Static Electricity Detector
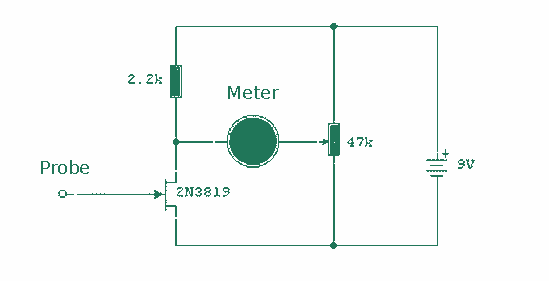
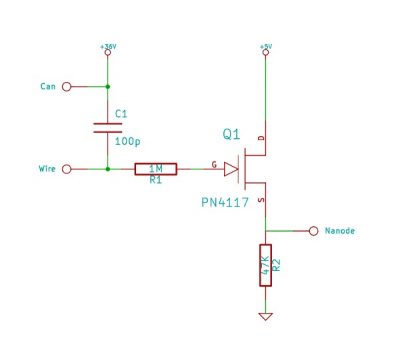
This circuit relies upon the extra high input impedance of a FET, and also demonstrates the gate terminals sensitivity to changes in voltage. The gate terminal here is left open circuit, connected only to the "probe" this being just a few inches of bare copper wire. With no fixed DC biasing, the gate terminal will respond to micro changes in voltage or "field strength". It is important not to make this circuit on veroboard or PCB material as this will reduce the effective gate impedance. More: Instead use an "open" construction technique soldering each component together. The probe should not be touched directly and is best insulated in a plastic pen sleeve. As static electricity can have either a positive or negative charge.
This circuit utilizes a Field Effect Transistor (FET) to achieve high input impedance, making it highly sensitive to small changes in voltage. The configuration involves leaving the gate terminal of the FET open, which allows it to detect minute variations in electric field strength. The use of a bare copper wire as a probe enhances the circuit's responsiveness to external electromagnetic influences.
To assemble the circuit, it is recommended to employ an open construction technique rather than using a printed circuit board (PCB) or veroboard. This approach minimizes parasitic capacitance and inductance that could otherwise affect the gate's performance and sensitivity. Components should be soldered together in a manner that maintains the integrity of the circuit's high impedance characteristics.
The probe, which is critical for the circuit's operation, should be handled with care. Direct contact with the probe can introduce unwanted noise or static discharge, which may compromise the circuit's accuracy. To mitigate this risk, it is advisable to insulate the probe within a non-conductive sleeve, such as a plastic pen casing. This insulation not only protects the probe but also helps to prevent interference from static electricity, which can carry either a positive or negative charge and affect the readings.
Overall, the circuit is designed for applications requiring high sensitivity to voltage changes, such as detecting static electricity or measuring weak electric fields. Proper construction and handling are essential to ensure accurate and reliable performance.This circuit relies upon the extra high input impedance of a FET, and also demonstrates the gate terminals sensitivity to changes in voltage. The gate terminal here is left open circuit, connected only to the "probe" this being just a few inches of bare copper wire.
With no fixed DC biasing, the gate terminal will respond to micro changes in voltage or "field strength". It is important not to make this circuit on veroboard or PCB material as this will reduce the effective gate impedance.
Instead use an "open" construction technique soldering each component together. The probe should not be touched directly and is best insulated in a plastic pen sleeve. As static electricity can have either a positive or nega 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes a Field Effect Transistor (FET) to achieve high input impedance, making it highly sensitive to small changes in voltage. The configuration involves leaving the gate terminal of the FET open, which allows it to detect minute variations in electric field strength. The use of a bare copper wire as a probe enhances the circuit's responsiveness to external electromagnetic influences.
To assemble the circuit, it is recommended to employ an open construction technique rather than using a printed circuit board (PCB) or veroboard. This approach minimizes parasitic capacitance and inductance that could otherwise affect the gate's performance and sensitivity. Components should be soldered together in a manner that maintains the integrity of the circuit's high impedance characteristics.
The probe, which is critical for the circuit's operation, should be handled with care. Direct contact with the probe can introduce unwanted noise or static discharge, which may compromise the circuit's accuracy. To mitigate this risk, it is advisable to insulate the probe within a non-conductive sleeve, such as a plastic pen casing. This insulation not only protects the probe but also helps to prevent interference from static electricity, which can carry either a positive or negative charge and affect the readings.
Overall, the circuit is designed for applications requiring high sensitivity to voltage changes, such as detecting static electricity or measuring weak electric fields. Proper construction and handling are essential to ensure accurate and reliable performance.This circuit relies upon the extra high input impedance of a FET, and also demonstrates the gate terminals sensitivity to changes in voltage. The gate terminal here is left open circuit, connected only to the "probe" this being just a few inches of bare copper wire.
With no fixed DC biasing, the gate terminal will respond to micro changes in voltage or "field strength". It is important not to make this circuit on veroboard or PCB material as this will reduce the effective gate impedance.
Instead use an "open" construction technique soldering each component together. The probe should not be touched directly and is best insulated in a plastic pen sleeve. As static electricity can have either a positive or nega 🔗 External reference