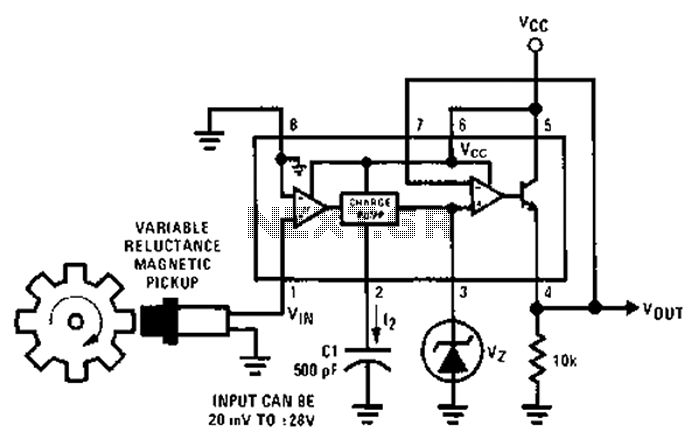
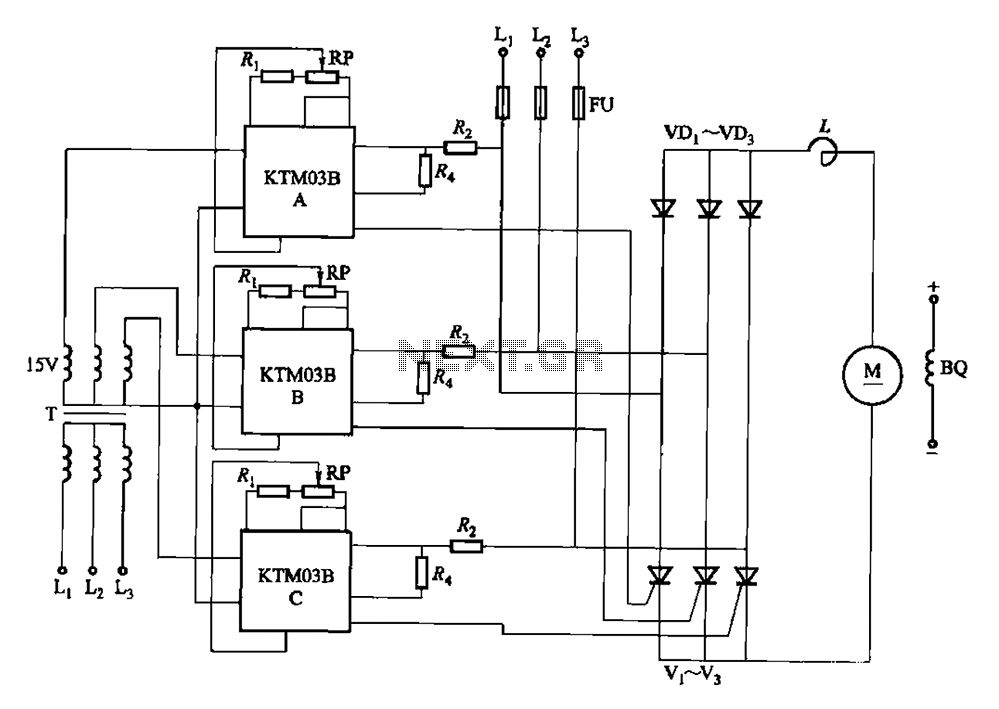
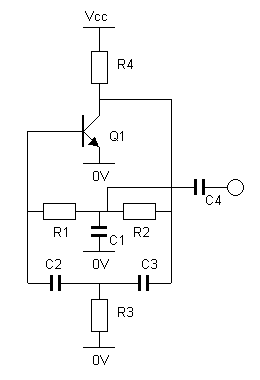
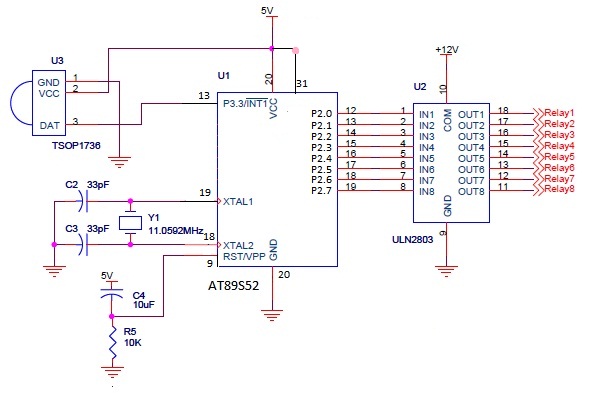
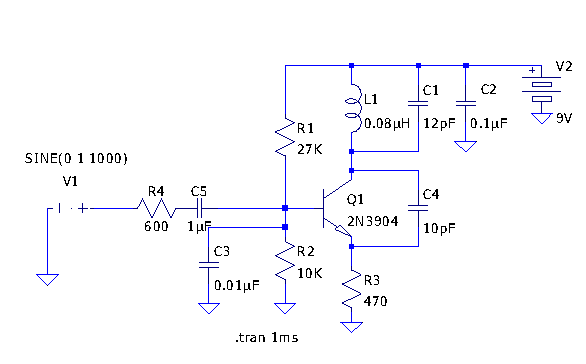
Single Chip Stereo FM Transmitter Circuit
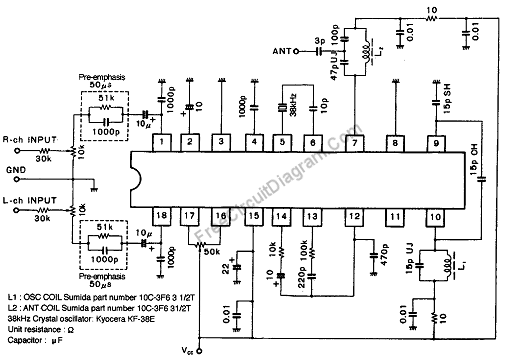
An FM modulator that modulates a carrier frequency with the composite signal, and an RF amplifier that provides enough power to be transmitted through an antenna. Here is the schematic diagram of the FM transmitter circuit: The core of this stereo FM transmitter...
An FM transmitter circuit typically consists of two main components: the FM modulator and the RF amplifier. The FM modulator is responsible for varying the frequency of a carrier wave in accordance with the input audio signal, which is often a composite signal that combines multiple audio channels. This modulation process enables the transmission of audio information over radio frequencies.
The RF amplifier serves to boost the power of the modulated signal to ensure it can be effectively transmitted through an antenna. The output power of the RF amplifier is crucial, as it determines the transmission range of the FM signal. The schematic diagram of the FM transmitter circuit illustrates the interconnection of these components, including the input for the audio signal, the modulator circuit, and the RF amplifier stage.
In a typical design, the FM modulator may utilize a varactor diode or a phase-locked loop (PLL) to achieve frequency modulation. The modulator's output is then fed into the RF amplifier, which may be a class C amplifier for efficient power handling. The antenna is connected to the output of the RF amplifier, allowing the modulated signal to be radiated into the environment.
Additional components such as filters may be included in the circuit to eliminate unwanted harmonics and ensure signal clarity. Proper design considerations should be made regarding the power supply, component ratings, and PCB layout to minimize interference and maximize performance. Overall, the FM transmitter circuit is a sophisticated assembly of electronic components designed to facilitate the wireless transmission of audio signals.an FM modulator that modulate a carrier frequency with the composite signal, and an RF amplifier that provide enough power to be transmitted through antenna. Here is the schematic diagram of theFM transmitter circuit: The core of this stereo FM tra.. 🔗 External reference
An FM transmitter circuit typically consists of two main components: the FM modulator and the RF amplifier. The FM modulator is responsible for varying the frequency of a carrier wave in accordance with the input audio signal, which is often a composite signal that combines multiple audio channels. This modulation process enables the transmission of audio information over radio frequencies.
The RF amplifier serves to boost the power of the modulated signal to ensure it can be effectively transmitted through an antenna. The output power of the RF amplifier is crucial, as it determines the transmission range of the FM signal. The schematic diagram of the FM transmitter circuit illustrates the interconnection of these components, including the input for the audio signal, the modulator circuit, and the RF amplifier stage.
In a typical design, the FM modulator may utilize a varactor diode or a phase-locked loop (PLL) to achieve frequency modulation. The modulator's output is then fed into the RF amplifier, which may be a class C amplifier for efficient power handling. The antenna is connected to the output of the RF amplifier, allowing the modulated signal to be radiated into the environment.
Additional components such as filters may be included in the circuit to eliminate unwanted harmonics and ensure signal clarity. Proper design considerations should be made regarding the power supply, component ratings, and PCB layout to minimize interference and maximize performance. Overall, the FM transmitter circuit is a sophisticated assembly of electronic components designed to facilitate the wireless transmission of audio signals.an FM modulator that modulate a carrier frequency with the composite signal, and an RF amplifier that provide enough power to be transmitted through antenna. Here is the schematic diagram of theFM transmitter circuit: The core of this stereo FM tra.. 🔗 External reference