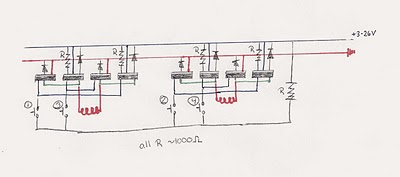
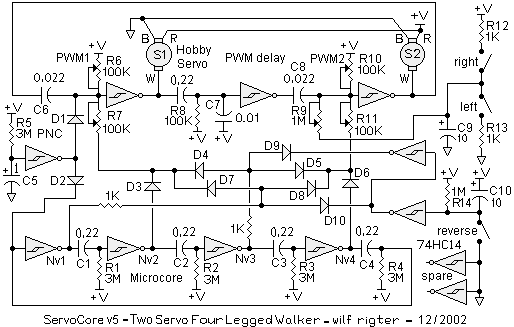
stepper motor interfacing connections
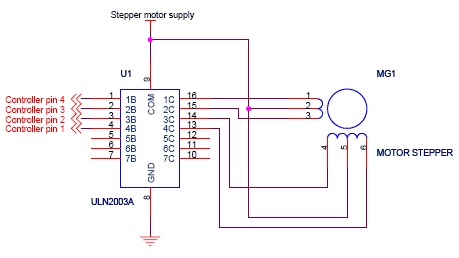
Stepper motor interfacing with a microcontroller. Full-step and half-step stepper control. Working principles and basics of stepper motors. Tutorial on 6-lead unipolar stepper motors and bipolar stepper motors.
Stepper motors are widely used in various applications requiring precise control of angular position, speed, and acceleration. They are particularly useful in robotics, CNC machinery, and 3D printers due to their ability to divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The interfacing of stepper motors with microcontrollers allows for the implementation of complex control algorithms that can enhance the performance of these motors.
The two primary types of stepper motors are unipolar and bipolar. A 6-lead unipolar stepper motor typically consists of two coils with a center tap, allowing for simpler control since current can flow in one direction through each coil. In contrast, bipolar stepper motors have two coils without a center tap, requiring more complex control circuitry to reverse the current direction.
Microcontrollers can control stepper motors in two main modes: full-step and half-step. In full-step mode, the motor is driven by energizing one coil at a time, resulting in a step size equal to the motor's step angle. Half-step mode alternates between energizing one coil and both coils together, effectively halving the step size and allowing for smoother motion and improved resolution.
To implement stepper motor control, a microcontroller can be programmed to send signals to a driver circuit that interfaces with the motor. The driver circuit is responsible for managing the current flowing through the motor coils and can include components such as H-bridges or dedicated stepper motor driver ICs. The microcontroller's output pins are connected to the driver inputs, and the control logic can be implemented using simple timing loops or more sophisticated control algorithms depending on the application's requirements.
In summary, interfacing a stepper motor with a microcontroller involves understanding the motor's operating principles, selecting the appropriate type of motor, and implementing control strategies to achieve the desired performance. This knowledge is essential for designing effective systems that utilize stepper motors for precise motion control.stepper motor interfacing with microcontroller. Full step and half step stepper control. working and basics of stepper motor. 6 lead unipolar stepper motor tutorial, Bipolar Stepper Motor tutorial.. 🔗 External reference
Stepper motors are widely used in various applications requiring precise control of angular position, speed, and acceleration. They are particularly useful in robotics, CNC machinery, and 3D printers due to their ability to divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The interfacing of stepper motors with microcontrollers allows for the implementation of complex control algorithms that can enhance the performance of these motors.
The two primary types of stepper motors are unipolar and bipolar. A 6-lead unipolar stepper motor typically consists of two coils with a center tap, allowing for simpler control since current can flow in one direction through each coil. In contrast, bipolar stepper motors have two coils without a center tap, requiring more complex control circuitry to reverse the current direction.
Microcontrollers can control stepper motors in two main modes: full-step and half-step. In full-step mode, the motor is driven by energizing one coil at a time, resulting in a step size equal to the motor's step angle. Half-step mode alternates between energizing one coil and both coils together, effectively halving the step size and allowing for smoother motion and improved resolution.
To implement stepper motor control, a microcontroller can be programmed to send signals to a driver circuit that interfaces with the motor. The driver circuit is responsible for managing the current flowing through the motor coils and can include components such as H-bridges or dedicated stepper motor driver ICs. The microcontroller's output pins are connected to the driver inputs, and the control logic can be implemented using simple timing loops or more sophisticated control algorithms depending on the application's requirements.
In summary, interfacing a stepper motor with a microcontroller involves understanding the motor's operating principles, selecting the appropriate type of motor, and implementing control strategies to achieve the desired performance. This knowledge is essential for designing effective systems that utilize stepper motors for precise motion control.stepper motor interfacing with microcontroller. Full step and half step stepper control. working and basics of stepper motor. 6 lead unipolar stepper motor tutorial, Bipolar Stepper Motor tutorial.. 🔗 External reference