Single Pushbutton Run-Stop Circuit
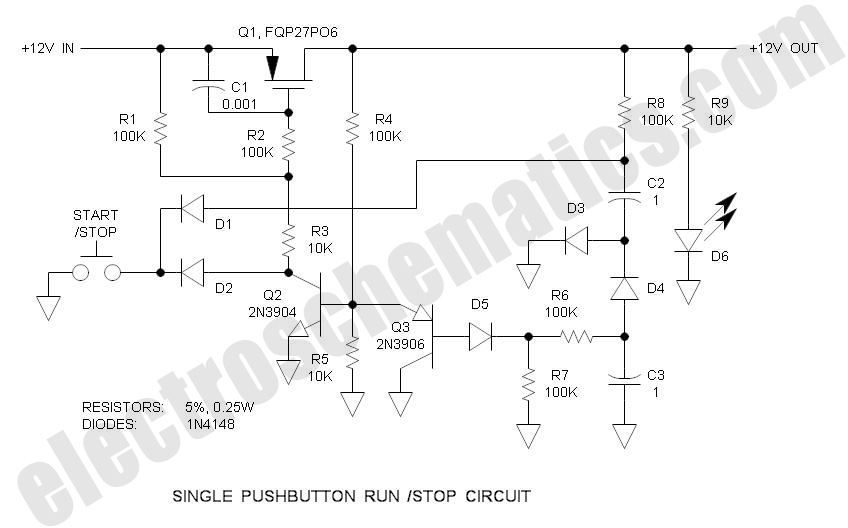
There are solutions to this problem—mechanical (push On/push Off switch), electromagnetic (latching relay), and electronic (CMOS logic), but few (if any) go...
In addressing the problem of circuit control, several methods are available, including mechanical, electromagnetic, and electronic solutions. Mechanical solutions typically involve a push On/Push Off switch, which provides a straightforward means of toggling power states. This type of switch is user-friendly and requires no additional components; however, it may not be suitable for applications requiring remote control or automation.
Electromagnetic solutions, such as latching relays, offer an alternative that can maintain their state without continuous power. A latching relay operates by using an electromagnetic coil to toggle between two stable states. This type of relay can be advantageous in applications where power conservation is critical since it does not require a constant power supply to maintain its position.
Electronic solutions, particularly those utilizing CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) logic, present a highly efficient and versatile option for circuit control. CMOS technology enables low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. A CMOS-based circuit can be designed to perform complex logic operations, allowing for sophisticated control mechanisms that can be tailored to specific requirements.
Each of these solutions has its advantages and limitations, and the choice among them will depend on the specific application requirements, including factors such as power consumption, complexity, and the need for manual versus automated control.There are solutions to this problem—mechanical (push On/push Off switch), electromagnetic (latching relay) and electronic (CMOS logic), but few (if any) go.. 🔗 External reference
In addressing the problem of circuit control, several methods are available, including mechanical, electromagnetic, and electronic solutions. Mechanical solutions typically involve a push On/Push Off switch, which provides a straightforward means of toggling power states. This type of switch is user-friendly and requires no additional components; however, it may not be suitable for applications requiring remote control or automation.
Electromagnetic solutions, such as latching relays, offer an alternative that can maintain their state without continuous power. A latching relay operates by using an electromagnetic coil to toggle between two stable states. This type of relay can be advantageous in applications where power conservation is critical since it does not require a constant power supply to maintain its position.
Electronic solutions, particularly those utilizing CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) logic, present a highly efficient and versatile option for circuit control. CMOS technology enables low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. A CMOS-based circuit can be designed to perform complex logic operations, allowing for sophisticated control mechanisms that can be tailored to specific requirements.
Each of these solutions has its advantages and limitations, and the choice among them will depend on the specific application requirements, including factors such as power consumption, complexity, and the need for manual versus automated control.There are solutions to this problem—mechanical (push On/push Off switch), electromagnetic (latching relay) and electronic (CMOS logic), but few (if any) go.. 🔗 External reference