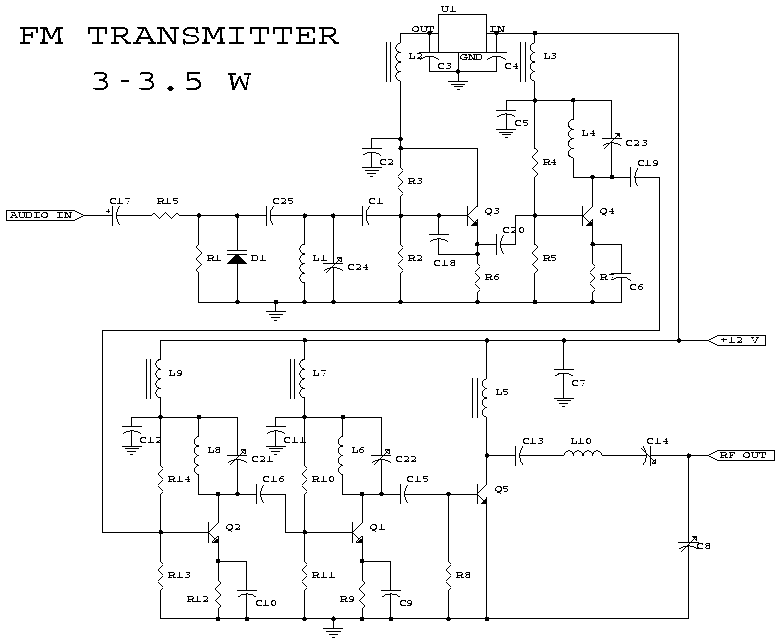
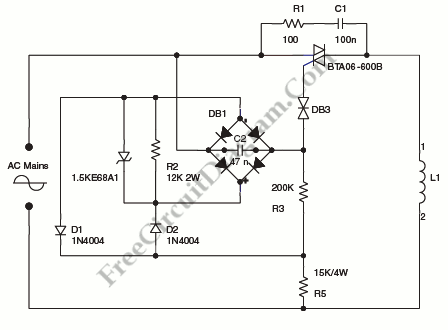
Soldering Iron Control Circuit
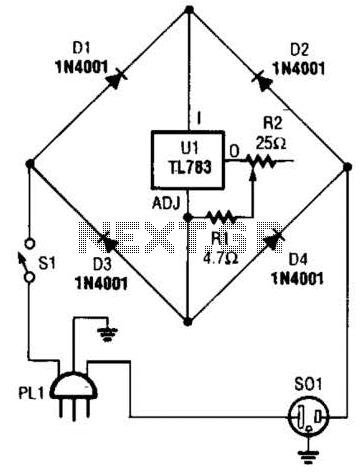
A current control circuit for temperature regulation of a soldering iron utilizes a high-voltage integrated regulator, TL783 (U1). With the specified component values, this circuit is suitable for use with a soldering iron rated at 25 W or less.
The circuit employs the TL783 voltage regulator, which is designed to provide a stable output voltage while allowing for adjustable current control. This feature is essential for maintaining the desired temperature of the soldering iron. The TL783 can handle input voltages up to 125 V and output currents of up to 700 mA, making it a robust choice for this application.
To implement this circuit, several key components are required. The input voltage should be appropriately selected based on the power supply available, ensuring it remains within the operational limits of the TL783. The output voltage can be adjusted using a potentiometer connected to the adjust pin of the regulator, allowing for fine-tuning of the soldering iron's temperature.
Additional components may include capacitors for stability and filtering, as well as resistors to set the desired output voltage. It is critical to choose these components based on the specific characteristics of the soldering iron being used. For a 25 W soldering iron, the output current should be limited to approximately 1 A, which can be achieved by selecting appropriate resistor values in the feedback loop of the TL783.
Thermal management is also a crucial consideration in this circuit design. The TL783 may require a heatsink to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially when operating near its maximum current rating. Proper layout and thermal considerations will enhance the reliability and performance of the soldering iron temperature control circuit.
Overall, this current control circuit provides an effective means of regulating the temperature of a soldering iron, ensuring optimal performance for soldering applications. A current control to temperature regulate a soldering iron uses a high-voltage integrated regulator, TL783 (Ul). With the component values specified, the circuit should be used with a soldering iron of 25 W or less. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs the TL783 voltage regulator, which is designed to provide a stable output voltage while allowing for adjustable current control. This feature is essential for maintaining the desired temperature of the soldering iron. The TL783 can handle input voltages up to 125 V and output currents of up to 700 mA, making it a robust choice for this application.
To implement this circuit, several key components are required. The input voltage should be appropriately selected based on the power supply available, ensuring it remains within the operational limits of the TL783. The output voltage can be adjusted using a potentiometer connected to the adjust pin of the regulator, allowing for fine-tuning of the soldering iron's temperature.
Additional components may include capacitors for stability and filtering, as well as resistors to set the desired output voltage. It is critical to choose these components based on the specific characteristics of the soldering iron being used. For a 25 W soldering iron, the output current should be limited to approximately 1 A, which can be achieved by selecting appropriate resistor values in the feedback loop of the TL783.
Thermal management is also a crucial consideration in this circuit design. The TL783 may require a heatsink to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially when operating near its maximum current rating. Proper layout and thermal considerations will enhance the reliability and performance of the soldering iron temperature control circuit.
Overall, this current control circuit provides an effective means of regulating the temperature of a soldering iron, ensuring optimal performance for soldering applications. A current control to temperature regulate a soldering iron uses a high-voltage integrated regulator, TL783 (Ul). With the component values specified, the circuit should be used with a soldering iron of 25 W or less. 🔗 External reference