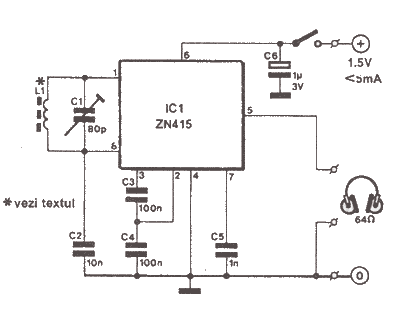
street light lamp circuit
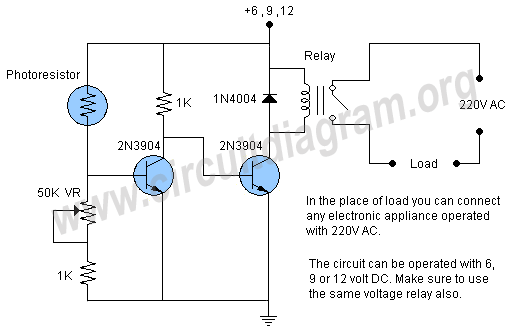
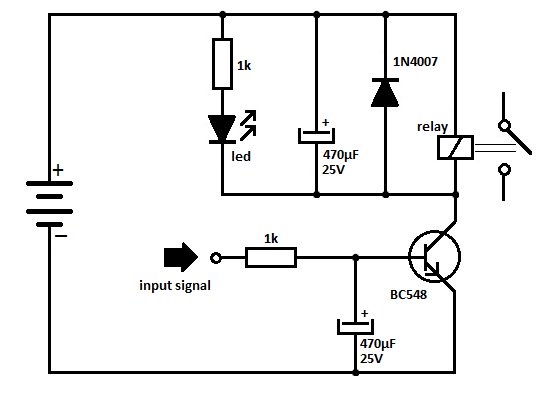
This project involves an automatic street light or lamp circuit designed to activate outdoor lights, such as garden lamps and night lights, automatically at sunset and turn them off at sunrise. The circuit is sensitive and versatile, capable of controlling any 220V AC device during the night and deactivating it during the day. To use this circuit, simply connect the device to the load point. A 220V plug socket can also be connected to the load point to accommodate various electronic devices, provided that the relay points can handle the specified load. The circuit is straightforward, utilizing two 2N3904 transistors along with a few other components. A 50K variable resistor (VR) is included to adjust the circuit's sensitivity to darkness. The circuit can operate at 6V, 9V, or 12V, but it is crucial to use a relay rated for the same voltage. This setup functions as a dark-detecting or light-sensor circuit. The two transistors in the circuit act as switches. When light strikes the light-dependent resistor (LDR), its resistance decreases, leading to an increase in voltage at the base of transistor Q1, which turns on while Q2 remains off. In the absence of light, the resistance of the LDR increases, turning off Q1 and increasing the voltage at the base of Q2, which subsequently activates the relay switch.
The automatic street light circuit primarily consists of a light-dependent resistor (LDR), two 2N3904 NPN transistors, a relay, and a variable resistor (VR) for sensitivity adjustment. The LDR plays a critical role in detecting ambient light levels. In bright conditions, the LDR's low resistance allows current to flow, keeping transistor Q1 in the off state, which in turn keeps Q2 off, preventing the relay from activating. As ambient light decreases at dusk, the LDR's resistance increases, which raises the voltage at the base of Q1, turning it on. This action also turns off Q2, allowing the relay to engage and power the connected load.
The circuit can be powered by a DC source of 6V, 9V, or 12V, with the relay being rated for the same voltage to ensure compatibility and proper operation. The variable resistor (50K VR) allows for fine-tuning of the light sensitivity, enabling the user to set the threshold at which the circuit activates based on the local lighting conditions.
The relay used in the circuit acts as a switch to control the higher voltage AC load. It is essential to select a relay that can handle the maximum load current and voltage to prevent damage or failure of the circuit. The simplicity of the design allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it an excellent choice for DIY enthusiasts looking to automate outdoor lighting solutions.Here is a very useful project of an automatic street light or lamp circuit which can be used to activate your outdoor lights like garden lamps, night lights etc. automatically when the sun set and turn off automatically when the sun rises. The circuit is quite sensitive and versatile and can be used to activate any 220 volt AC device at night and
turn off in day all you have to do is simply connect the device with the load point. You can also connect a 220V plug socket with the load point to connect different electronic devices but make sure the relay points can able to handle the provided load. The circuit is simple using two 2N3904 transistors and few other components. The 50K VR (Variable Resistor) is used to adjust the circuit to activate the relay on the required darkness.
The circuit can be operated with 6 volts, 9 volts and 12 volts but it is important to use the same voltage relay also. The circuit is actually a dark detecting circuit or we can also say it dark / light sensor circuit. The two transistor used in the circuit are working as switches. When light falls on the LDR its resistance decreases and the voltage at the base of Q1 will increase which will switch on the Q1 and the Q2 will remain switch off.
When there is no light on the surface of the LDR its resistor increases, which will switch off the transistor Q1 and the voltage at the base of Q2 increases and hence the transistor Q2 will switch on and activates the relay switch. 🔗 External reference
The automatic street light circuit primarily consists of a light-dependent resistor (LDR), two 2N3904 NPN transistors, a relay, and a variable resistor (VR) for sensitivity adjustment. The LDR plays a critical role in detecting ambient light levels. In bright conditions, the LDR's low resistance allows current to flow, keeping transistor Q1 in the off state, which in turn keeps Q2 off, preventing the relay from activating. As ambient light decreases at dusk, the LDR's resistance increases, which raises the voltage at the base of Q1, turning it on. This action also turns off Q2, allowing the relay to engage and power the connected load.
The circuit can be powered by a DC source of 6V, 9V, or 12V, with the relay being rated for the same voltage to ensure compatibility and proper operation. The variable resistor (50K VR) allows for fine-tuning of the light sensitivity, enabling the user to set the threshold at which the circuit activates based on the local lighting conditions.
The relay used in the circuit acts as a switch to control the higher voltage AC load. It is essential to select a relay that can handle the maximum load current and voltage to prevent damage or failure of the circuit. The simplicity of the design allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it an excellent choice for DIY enthusiasts looking to automate outdoor lighting solutions.Here is a very useful project of an automatic street light or lamp circuit which can be used to activate your outdoor lights like garden lamps, night lights etc. automatically when the sun set and turn off automatically when the sun rises. The circuit is quite sensitive and versatile and can be used to activate any 220 volt AC device at night and
turn off in day all you have to do is simply connect the device with the load point. You can also connect a 220V plug socket with the load point to connect different electronic devices but make sure the relay points can able to handle the provided load. The circuit is simple using two 2N3904 transistors and few other components. The 50K VR (Variable Resistor) is used to adjust the circuit to activate the relay on the required darkness.
The circuit can be operated with 6 volts, 9 volts and 12 volts but it is important to use the same voltage relay also. The circuit is actually a dark detecting circuit or we can also say it dark / light sensor circuit. The two transistor used in the circuit are working as switches. When light falls on the LDR its resistance decreases and the voltage at the base of Q1 will increase which will switch on the Q1 and the Q2 will remain switch off.
When there is no light on the surface of the LDR its resistor increases, which will switch off the transistor Q1 and the voltage at the base of Q2 increases and hence the transistor Q2 will switch on and activates the relay switch. 🔗 External reference