Step-Down Charge Pump Regulator for USB Powered Devices
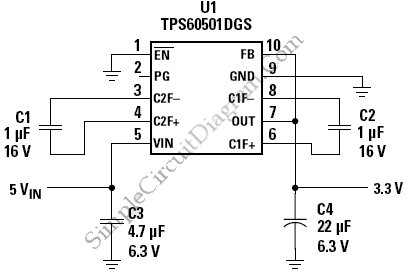
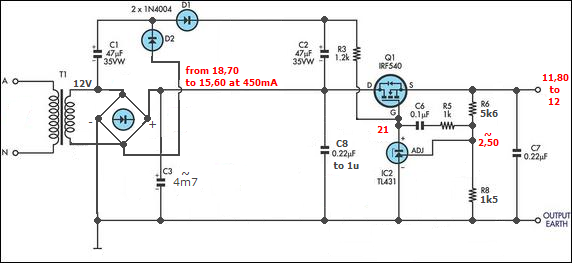
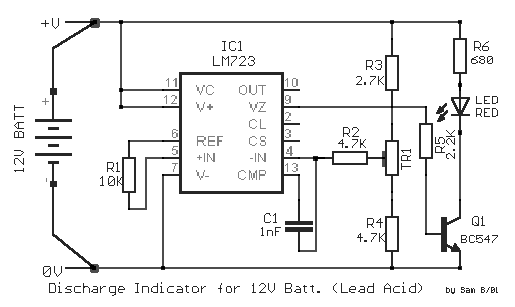
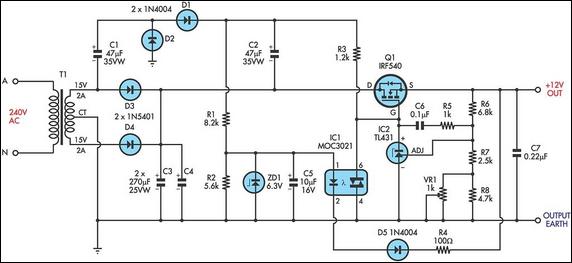
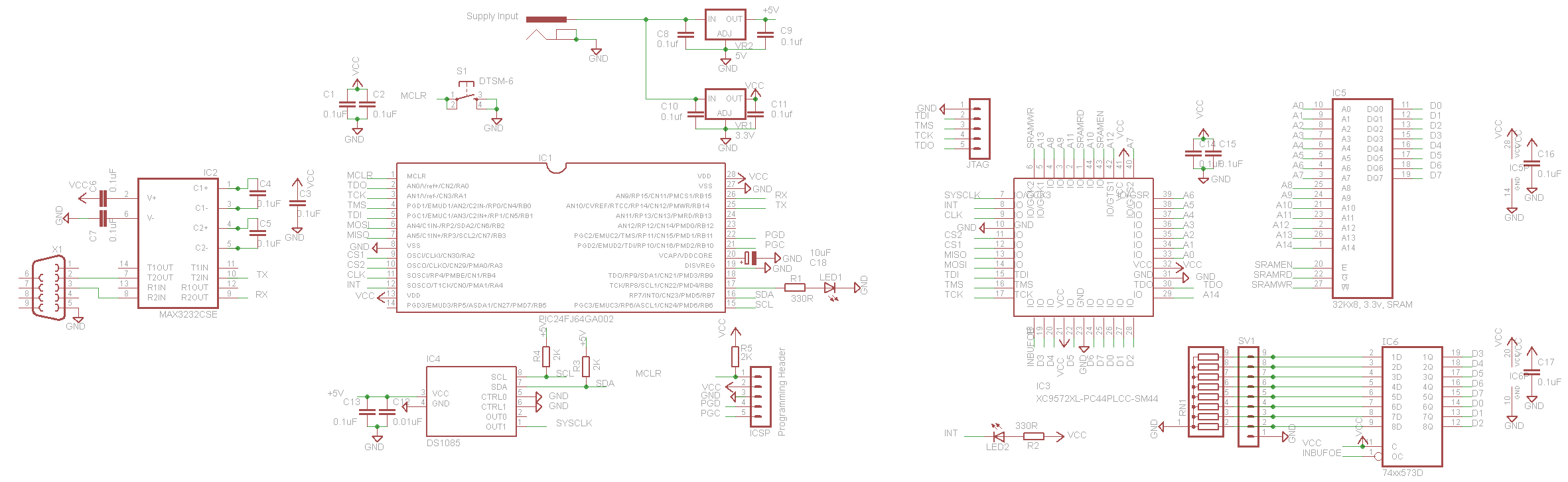
This is a circuit of a step-down charge pump regulator for USB-powered devices. The critical design parameter of this circuit is the circuit area.
The step-down charge pump regulator is designed to efficiently convert a higher input voltage from USB sources (typically 5V) to a lower output voltage suitable for powering various electronic components. This type of regulator utilizes capacitors as energy storage elements and switches to control the flow of energy, enabling voltage reduction through a series of charge and discharge cycles.
Key components of the circuit include a switching control IC, capacitors, and diodes. The switching control IC manages the timing and operation of the switches, ensuring that the charge pump operates at the desired frequency for optimal efficiency. Capacitors are used to store and transfer charge, while diodes prevent reverse current flow, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and within the specified limits.
The design must consider the physical area occupied by the components, as minimizing circuit area is crucial for integration into compact USB-powered devices. Careful selection of components, such as low-profile capacitors and integrated circuits, can significantly reduce the overall footprint of the circuit. Additionally, the layout of the PCB should be optimized to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance, which can adversely affect performance.
Thermal management is also an essential aspect of the design. The charge pump's efficiency can lead to heat generation, particularly under load conditions. Proper heat dissipation techniques, such as using thermal vias and adequate copper planes, should be employed to ensure reliable operation.
In summary, the step-down charge pump regulator circuit is a critical component for USB-powered devices, with its design focused on minimizing area while maintaining efficiency and thermal performance.this is a circuit of Step-Down Charge Pump Regulator for USB Powered Devices. The critical design parameter of this circuit is the circuit area. To solve this.. 🔗 External reference
The step-down charge pump regulator is designed to efficiently convert a higher input voltage from USB sources (typically 5V) to a lower output voltage suitable for powering various electronic components. This type of regulator utilizes capacitors as energy storage elements and switches to control the flow of energy, enabling voltage reduction through a series of charge and discharge cycles.
Key components of the circuit include a switching control IC, capacitors, and diodes. The switching control IC manages the timing and operation of the switches, ensuring that the charge pump operates at the desired frequency for optimal efficiency. Capacitors are used to store and transfer charge, while diodes prevent reverse current flow, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and within the specified limits.
The design must consider the physical area occupied by the components, as minimizing circuit area is crucial for integration into compact USB-powered devices. Careful selection of components, such as low-profile capacitors and integrated circuits, can significantly reduce the overall footprint of the circuit. Additionally, the layout of the PCB should be optimized to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance, which can adversely affect performance.
Thermal management is also an essential aspect of the design. The charge pump's efficiency can lead to heat generation, particularly under load conditions. Proper heat dissipation techniques, such as using thermal vias and adequate copper planes, should be employed to ensure reliable operation.
In summary, the step-down charge pump regulator circuit is a critical component for USB-powered devices, with its design focused on minimizing area while maintaining efficiency and thermal performance.this is a circuit of Step-Down Charge Pump Regulator for USB Powered Devices. The critical design parameter of this circuit is the circuit area. To solve this.. 🔗 External reference