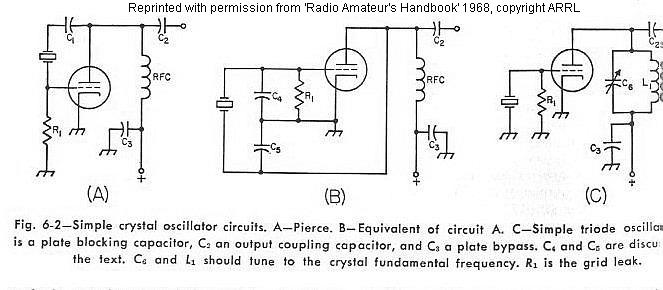
Single-phase motor energy consumption of the two brake circuits
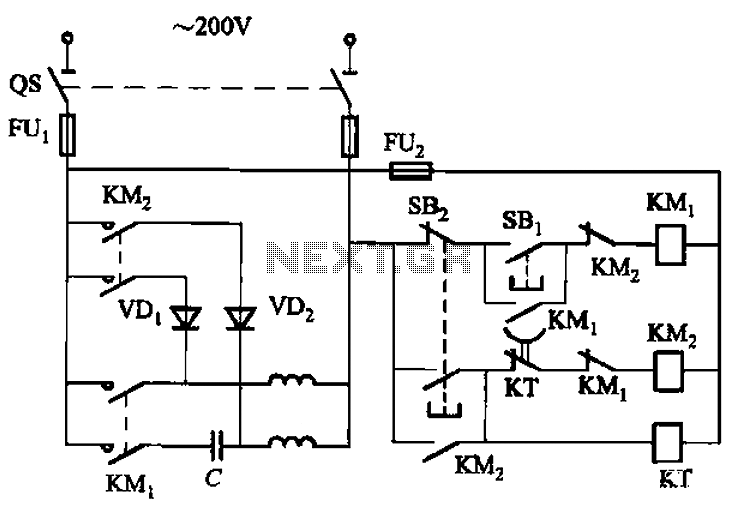
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-150 involves a contactor (KM1) that releases when the system is shut down. The contactor KM2 is energized, allowing a 220V AC power supply to flow through diodes VD1 and VD2, which serve as rectifiers. This configuration applies DC current to the motor's primary and secondary windings, effectively engaging the motor's braking mechanism. After a predetermined delay of 0.2 seconds (adjustable), the time relay (KT) deactivates, concluding the braking process.
The described circuit utilizes a contactor system to manage the operation of an electric motor during shutdown scenarios. The initial release of contactor KM1 signifies that the system is no longer operational. However, contactor KM2 remains engaged to facilitate the application of a 220V AC power supply. The path through diodes VD1 and VD2 is critical, as these components convert the AC voltage to DC, allowing for effective braking by applying the appropriate current to the motor windings.
The braking process is a crucial safety feature that prevents the motor from coasting to a stop, which could lead to mechanical wear or operational hazards. The use of a time relay (KT) introduces an adjustable delay, allowing for fine-tuning of the braking duration based on the specific requirements of the application. This flexibility ensures that the braking action can be adapted to different load conditions or operational scenarios.
In summary, the circuit's design integrates contactors, diodes, and a time relay to create a reliable braking mechanism for electric motors, enhancing both performance and safety during shutdown procedures. The careful selection of components and their arrangement in the circuit is essential for achieving the desired braking characteristics and operational reliability. Circuit shown in Figure 3-150. When shut down, the contactor KM1 released. KMz pull, 220V AC power supply through the diode VDi, VD2 rectifier, the motor primary and secondary windings with DC current braking, the electric motor into the brake status. After a delay (0. 2-ls, adjustable), time relay KT releases, ending the braking process.
The described circuit utilizes a contactor system to manage the operation of an electric motor during shutdown scenarios. The initial release of contactor KM1 signifies that the system is no longer operational. However, contactor KM2 remains engaged to facilitate the application of a 220V AC power supply. The path through diodes VD1 and VD2 is critical, as these components convert the AC voltage to DC, allowing for effective braking by applying the appropriate current to the motor windings.
The braking process is a crucial safety feature that prevents the motor from coasting to a stop, which could lead to mechanical wear or operational hazards. The use of a time relay (KT) introduces an adjustable delay, allowing for fine-tuning of the braking duration based on the specific requirements of the application. This flexibility ensures that the braking action can be adapted to different load conditions or operational scenarios.
In summary, the circuit's design integrates contactors, diodes, and a time relay to create a reliable braking mechanism for electric motors, enhancing both performance and safety during shutdown procedures. The careful selection of components and their arrangement in the circuit is essential for achieving the desired braking characteristics and operational reliability. Circuit shown in Figure 3-150. When shut down, the contactor KM1 released. KMz pull, 220V AC power supply through the diode VDi, VD2 rectifier, the motor primary and secondary windings with DC current braking, the electric motor into the brake status. After a delay (0. 2-ls, adjustable), time relay KT releases, ending the braking process.