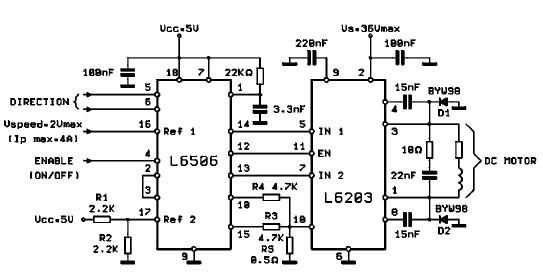
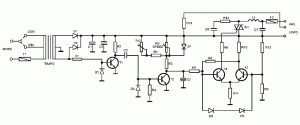
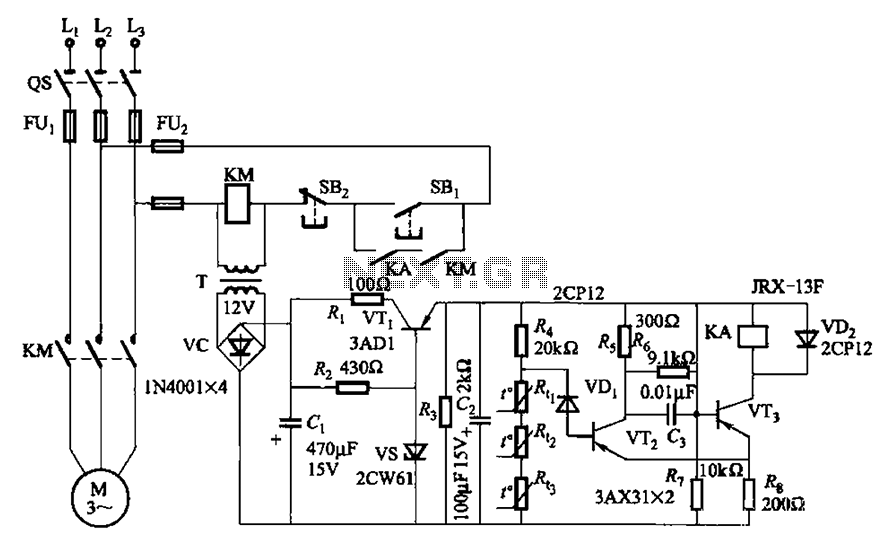
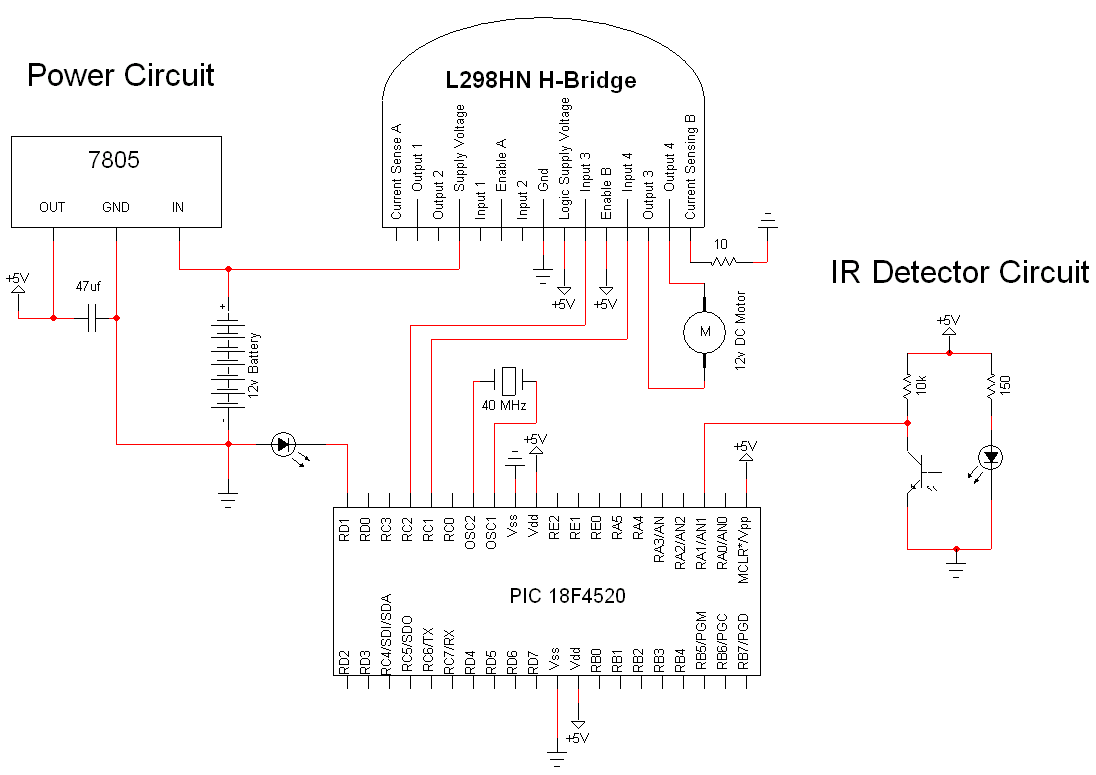
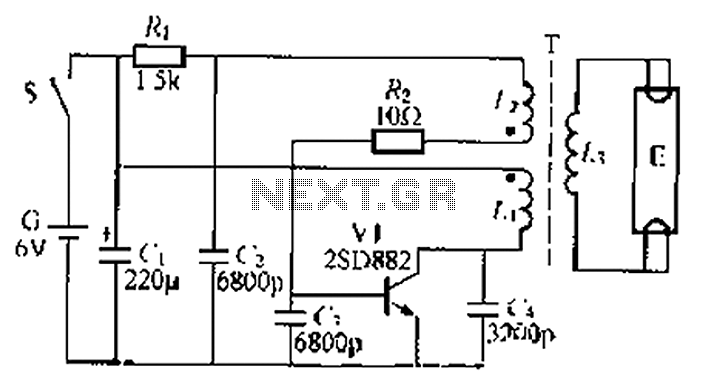
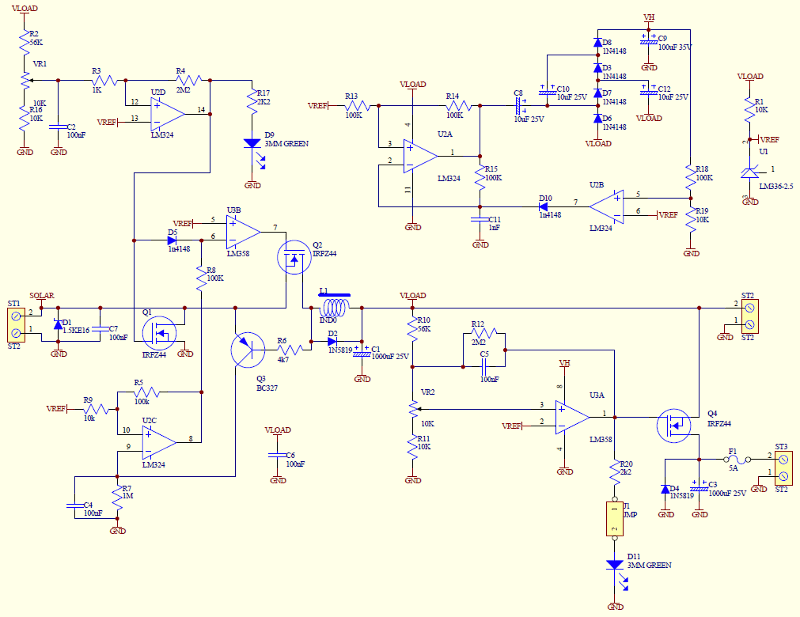
Solar Powered Motor
Diodes can be utilized instead of pull-up resistors, while isolating the DC load from the trigger circuit through junction drops and a 10nF capacitor. Excessive power from the solar cell may cause the motor to operate too frequently or continuously. This issue can be mitigated by placing a 100K ohm resistor in series with the solar cell.
The circuit leverages diodes to replace traditional pull-up resistors, which enhances efficiency by reducing power consumption. The isolation of the DC load from the trigger circuit is crucial for preventing feedback that could lead to erratic motor operation. This is achieved through the use of junction drops, which help manage voltage levels, and a 10nF capacitor that acts as a filter to smooth out any fluctuations in the signal.
The concern regarding excessive power from the solar cell is valid, as it can lead to unintended motor activation. To address this, a 100K ohm resistor is strategically placed in series with the solar cell. This resistor acts as a current limiter, ensuring that the voltage and current supplied to the motor remain within acceptable levels, thus preventing continuous operation or overheating.
In summary, the combination of diodes, a capacitor, and a series resistor creates a robust circuit design that effectively manages power levels, enhances performance, and ensures reliable operation of the motor under varying conditions. This design approach is particularly beneficial in solar-powered applications where fluctuating power levels can pose challenges.By using diodes in place of pull up resistors, and by isolating the DC load from the trigger circuit via junction drops and the 10nF capacitor. If there is too much power comming from the solar cell then the motor might run too often or even continuously.
You can avoid this by putting a 100K ohm resistor in serieswith the solar cell. 🔗 External reference
The circuit leverages diodes to replace traditional pull-up resistors, which enhances efficiency by reducing power consumption. The isolation of the DC load from the trigger circuit is crucial for preventing feedback that could lead to erratic motor operation. This is achieved through the use of junction drops, which help manage voltage levels, and a 10nF capacitor that acts as a filter to smooth out any fluctuations in the signal.
The concern regarding excessive power from the solar cell is valid, as it can lead to unintended motor activation. To address this, a 100K ohm resistor is strategically placed in series with the solar cell. This resistor acts as a current limiter, ensuring that the voltage and current supplied to the motor remain within acceptable levels, thus preventing continuous operation or overheating.
In summary, the combination of diodes, a capacitor, and a series resistor creates a robust circuit design that effectively manages power levels, enhances performance, and ensures reliable operation of the motor under varying conditions. This design approach is particularly beneficial in solar-powered applications where fluctuating power levels can pose challenges.By using diodes in place of pull up resistors, and by isolating the DC load from the trigger circuit via junction drops and the 10nF capacitor. If there is too much power comming from the solar cell then the motor might run too often or even continuously.
You can avoid this by putting a 100K ohm resistor in serieswith the solar cell. 🔗 External reference