Smoke Alarm Circuit
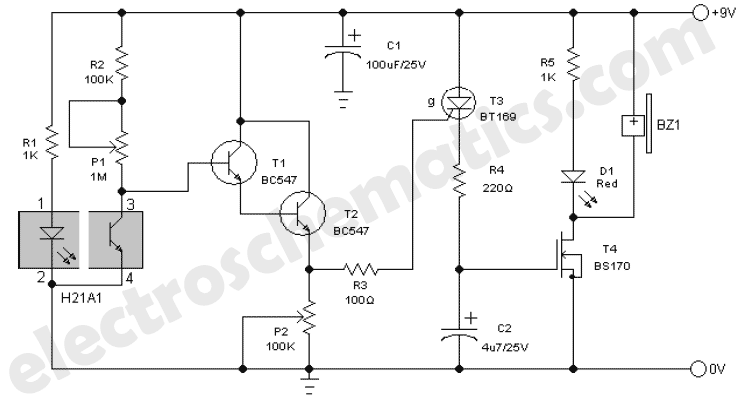
The original smoke alarm circuit has several issues that have disappointed hobbyists and students. Instead of attempting to fix these problems, an update has been created using the well-known LM741 operational amplifier. This new design is simpler, more conventional, easier to understand, and offers significantly improved battery life. The photo-interrupter utilized is an optical coupler with separated elements creating a slot. Any object entering this slot reduces the current transfer ratio (output current/input current). The H21B1 Darlington device was used, as the H21A1 was unavailable. The H21B1 proved to be a superior choice, requiring much less LED current. Since the H21A1/H21B1 series is no longer available from DigiKey, a currently available and more affordable alternative, the Sharp GP series, has been selected. Sharp is recognized as a leader in this product category. Although the use of the Darlington device is recommended, alternatives exist for those with non-Darlington versions. The smoke alarm schematic includes these alternative devices and circuits, which, while not tested, are considered viable. Initial skepticism regarding the technique's effectiveness led to testing a photo-interrupter with smoke, resulting in successful operation as demonstrated by oscillograph readings. The oscillograph also indicated the effects of inserting a transparent poly film into the gap, producing a lower voltage signature. Testing continued with the film instead of smoke for ease. Ambient light impacts the output voltage, with a variation of approximately ±0.1V noted; however, shielding may be necessary if external light sources pose a problem. The LM741 is a suitable choice, but a low-power substitute (TI TL061) was found to reduce battery current, achieving a load of only 1.1mA. The LM741 operates as a comparator/Schmitt trigger, with the inverting input biased at 4.2V (half of Vcc). The photo-transistor collector voltage is adjusted to 4.0V via resistor R2. A decrease in the current transfer ratio causes the collector voltage to rise above 4.2V, triggering the op amp's output to go positive and activating the MOSFET. The MOSFET's drain voltage drops to zero, and capacitor C1 provides a positive feedback signal to the inverting input through resistor R8. The time constant of R8 and C1 ensures that the LED and siren remain active for at least one second after smoke is no longer detected. Capacitor C1 must be a film or ceramic type due to the reversal of voltage polarity. Resistor R1 is chosen to provide approximately 4V at the photo-transistor collector with R2 at a midpoint value, with its resistance dependent on the photo-interrupter's transfer ratio, which may vary significantly (up to 40:1). This selection allows R2 to be adjusted for operational needs. The question marks on the schematics indicate areas requiring actual resistance determination; in practice, one device required a 10K resistor while another needed 22K.
The updated smoke alarm circuit provides a robust solution for smoke detection by integrating an LM741 op-amp as a comparator to enhance performance and reliability. The design leverages a photo-interrupter, which effectively detects smoke by monitoring changes in current transfer ratios caused by obstructions in the light path. The use of a Darlington pair, specifically the H21B1, allows for lower power consumption while maintaining sensitivity. The transition to the Sharp GP series as a replacement for the discontinued H21A1/H21B1 series ensures continued availability of components for hobbyists and engineers alike.
The circuit's design prioritizes ease of understanding and implementation, making it suitable for educational purposes. The comparator configuration provides a clear threshold for smoke detection, with the op-amp output driving a MOSFET to activate an alarm system. The feedback mechanism involving capacitor C1 ensures that the alarm remains engaged for a brief period after smoke is cleared, preventing false negatives due to transient conditions.
The selection of resistors and capacitors is critical for fine-tuning the circuit to specific applications, allowing adjustments based on the characteristics of the photo-interrupter used. This flexibility is essential for achieving optimal performance across varying environmental conditions and component tolerances. Overall, the redesigned smoke alarm circuit represents a significant improvement over its predecessor, offering enhanced functionality, simplicity, and efficiency.The original smoke alarm circuit has some problems and has left some hobbyists and students disappointed. Rather than to attempt to solve its many problems, I have created an update that uses the venerable LM741 op amp.
It is simpler, more conventional, easier to understand and has much better battery life. The photo-interrupter is simply an opti cal coupler with the elements separated with a slot. Anything that enters this slot reduces the current transfer ratio (output current /input current). I used the H21B1 Darlington device since I did not have the H21A1 on hand. I am glad I did, because I learned that it is a better device, requiring far less LED current. Since the H21A1 /H21B1 series is no longer available from DigiKey, I selected a currently available, more inexpensive device ”the Sharp GP series ”see schematic(s) for details. Sharp appears to be the leader in this product. Although, I recommend the Darlington device, do not despair if you have the non-Darlington version. See the smoke alarm schematic for alternative devices /circuits. These were not tested, but I see no reason why they are not viable. I had my doubts as to the effectiveness of the technique, so I tested a photo-interrupter with smoke.
The oscillograph demonstrates what happens to the photo-transistor collector voltage when the gap is obscured with smoke from my soldering iron as it melted rosin core solder. Cool! It does work. The oscillograph also has a trace showing what happens when a transparent poly film is inserted into the gap.
It has a lower signature. I figured if it could see this effectively, it is an easier test, so the remaining testing is with film rather than smoke. Ambient light also affects the output voltage. In my case, it was only about ±0. 1V, but the sensor may need to be shielded from outside light sources if it is a problem. The old LM741 is a good choice, but I also found a low power substitute (TI TL061) that reduces battery current ”see schematic for details.
As it is, battery load is only 1. 1mA ”not bad! The LM741 is applied as a comparator /Schmitt trigger. The voltage on the inverting input is biased at 4. 2V (half of Vcc). The collector of the photo-transistor is adjusted via R2 for 4. 0V. Any reduction of the current transfer ratio causes the collector voltage to increase beyond 4. 2V. At this point, the output voltage of the op amp goes positive and turns on the MOSFET. The drain of the MOSFET drops to zero volts and C1 couples a positive feedback signal to the inverting input via R8. The R*C of R8 & C1 causes the LED & siren to stay on for at least 1sec after the smoke has cleared. C1 has to be either film or ceramic because the voltage polarity reverses. R1 must be selected to provide approx 4V at the collector of the photo-transistor with R2 centered. Its resistance is a function of photo-interrupter transfer ratio and may vary as much as 40:1. When this is selected, R2 will be within range of making operational adjustments. The question marks on the schematics are for this purpose ”actual resistance must be determined. In my smoke alarm circuit, one device required 10K while the other required 22K. 🔗 External reference
The updated smoke alarm circuit provides a robust solution for smoke detection by integrating an LM741 op-amp as a comparator to enhance performance and reliability. The design leverages a photo-interrupter, which effectively detects smoke by monitoring changes in current transfer ratios caused by obstructions in the light path. The use of a Darlington pair, specifically the H21B1, allows for lower power consumption while maintaining sensitivity. The transition to the Sharp GP series as a replacement for the discontinued H21A1/H21B1 series ensures continued availability of components for hobbyists and engineers alike.
The circuit's design prioritizes ease of understanding and implementation, making it suitable for educational purposes. The comparator configuration provides a clear threshold for smoke detection, with the op-amp output driving a MOSFET to activate an alarm system. The feedback mechanism involving capacitor C1 ensures that the alarm remains engaged for a brief period after smoke is cleared, preventing false negatives due to transient conditions.
The selection of resistors and capacitors is critical for fine-tuning the circuit to specific applications, allowing adjustments based on the characteristics of the photo-interrupter used. This flexibility is essential for achieving optimal performance across varying environmental conditions and component tolerances. Overall, the redesigned smoke alarm circuit represents a significant improvement over its predecessor, offering enhanced functionality, simplicity, and efficiency.The original smoke alarm circuit has some problems and has left some hobbyists and students disappointed. Rather than to attempt to solve its many problems, I have created an update that uses the venerable LM741 op amp.
It is simpler, more conventional, easier to understand and has much better battery life. The photo-interrupter is simply an opti cal coupler with the elements separated with a slot. Anything that enters this slot reduces the current transfer ratio (output current /input current). I used the H21B1 Darlington device since I did not have the H21A1 on hand. I am glad I did, because I learned that it is a better device, requiring far less LED current. Since the H21A1 /H21B1 series is no longer available from DigiKey, I selected a currently available, more inexpensive device ”the Sharp GP series ”see schematic(s) for details. Sharp appears to be the leader in this product. Although, I recommend the Darlington device, do not despair if you have the non-Darlington version. See the smoke alarm schematic for alternative devices /circuits. These were not tested, but I see no reason why they are not viable. I had my doubts as to the effectiveness of the technique, so I tested a photo-interrupter with smoke.
The oscillograph demonstrates what happens to the photo-transistor collector voltage when the gap is obscured with smoke from my soldering iron as it melted rosin core solder. Cool! It does work. The oscillograph also has a trace showing what happens when a transparent poly film is inserted into the gap.
It has a lower signature. I figured if it could see this effectively, it is an easier test, so the remaining testing is with film rather than smoke. Ambient light also affects the output voltage. In my case, it was only about ±0. 1V, but the sensor may need to be shielded from outside light sources if it is a problem. The old LM741 is a good choice, but I also found a low power substitute (TI TL061) that reduces battery current ”see schematic for details.
As it is, battery load is only 1. 1mA ”not bad! The LM741 is applied as a comparator /Schmitt trigger. The voltage on the inverting input is biased at 4. 2V (half of Vcc). The collector of the photo-transistor is adjusted via R2 for 4. 0V. Any reduction of the current transfer ratio causes the collector voltage to increase beyond 4. 2V. At this point, the output voltage of the op amp goes positive and turns on the MOSFET. The drain of the MOSFET drops to zero volts and C1 couples a positive feedback signal to the inverting input via R8. The R*C of R8 & C1 causes the LED & siren to stay on for at least 1sec after the smoke has cleared. C1 has to be either film or ceramic because the voltage polarity reverses. R1 must be selected to provide approx 4V at the collector of the photo-transistor with R2 centered. Its resistance is a function of photo-interrupter transfer ratio and may vary as much as 40:1. When this is selected, R2 will be within range of making operational adjustments. The question marks on the schematics are for this purpose ”actual resistance must be determined. In my smoke alarm circuit, one device required 10K while the other required 22K. 🔗 External reference