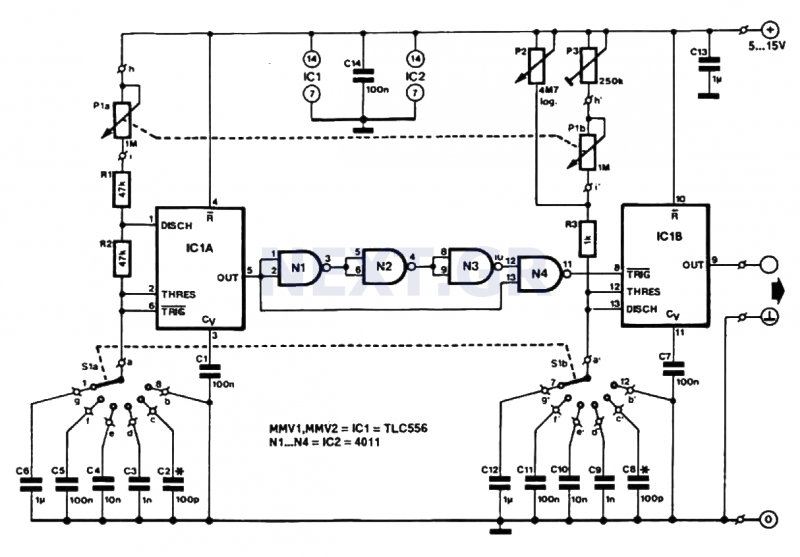
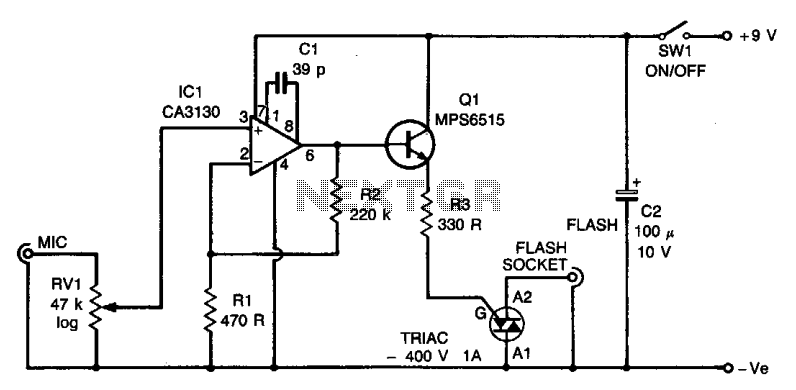
Sound Effects Generator
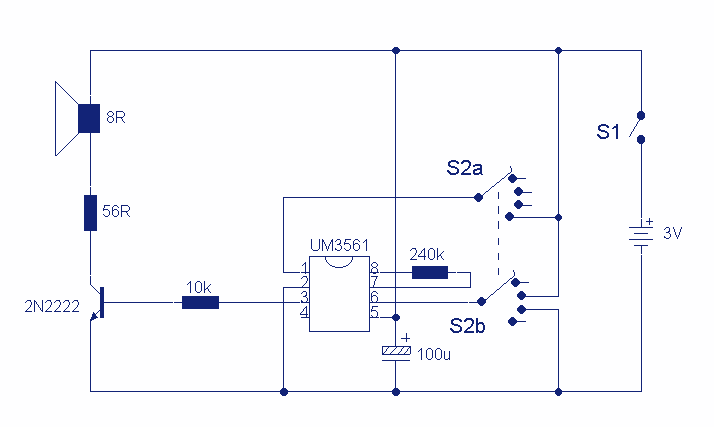
This circuit uses a UM3561 IC to produce four different sound effects. Nothing too complicated here. The IC produces all the sound effects, the output at Pin 3 being amplified by the transistor. A 64 ohm loudspeaker can be substituted in place of the 56 ohm resistor and 8 ohm loudspeaker. The 2 pole 4 way switch controls the sound effects. Position 1 (as drawn) being a Police siren, position 2 is a fire engine sound, 3 is an ambulance and position 4 is a machine gun effect. The IC is manufactured by UMC and was available from Maplin electronics code UJ45Y. At the time of writing this has no
The circuit utilizes the UM3561 integrated circuit (IC), which is specifically designed for generating sound effects. The UM3561 can produce a variety of audio signals, which are commonly used in toys and novelty devices. The circuit configuration allows for four distinct sound effects to be selected using a two-pole, four-way switch.
In this design, the output from Pin 3 of the UM3561 is connected to a transistor, which serves to amplify the audio signal before it is sent to the speaker. The transistor acts as a signal booster, ensuring that the sound produced is loud enough for practical use. The output can drive a loudspeaker, and while the circuit design specifies a combination of a 56-ohm resistor and an 8-ohm speaker, a 64-ohm loudspeaker can be used as an alternative. This flexibility allows for variations in sound output based on the components available.
The sound effects generated by the UM3561 include a police siren, fire engine sound, ambulance siren, and a machine gun effect, corresponding to the four positions of the switch. Each position connects different internal configurations of the IC, which alters the frequency and waveform of the output sound, creating distinct audio experiences.
The UM3561 IC is manufactured by UMC, and it is important to note that sourcing this component may require checking with electronics suppliers, as availability can vary. This circuit is relatively straightforward, making it suitable for hobbyists and those looking to explore sound generation in electronic projects.This circuit uses a UM3561 IC to produce four different sound effects. Nothing too complicated here. The IC produces all the sound effects, the output at Pin 3 being amplified by the transistor. A 64 ohm loudspeaker can be substituted in place of the 56 ohm resistor and 8 ohm loudspeaker. The 2 pole 4 way switch controls the sound effects. Position 1 (as drawn) being a Police siren, position 2 is a fire engine sound, 3 is an ambulance and position 4 is a machine gun effect. The IC is manufactured by UMC and was available from Maplin electronics code UJ45Y. At the time of writing this has no 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the UM3561 integrated circuit (IC), which is specifically designed for generating sound effects. The UM3561 can produce a variety of audio signals, which are commonly used in toys and novelty devices. The circuit configuration allows for four distinct sound effects to be selected using a two-pole, four-way switch.
In this design, the output from Pin 3 of the UM3561 is connected to a transistor, which serves to amplify the audio signal before it is sent to the speaker. The transistor acts as a signal booster, ensuring that the sound produced is loud enough for practical use. The output can drive a loudspeaker, and while the circuit design specifies a combination of a 56-ohm resistor and an 8-ohm speaker, a 64-ohm loudspeaker can be used as an alternative. This flexibility allows for variations in sound output based on the components available.
The sound effects generated by the UM3561 include a police siren, fire engine sound, ambulance siren, and a machine gun effect, corresponding to the four positions of the switch. Each position connects different internal configurations of the IC, which alters the frequency and waveform of the output sound, creating distinct audio experiences.
The UM3561 IC is manufactured by UMC, and it is important to note that sourcing this component may require checking with electronics suppliers, as availability can vary. This circuit is relatively straightforward, making it suitable for hobbyists and those looking to explore sound generation in electronic projects.This circuit uses a UM3561 IC to produce four different sound effects. Nothing too complicated here. The IC produces all the sound effects, the output at Pin 3 being amplified by the transistor. A 64 ohm loudspeaker can be substituted in place of the 56 ohm resistor and 8 ohm loudspeaker. The 2 pole 4 way switch controls the sound effects. Position 1 (as drawn) being a Police siren, position 2 is a fire engine sound, 3 is an ambulance and position 4 is a machine gun effect. The IC is manufactured by UMC and was available from Maplin electronics code UJ45Y. At the time of writing this has no 🔗 External reference