Stair case wiring circuit diagram OR How to control a lamp from two different places by two 2-way switches
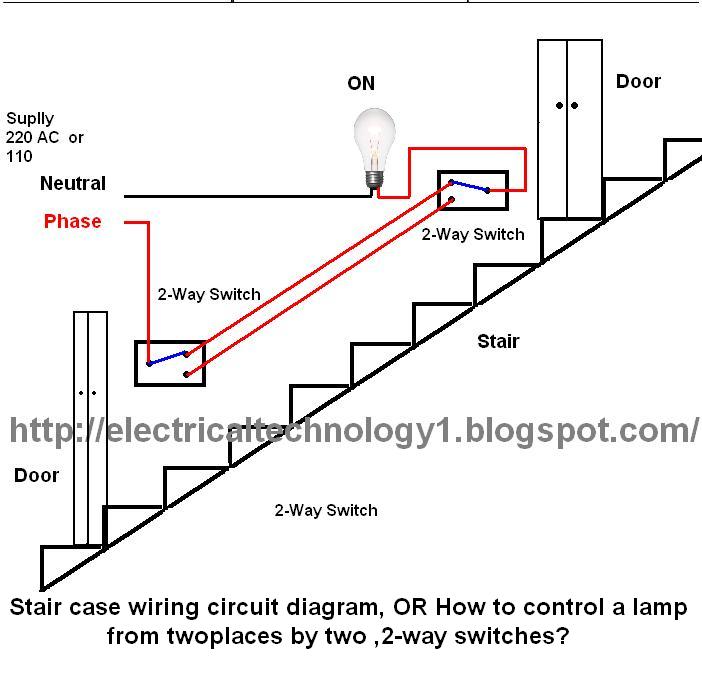
The circuit is complete, and the bulb is ON. To turn OFF the bulb from the upper switch at the top of the stairs, simply turn OFF the switch, which will break the circuit and turn the bulb OFF. The bulb can be turned ON again by activating the same switch. In other words, the bulb can be controlled from the upper switch at the top of the stairs. Similarly, the same control can be achieved from the lower switch at the bottom of the stairs. Returning to the circuit in the picture, when the circuit is complete, the bulb remains ON. To turn OFF the bulb from the lower switch, simply turn OFF the switch, breaking the circuit and turning the bulb OFF. The bulb can be turned ON again by activating this switch. This is a staircase circuit diagram that allows control of a bulb from two different locations. The bulb can be switched OFF and ON from both switches simultaneously, enabling control from both the upper and lower switches.
The staircase circuit, commonly referred to as a two-way switching circuit, utilizes two switches to control a single load, such as a light bulb, from two different locations. This configuration is particularly useful in staircases or long hallways where accessibility to a switch from both ends is desired.
In the typical wiring setup, the two switches are connected in a way that allows them to control the same light fixture. Each switch has three terminals: one common terminal and two traveler terminals. The common terminal connects to the power source or the load (the bulb), while the traveler terminals connect to the corresponding traveler terminals of the other switch.
When the first switch is toggled, it either connects or disconnects the circuit, allowing current to flow to the bulb or interrupting it. The second switch can then be used to reverse the state of the bulb, effectively allowing the user to turn the light ON or OFF regardless of the position of the other switch. This creates a versatile control system that enhances convenience and safety in areas where lighting is essential.
In summary, this two-way switching circuit enables efficient control of lighting from multiple locations, ensuring that the user can operate the light fixture from both the upper and lower positions of the staircase. The design promotes ease of use and flexibility in lighting control, making it an essential feature in modern electrical installations.You can see that circuit is complete and bulb is ON. Suppose you want to OFF bulb from the upper switch at top of stair, simply Switch OFF the switch then circuit will break and the bulb will be OFF. You can switch ON the bulb again to switch ON this Switch. In other words you can OFF and ON bulb from upper switch at the top of stair. Obviously; you can do same from the upper and bottom switch, so let`s see how we can do that from that switch at the bottom of stair. Now return to circuit again in the pic, In this case you can see that circuit is complete and bulb is ON.
Suppose you want to OFF the bulb from the lower switch at bottom of stair. Simply OFF the switch, then again circuit will break and the bulb will be OFF. You can switch ON the bulb again to switch ON this Switch This is a stair case circuit diagram by which we can control a bulb from two different places. We can switch OFF and Switch ON the bulb from both switches at the same time. in other words we can control (OFF or ON) the bulb from upper and lower switches. 🔗 External reference
The staircase circuit, commonly referred to as a two-way switching circuit, utilizes two switches to control a single load, such as a light bulb, from two different locations. This configuration is particularly useful in staircases or long hallways where accessibility to a switch from both ends is desired.
In the typical wiring setup, the two switches are connected in a way that allows them to control the same light fixture. Each switch has three terminals: one common terminal and two traveler terminals. The common terminal connects to the power source or the load (the bulb), while the traveler terminals connect to the corresponding traveler terminals of the other switch.
When the first switch is toggled, it either connects or disconnects the circuit, allowing current to flow to the bulb or interrupting it. The second switch can then be used to reverse the state of the bulb, effectively allowing the user to turn the light ON or OFF regardless of the position of the other switch. This creates a versatile control system that enhances convenience and safety in areas where lighting is essential.
In summary, this two-way switching circuit enables efficient control of lighting from multiple locations, ensuring that the user can operate the light fixture from both the upper and lower positions of the staircase. The design promotes ease of use and flexibility in lighting control, making it an essential feature in modern electrical installations.You can see that circuit is complete and bulb is ON. Suppose you want to OFF bulb from the upper switch at top of stair, simply Switch OFF the switch then circuit will break and the bulb will be OFF. You can switch ON the bulb again to switch ON this Switch. In other words you can OFF and ON bulb from upper switch at the top of stair. Obviously; you can do same from the upper and bottom switch, so let`s see how we can do that from that switch at the bottom of stair. Now return to circuit again in the pic, In this case you can see that circuit is complete and bulb is ON.
Suppose you want to OFF the bulb from the lower switch at bottom of stair. Simply OFF the switch, then again circuit will break and the bulb will be OFF. You can switch ON the bulb again to switch ON this Switch This is a stair case circuit diagram by which we can control a bulb from two different places. We can switch OFF and Switch ON the bulb from both switches at the same time. in other words we can control (OFF or ON) the bulb from upper and lower switches. 🔗 External reference