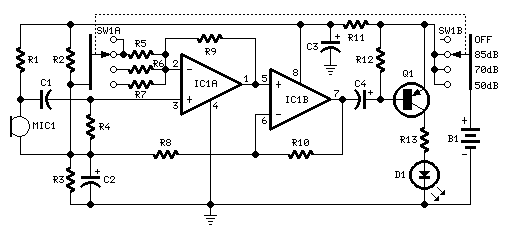
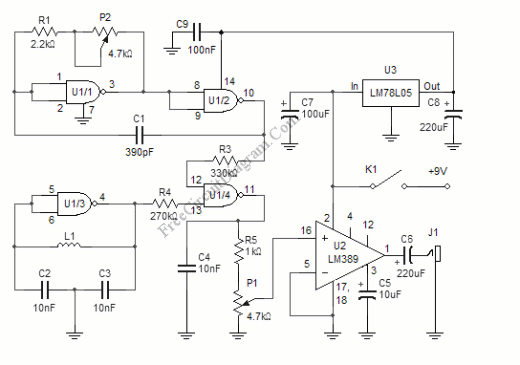
Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Operating Principle Phase Detector VCO LPF
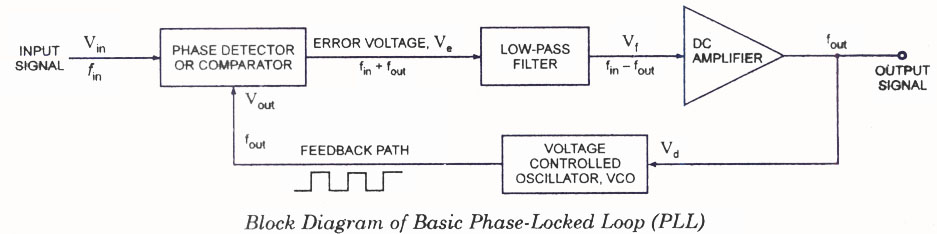
The operating principle of a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) is illustrated with a block diagram that includes a Phase Detector, Voltage Controlled Oscillator, and Low Pass Filter.
A Phase Locked Loop (PLL) is an essential electronic circuit used in various applications such as frequency synthesis, demodulation, and clock recovery. The core functionality of a PLL is to synchronize an output signal's phase and frequency with a reference signal. The primary components of a PLL include a Phase Detector (PD), a Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO), and a Low Pass Filter (LPF).
The Phase Detector compares the phase of the input reference signal with the phase of the output signal from the VCO. The output of the Phase Detector is a voltage signal that represents the phase difference between these two signals. This voltage signal is then passed through the Low Pass Filter, which smooths out the high-frequency components and provides a steady control voltage.
The control voltage generated by the LPF is fed into the Voltage Controlled Oscillator. The VCO generates an output frequency that is proportional to the input control voltage. When the PLL is locked, the output frequency of the VCO matches the frequency of the reference signal, and the phase difference is minimized.
In summary, the PLL operates by continuously adjusting the VCO based on the phase difference detected by the PD, ensuring that the output signal remains in phase and frequency with the reference signal. This feedback mechanism allows for stable and accurate signal processing, making PLLs critical in communication systems, signal processing, and clock generation applications.Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Operating Principle with block diagram showing Phase Detector, Voltage Controlled Oscillator, Low Pass Filter.. 🔗 External reference
A Phase Locked Loop (PLL) is an essential electronic circuit used in various applications such as frequency synthesis, demodulation, and clock recovery. The core functionality of a PLL is to synchronize an output signal's phase and frequency with a reference signal. The primary components of a PLL include a Phase Detector (PD), a Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO), and a Low Pass Filter (LPF).
The Phase Detector compares the phase of the input reference signal with the phase of the output signal from the VCO. The output of the Phase Detector is a voltage signal that represents the phase difference between these two signals. This voltage signal is then passed through the Low Pass Filter, which smooths out the high-frequency components and provides a steady control voltage.
The control voltage generated by the LPF is fed into the Voltage Controlled Oscillator. The VCO generates an output frequency that is proportional to the input control voltage. When the PLL is locked, the output frequency of the VCO matches the frequency of the reference signal, and the phase difference is minimized.
In summary, the PLL operates by continuously adjusting the VCO based on the phase difference detected by the PD, ensuring that the output signal remains in phase and frequency with the reference signal. This feedback mechanism allows for stable and accurate signal processing, making PLLs critical in communication systems, signal processing, and clock generation applications.Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Operating Principle with block diagram showing Phase Detector, Voltage Controlled Oscillator, Low Pass Filter.. 🔗 External reference