are to protect circuit if junction contacts heaters or the earth gets broken. The RC is to filter out 50Hz pick up in thermocouple wires if near heater wiring and also reduces reading jumps when high current three phase contacter operates.
The Pull-up 10M is when a Thermocouple breaks the output of circuit will be max. This is open sensor protection, in case Thermocouple breaks, Required only in industrial temperature controllers for protection. This means it will be 3. 5V which should make you turn off the heater in software. The other opamp is for further amplification as OP07 is set to around 30 gain and offset has to be adjusted with R9.
If OP07 is kept in > 100 gain it may be difficult to adjust offset of 75uV. If you need very high gain in the first stage use some instrumentation amplifier or chopper stabilized amplifier. I am not very sure. 🔗 External reference