Sound Card Interfacing for RTTY PSK31 and SSTV
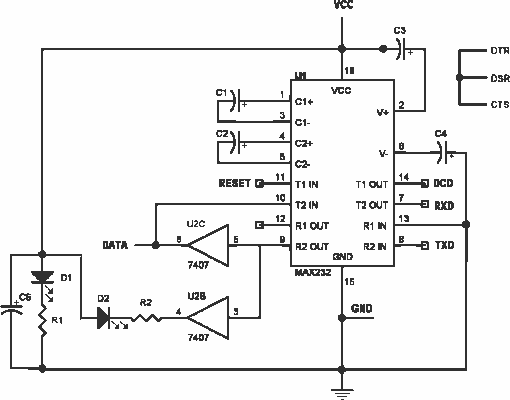
The circuit described is recommended for SSTV applications utilizing a sound card connected to a computer. It follows the JVComm style of interface and can also be employed for RTTY and PSK31 applications. Many users modify this circuit to incorporate 1:1 isolation transformers within the speaker output and line-in or microphone input lines. These isolation transformers are essential for preventing ground loops from introducing hum and interference into the transmitted signals. The circuit is applicable for WinRtty to receive RTTY signals via the sound card and is effective in SSTV and PSK31 modes as well. It can be integrated into the JVComm interface as previously discussed. It is important to note that the sound board and receiver are transposed in the two circuits. The circuit is also used in WinRtty for transmitting RTTY signals through the sound card, and it does not include a PTT component, relying instead on VOX for transmit control. This circuit is similarly applicable to SSTV and PSK31 modes and functions effectively across all three applications. For those requiring FSK capability along with Push-To-Talk (PTT), a specific circuit is utilized with WinRtty to provide FSK RTTY functionality and a PTT circuit for the program. This circuit can be used in various applications and may replace the one in the JVComm interface. The configuration for the RS-232 conversion depends on the transmitter's FSK input, which can typically mirror the circuit shown for the PTT connection: employing an opto-isolator with a series resistor to convert RS-232 levels for open/close keying. The PTT-related portion of this circuit can also substitute the PTT circuit in the JVComm interface previously described.
The circuit serves as a versatile interface for digital communication modes, specifically SSTV, RTTY, and PSK31, leveraging a computer's sound card for signal processing. The use of isolation transformers is a critical enhancement, designed to mitigate potential ground loop issues that can introduce unwanted noise into the system. By integrating these transformers, the circuit ensures a cleaner signal transmission, which is paramount for maintaining the integrity of the digital signals being processed.
In terms of functionality, the circuit is adept at receiving and transmitting RTTY signals when used with the WinRtty application. The design is such that it can seamlessly switch between receiving and transmitting modes, although it does not include a traditional PTT switch. Instead, it employs Voice Operated Transmission (VOX) technology to control the transmission state, which can be advantageous in scenarios where hands-free operation is preferred.
For users looking for frequency shift keying (FSK) capabilities, the circuit can be adapted to include a PTT function. This is achieved through an additional configuration that allows for RS-232 level conversion, using an opto-isolator to interface with the transmitter. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for a wide range of applications beyond its initial design, allowing it to be tailored to specific user requirements.
In summary, the circuit is not only effective for SSTV, RTTY, and PSK31 applications but is also adaptable for various digital communication needs, making it a valuable tool for amateur radio enthusiasts and professionals alike.The above circuit is recommended for use in SSTV applications with use of the sound card with a computer. This is the JVComm style of interface. This circuit may also be used for RTTY and PSK31 applications. Many users modify the above circuit to include 1:1 isolation transformers within the Speaker out and Line-in or microphone in lines.
These isolation transformers are used to preclude ground loops within a system from introducing hum and interference on the transmitted signals. The following circuit is used in applications of WinRtty for receiving RTTY signals using the sound card.
This circuit is also applicable to SSTV and PSK31 modes and works well in all three applications. This circuit may be implemented into the JVComm interface shown above as discussed in the JVComm interface text. Note that the sound board and receiver are transposed in the two circuits. The following circuit is used in applications of WinRtty for transmitting RTTY signals using the sound card.
Notice this circuit does not have a PTT component and relies on VOX for transmit control. This circuit is also applicable to SSTV and PSK31 modes and works well in all three applications. This circuit may be implemented into the JVComm interface shown above as discussed in the JVComm interface text. Note that the sound board and transmitter are transposed in the two circuits. So you say I want FSK capability as well as Push-To-Talk (PTT). The following circuit is used with WinRtty to provide capability for FSK Rtty and a PTT circuit for the program.
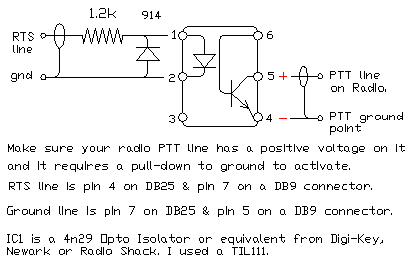
This circuit may be used in many applications and may be substituted for the circuit contained in the JVComm interface shown above. What goes in the RS-232 conversion box depends on your transmitters FSK input. Odds are, it can be exactly the same as the circuit shown for the PTT connect: use an opto-isolator with a series resistor to convert the RS-232 levels to open/close keying.
The portion of this circuit related to PTT may also be used instead of the PTT circuit in the JVComm interface described above. 🔗 External reference
The circuit serves as a versatile interface for digital communication modes, specifically SSTV, RTTY, and PSK31, leveraging a computer's sound card for signal processing. The use of isolation transformers is a critical enhancement, designed to mitigate potential ground loop issues that can introduce unwanted noise into the system. By integrating these transformers, the circuit ensures a cleaner signal transmission, which is paramount for maintaining the integrity of the digital signals being processed.
In terms of functionality, the circuit is adept at receiving and transmitting RTTY signals when used with the WinRtty application. The design is such that it can seamlessly switch between receiving and transmitting modes, although it does not include a traditional PTT switch. Instead, it employs Voice Operated Transmission (VOX) technology to control the transmission state, which can be advantageous in scenarios where hands-free operation is preferred.
For users looking for frequency shift keying (FSK) capabilities, the circuit can be adapted to include a PTT function. This is achieved through an additional configuration that allows for RS-232 level conversion, using an opto-isolator to interface with the transmitter. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for a wide range of applications beyond its initial design, allowing it to be tailored to specific user requirements.
In summary, the circuit is not only effective for SSTV, RTTY, and PSK31 applications but is also adaptable for various digital communication needs, making it a valuable tool for amateur radio enthusiasts and professionals alike.The above circuit is recommended for use in SSTV applications with use of the sound card with a computer. This is the JVComm style of interface. This circuit may also be used for RTTY and PSK31 applications. Many users modify the above circuit to include 1:1 isolation transformers within the Speaker out and Line-in or microphone in lines.
These isolation transformers are used to preclude ground loops within a system from introducing hum and interference on the transmitted signals. The following circuit is used in applications of WinRtty for receiving RTTY signals using the sound card.
This circuit is also applicable to SSTV and PSK31 modes and works well in all three applications. This circuit may be implemented into the JVComm interface shown above as discussed in the JVComm interface text. Note that the sound board and receiver are transposed in the two circuits. The following circuit is used in applications of WinRtty for transmitting RTTY signals using the sound card.
Notice this circuit does not have a PTT component and relies on VOX for transmit control. This circuit is also applicable to SSTV and PSK31 modes and works well in all three applications. This circuit may be implemented into the JVComm interface shown above as discussed in the JVComm interface text. Note that the sound board and transmitter are transposed in the two circuits. So you say I want FSK capability as well as Push-To-Talk (PTT). The following circuit is used with WinRtty to provide capability for FSK Rtty and a PTT circuit for the program.
This circuit may be used in many applications and may be substituted for the circuit contained in the JVComm interface shown above. What goes in the RS-232 conversion box depends on your transmitters FSK input. Odds are, it can be exactly the same as the circuit shown for the PTT connect: use an opto-isolator with a series resistor to convert the RS-232 levels to open/close keying.
The portion of this circuit related to PTT may also be used instead of the PTT circuit in the JVComm interface described above. 🔗 External reference