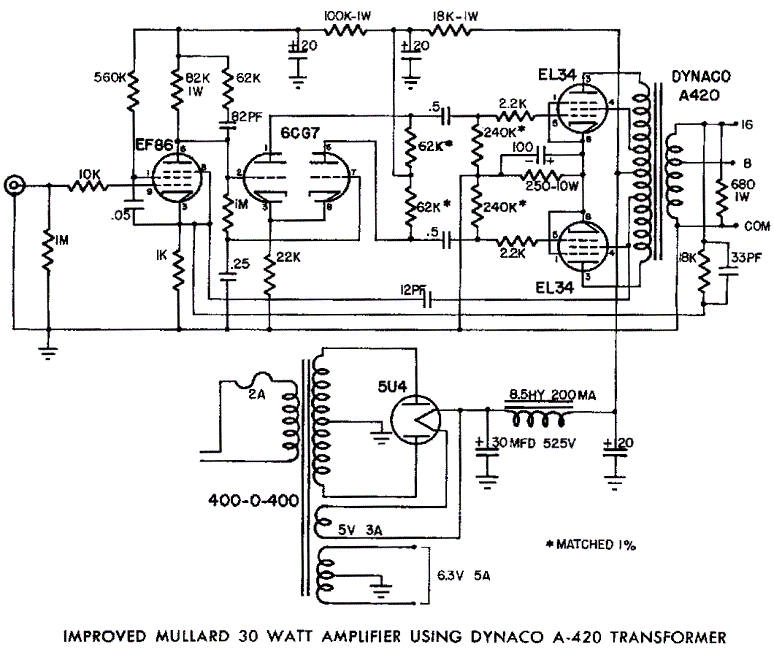
solar battery charger circuit schematic
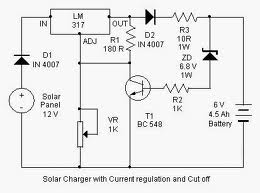
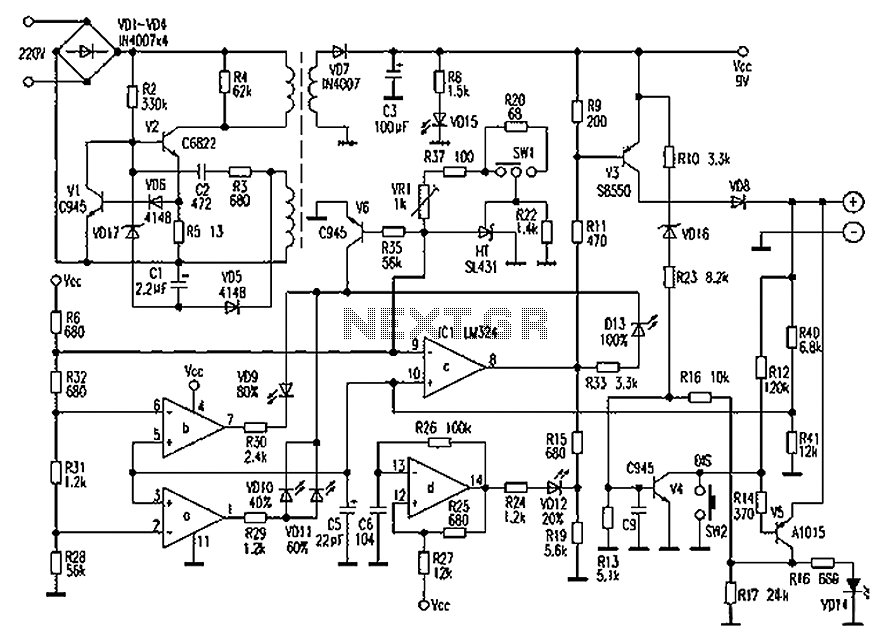
By adjusting the Adjust pin, the output voltage and current can be regulated. A variable resistor (VR) is connected between the Adjust pin and ground to achieve an output voltage of 9 volts to the battery. Resistor R3 limits the charging current, while diode D2 prevents the discharge of current from the battery. Transistor T1 and Zener diode ZD function as a cutoff switch when the battery is fully charged. Normally, T1 remains off, allowing the battery to receive charging current. When the terminal voltage of the battery exceeds 6.8 volts, the Zener diode conducts and supplies base current to T1.
The described circuit operates as a battery charger with adjustable output voltage and current regulation. The Adjust pin serves as a control point for the charging voltage, and the variable resistor (VR) allows fine-tuning of this voltage to ensure optimal charging conditions for the battery, which is set at 9 volts in this configuration.
The inclusion of resistor R3 is critical as it restricts the charging current to a safe level, preventing potential damage to the battery from excessive current. The diode D2 plays an essential role in maintaining the integrity of the charging circuit by blocking reverse current flow, thus ensuring that the battery does not discharge back into the charger when it is not in operation.
Transistor T1 is utilized as a switch in conjunction with the Zener diode ZD. Under normal operating conditions, T1 remains in the off state, allowing the charging current to flow to the battery. However, when the battery's terminal voltage rises above the Zener voltage of 6.8 volts, ZD begins to conduct, providing sufficient base current to turn on T1. This action effectively disconnects the charging current from the battery, preventing overcharging and ensuring the longevity of the battery.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes safety and efficiency in battery charging, leveraging components such as resistors, diodes, and transistors to create a reliable and adjustable charging solution. Proper selection of components and values is crucial to achieving the desired performance and protecting both the battery and the charging circuit.By adjusting its Adjust pin, output voltage and current can beregulated. VR is placed between the adjust pin and ground to provide an output voltage of 9 volts tothe battery. Resistor R3 Restrict the charging current and diode D2 prevents discharge ofcurrent from the battery.
Transistor T1 and Zener diode ZD act as a cut off switch whenthe battery is full. Normally T1 is off and battery gets charging current. When the terminal voltage of the battery rises above 6. 8 volts, Zener conducts andprovides base current to T1. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a battery charger with adjustable output voltage and current regulation. The Adjust pin serves as a control point for the charging voltage, and the variable resistor (VR) allows fine-tuning of this voltage to ensure optimal charging conditions for the battery, which is set at 9 volts in this configuration.
The inclusion of resistor R3 is critical as it restricts the charging current to a safe level, preventing potential damage to the battery from excessive current. The diode D2 plays an essential role in maintaining the integrity of the charging circuit by blocking reverse current flow, thus ensuring that the battery does not discharge back into the charger when it is not in operation.
Transistor T1 is utilized as a switch in conjunction with the Zener diode ZD. Under normal operating conditions, T1 remains in the off state, allowing the charging current to flow to the battery. However, when the battery's terminal voltage rises above the Zener voltage of 6.8 volts, ZD begins to conduct, providing sufficient base current to turn on T1. This action effectively disconnects the charging current from the battery, preventing overcharging and ensuring the longevity of the battery.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes safety and efficiency in battery charging, leveraging components such as resistors, diodes, and transistors to create a reliable and adjustable charging solution. Proper selection of components and values is crucial to achieving the desired performance and protecting both the battery and the charging circuit.By adjusting its Adjust pin, output voltage and current can beregulated. VR is placed between the adjust pin and ground to provide an output voltage of 9 volts tothe battery. Resistor R3 Restrict the charging current and diode D2 prevents discharge ofcurrent from the battery.
Transistor T1 and Zener diode ZD act as a cut off switch whenthe battery is full. Normally T1 is off and battery gets charging current. When the terminal voltage of the battery rises above 6. 8 volts, Zener conducts andprovides base current to T1. 🔗 External reference