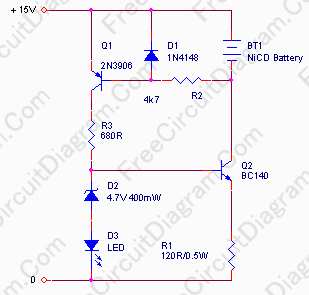
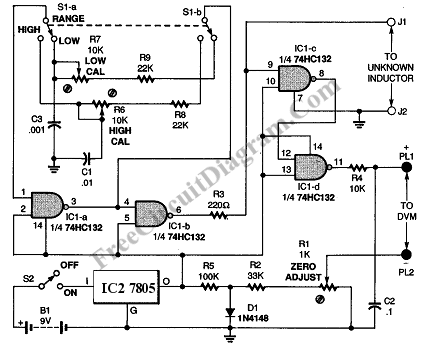
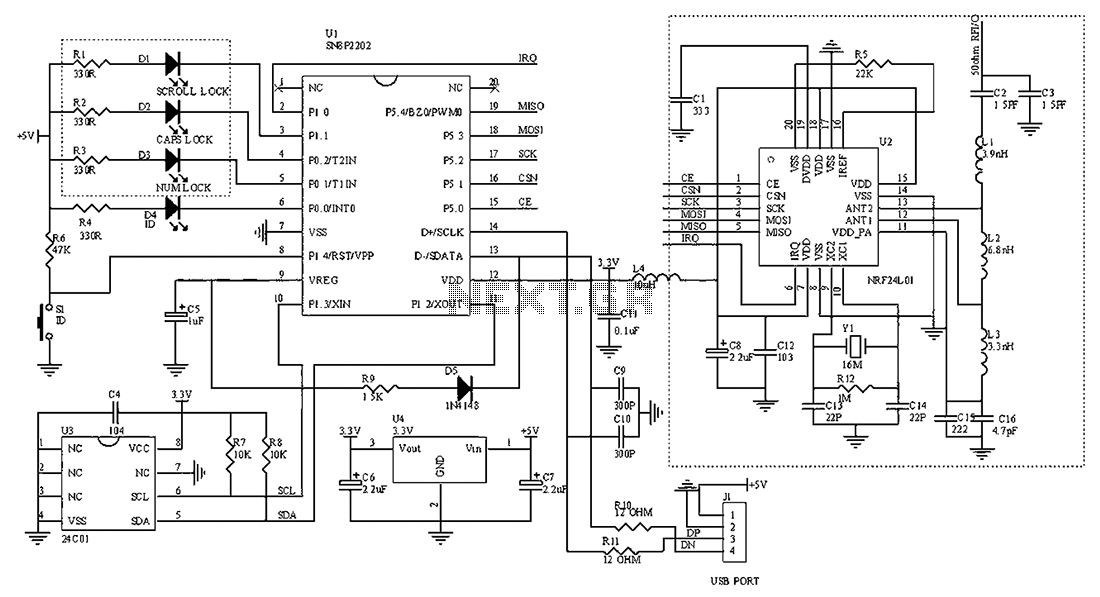
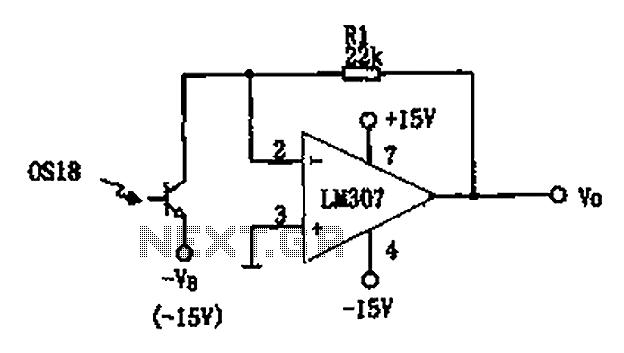
Single-phase motor stepless thyristor circuit 2
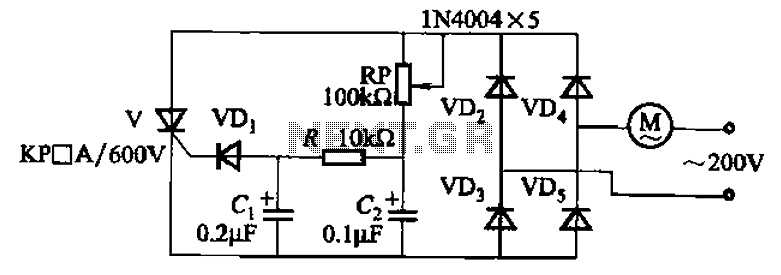
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-11 employs a unidirectional thyristor control mechanism. An adjustable potentiometer, designated as RP, is utilized to continuously modify the motor speed.
The circuit utilizes a unidirectional thyristor, also known as a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR), which allows current to flow in one direction only. This characteristic is fundamental in controlling the power delivered to the motor. The thyristor is triggered into conduction by a gate signal, which can be controlled by the adjustment of the potentiometer RP.
The potentiometer RP is connected in such a way that its resistance can be varied, thereby altering the voltage applied to the gate of the thyristor. By adjusting RP, the phase angle at which the thyristor is triggered can be modified, leading to changes in the average voltage supplied to the motor. This results in a corresponding change in the motor's speed.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against reverse voltage, capacitors for filtering, and resistors to limit current. The configuration of these components is essential for ensuring stable operation and preventing damage to the thyristor and motor.
In practical applications, this type of circuit is often used in variable speed drives for DC motors, where precise control over speed is necessary for various industrial and automation tasks. The simplicity of the design combined with the effectiveness of the thyristor control makes it a popular choice in many electronic speed control applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-11. It uses a one-way thyristor control. Adjustment potentiometer RP, continuously changing the motor speed.
The circuit utilizes a unidirectional thyristor, also known as a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR), which allows current to flow in one direction only. This characteristic is fundamental in controlling the power delivered to the motor. The thyristor is triggered into conduction by a gate signal, which can be controlled by the adjustment of the potentiometer RP.
The potentiometer RP is connected in such a way that its resistance can be varied, thereby altering the voltage applied to the gate of the thyristor. By adjusting RP, the phase angle at which the thyristor is triggered can be modified, leading to changes in the average voltage supplied to the motor. This results in a corresponding change in the motor's speed.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against reverse voltage, capacitors for filtering, and resistors to limit current. The configuration of these components is essential for ensuring stable operation and preventing damage to the thyristor and motor.
In practical applications, this type of circuit is often used in variable speed drives for DC motors, where precise control over speed is necessary for various industrial and automation tasks. The simplicity of the design combined with the effectiveness of the thyristor control makes it a popular choice in many electronic speed control applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-11. It uses a one-way thyristor control. Adjustment potentiometer RP, continuously changing the motor speed.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713