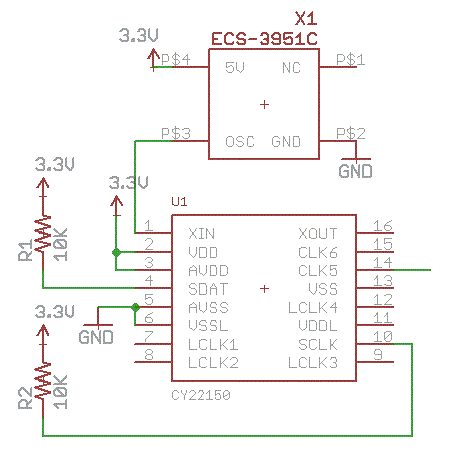
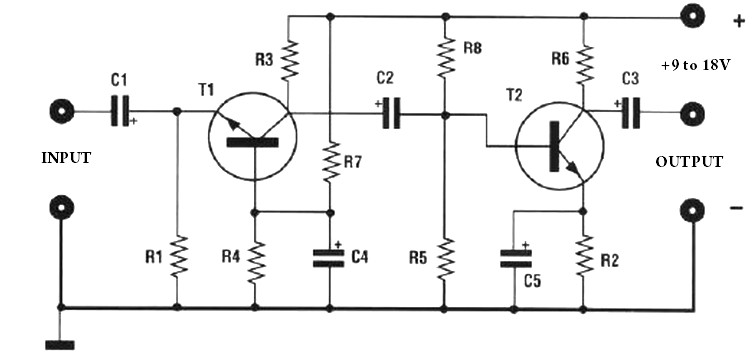
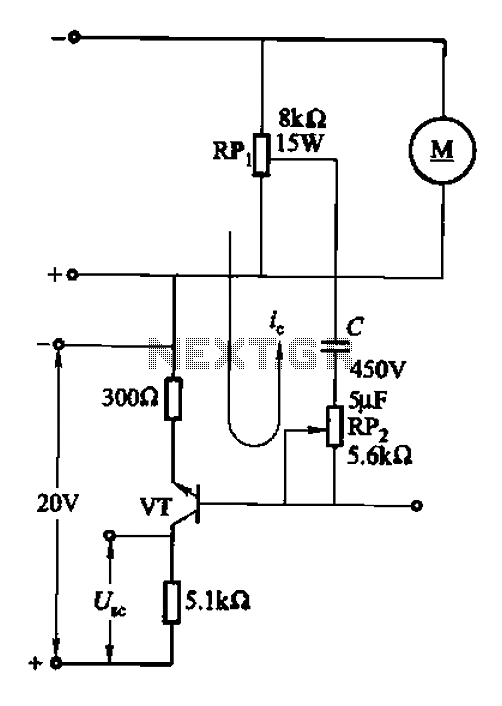
2.4G wireless keyboard receiver part of the circuit
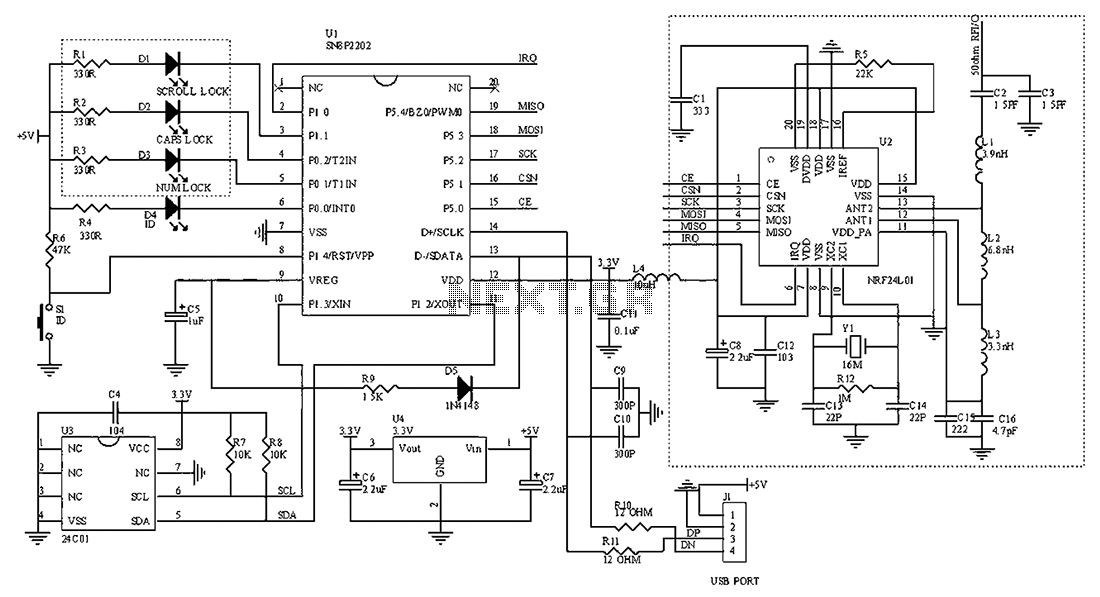
The circuit diagram for the receiving portion of a 2.4 GHz wireless keyboard is presented below.
The 2.4 GHz wireless keyboard receiving circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to receive and process signals transmitted from the keyboard. The main components include an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) receiver module, a microcontroller, and associated passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
The antenna is responsible for capturing the RF signals transmitted by the wireless keyboard. It is designed to operate efficiently at 2.4 GHz, ensuring optimal reception of the signals. The RF receiver module demodulates the incoming signals, converting them from radio frequency to baseband signals that can be processed by the microcontroller.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit of the receiving circuit. It interprets the demodulated signals, translating them into commands that correspond to keystrokes made on the keyboard. The microcontroller may also include firmware that manages the communication protocol and handles any error correction necessary for reliable data transmission.
Additionally, passive components such as capacitors and resistors are used to filter noise and stabilize the power supply to the RF receiver and microcontroller. Proper design of the power supply circuit is crucial to ensure that the components operate within their specified voltage and current ranges, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the wireless keyboard system.
In summary, the 2.4 GHz wireless keyboard receiving circuit integrates an antenna, RF receiver, microcontroller, and passive components to effectively receive and process wireless signals, enabling seamless communication between the keyboard and the host device. This design is essential for achieving the desired user experience in wireless keyboard applications.2.4G wireless keyboard receiving portion circuit diagram as follows:
The 2.4 GHz wireless keyboard receiving circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to receive and process signals transmitted from the keyboard. The main components include an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) receiver module, a microcontroller, and associated passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
The antenna is responsible for capturing the RF signals transmitted by the wireless keyboard. It is designed to operate efficiently at 2.4 GHz, ensuring optimal reception of the signals. The RF receiver module demodulates the incoming signals, converting them from radio frequency to baseband signals that can be processed by the microcontroller.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit of the receiving circuit. It interprets the demodulated signals, translating them into commands that correspond to keystrokes made on the keyboard. The microcontroller may also include firmware that manages the communication protocol and handles any error correction necessary for reliable data transmission.
Additionally, passive components such as capacitors and resistors are used to filter noise and stabilize the power supply to the RF receiver and microcontroller. Proper design of the power supply circuit is crucial to ensure that the components operate within their specified voltage and current ranges, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the wireless keyboard system.
In summary, the 2.4 GHz wireless keyboard receiving circuit integrates an antenna, RF receiver, microcontroller, and passive components to effectively receive and process wireless signals, enabling seamless communication between the keyboard and the host device. This design is essential for achieving the desired user experience in wireless keyboard applications.2.4G wireless keyboard receiving portion circuit diagram as follows: