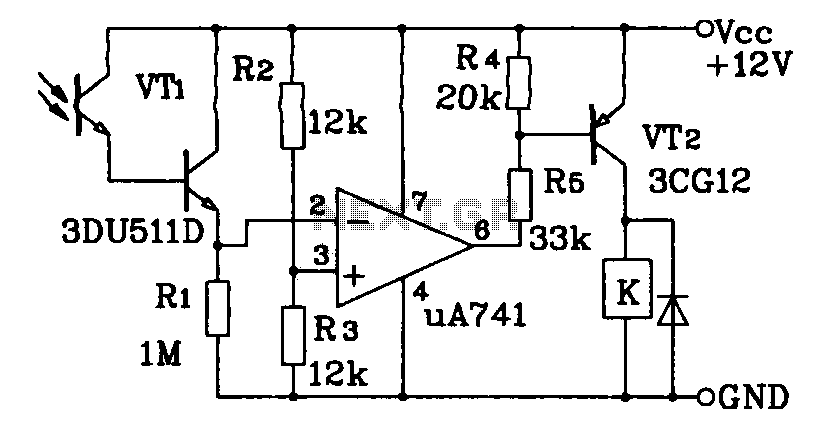
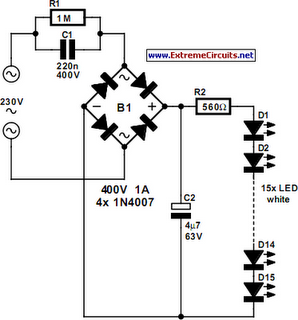
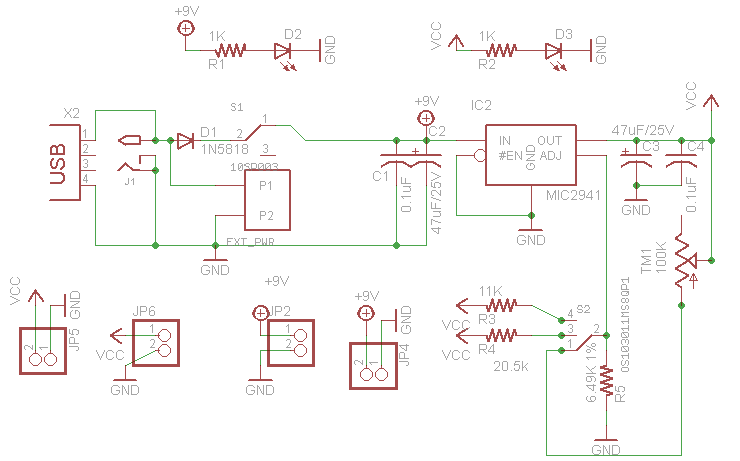
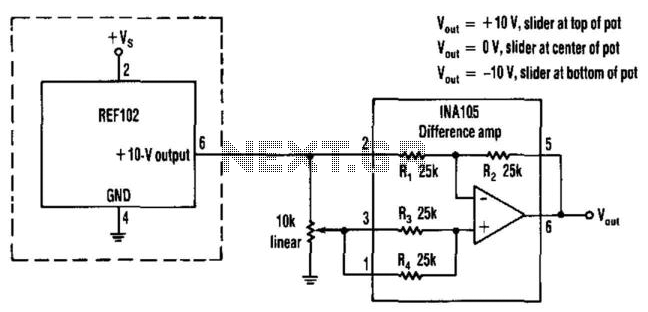
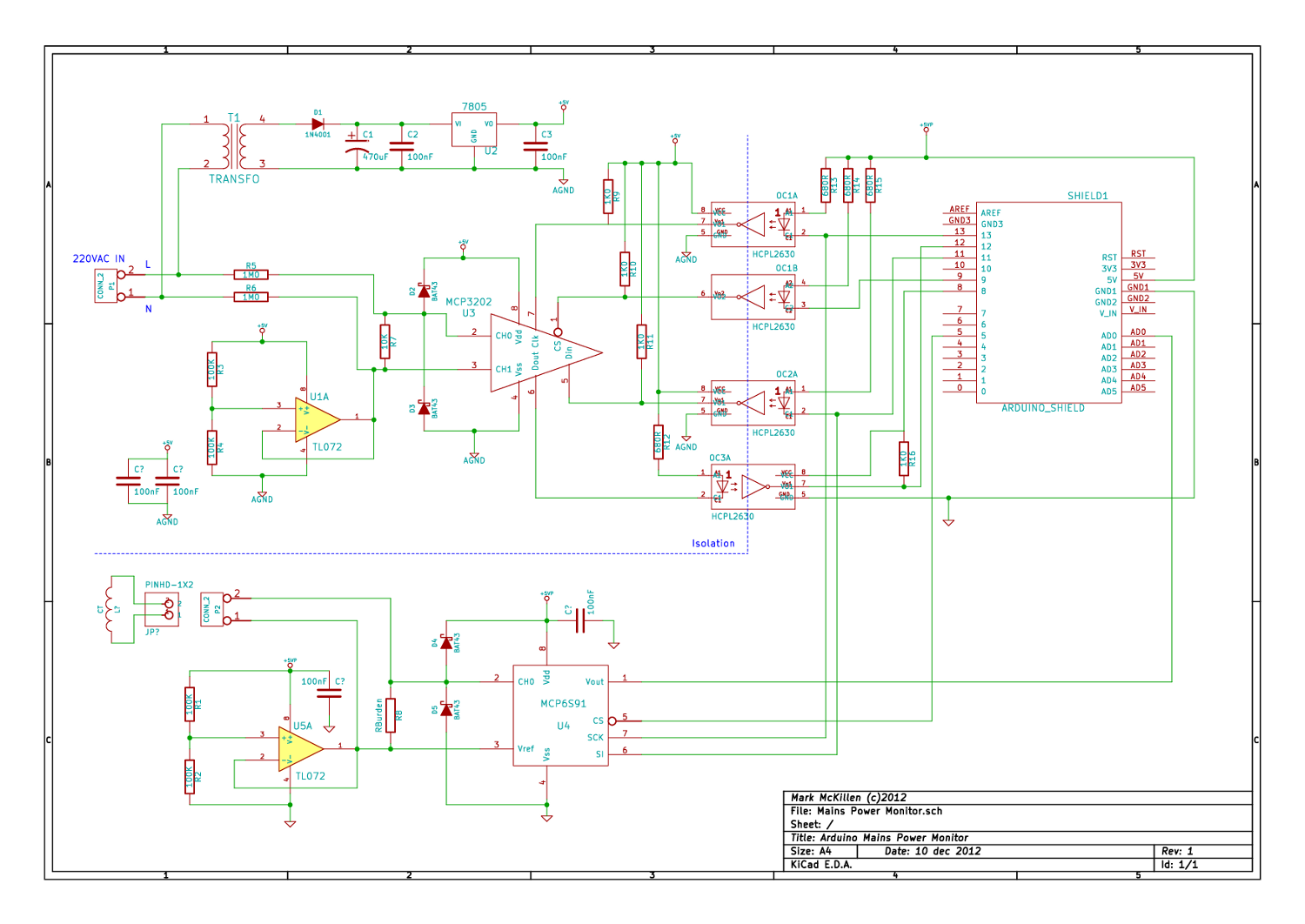
Structural analysis of switching power supply
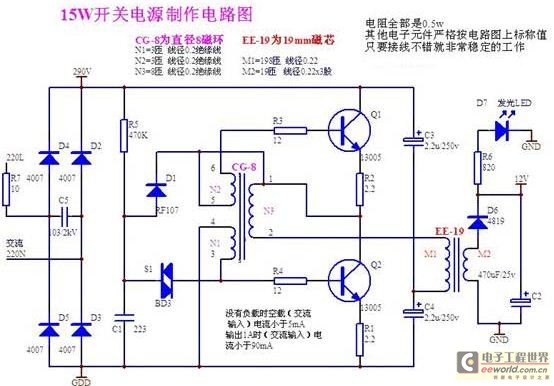
A daily switching power supply primarily provides direct current (DC) power to electronic devices. The required DC voltage for electronic devices typically ranges from several volts to over ten volts, while the input voltage from the mains supply is either 220V or 110V, with a frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz. The purpose of a switching power supply is to convert high-voltage alternating current (AC) from the mains into low-voltage direct current (DC). This process involves directly commutating the mains frequency AC, eliminating the need for bulky transformers, which reduces overall weight. The rectifier produces a high-voltage DC output, which is then filtered through capacitors, resulting in a mean voltage of approximately 300V to 310V. This high-voltage DC is fed into an inverter, which converts it into high-frequency AC at operating frequencies ranging from tens to several hundred kilohertz. The inverter's output connects to the primary side of a high-frequency step-down transformer, allowing for a significant reduction in size and weight compared to traditional mains frequency transformers. The high-frequency AC produced by the inverter is subsequently stepped down and processed to meet the load requirements, including functions such as commutation and voltage regulation. Generally, the rectifying circuit is an uncontrolled type, and depending on power capacity, it can be single-phase or three-phase. Switching power supplies exhibit excellent input interference characteristics due to their multi-step series circuit design, making them more resistant to input surges compared to linear power supplies, achieving voltage stability of 0.5% to 1%. The switching power module, as an integrated electronic device, requires careful consideration of several factors during application. With high operating efficiency, often exceeding 80%, it is essential to accurately measure the maximum current absorption of the connected electrical equipment to ensure optimal performance. Switching power supplies may generate more interference than linear power supplies, necessitating measures for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), including the use of electric-wave filters. Additionally, protective functions against overload, overheating, and short circuits must be incorporated into the design, ensuring that the protective circuit parameters align with the operational characteristics of the connected equipment to prevent damage.
A switching power supply circuit typically consists of several key components: an input filter, a rectifier, a high-frequency inverter, a transformer, and an output stage. The input filter serves to eliminate high-frequency noise and protect the power supply from voltage spikes. The rectifier converts the incoming AC voltage to DC, utilizing diodes arranged in a bridge configuration for single-phase systems or more complex arrangements for three-phase systems.
The inverter is a critical component that transforms the rectified DC voltage into high-frequency AC. This is achieved using switching devices such as MOSFETs or IGBTs, which rapidly turn on and off to create a pulse-width modulated (PWM) output. The frequency of the output can be adjusted to optimize performance and efficiency.
Following the inverter, a high-frequency transformer steps down the voltage to the desired level. The transformer is designed to operate at high frequencies, significantly reducing its size and weight compared to traditional transformers.
The output stage includes rectification and filtering to convert the high-frequency AC back into a stable DC voltage suitable for powering electronic devices. Capacitors and inductors are used in this stage to smooth out the output voltage and minimize ripple.
In summary, a switching power supply is an efficient and compact solution for providing DC power to electronic devices, utilizing advanced circuitry and components to achieve high performance and reliability while ensuring electromagnetic compatibility and protection against various electrical faults.Daily switching power supply, mainly offer the direct current power supply for electronic device and supply power. The required direct-current volts of the electronic device, ranges are generally all between several volts and more than ten volts, and the voltage of exchanging Piower supply of city power is 220V 110V, The frequency is 50Hz 60Hz.
T he function of switching power supply is to vary the mains frequency alternating current of a high voltage class into the direct current of a low voltage class. The alternating current of mains frequency is commutated directly, save bulky mains frequency with big weight and commutate the voltage transformer after entering the switching power supply.
The rectifier is outputted for very high direct current of voltage, the voltage after commutating passes the capacitor filtering, the mean value of the voltage is 300V 310V. The direct current of the high voltage class is sent to the input end of the inverter, vary by the inverter, turn into upper voltage, high-frequency alternating current.
The variety operating frequency of the inverter of the switching power supply is in dozens of to several hundred KHz ranges at present. The exchange electric energy that the inverter exported, connect the primary side of the high-frequency step-down transformer, exchange the mains frequency of the electric frequency ratio much higher because of the high frequency that is produced by the inverter, so the volume of the high-frequency voltage transformer is much smaller than with the mains frequency voltage transformer of the capacity, have reduced volume and weight of the whole power fundamentally.
The high-frequency alternating current that the inverter produce, after the high-frequency voltage transformer steps down, links such as commutating, voltage regulation, etc. , can vary the undervoltage direct current which accords with the load requirement out, supply load. The rectifying circuit of mains frequency is generally uncontrolled rectifying circuit, according to the magnitude of the power capacity, can single-phase commutate, generally choose the structure of single-phase bridge, the high-capacity switching power supply can use the three-phase a.
c. voltage supply. The switching power supply is in inputting the interference-free characteristic, because the characteristic multistep connects in series of its one`s own circuit structure, It is passed that general input interference such as surge voltage is very difficult, have the advantage of being greater compared with linear power in outputting voltage stability this technical indicator, it outputs reachable 0. 5% to 1% of voltage stability. The switch power module is as a kind of electric and electronic integrated device, should pay attention to the following several points in application.
Because the operating efficiency of the switching power supply is high, can generally be more than 80%, so on the choice of its output current, should measure or calculate and use the maximum absorption current of the electrical equipment accurately, in order to make the switching power supply that is chosen have high performance-cost ratio, Switching power supply will produce more interference than linear power, responsive to spend the electrical equipment to common-mode interference, should take and earth and shield the measure, so there are EMC electromagnetic compatibility electric-wave filters in the switching power supply. The switching power supply must have excessive load, excessive heating, short out etc. to protect the function in the design, so should first choose to protect the switch power module with complete function during design, and the technical parameter of its protective circuit answers and uses the operating characteristic of the electrical equipment to be assorted, in order to avoid damaging and using the electrical equipment or switching power supply.
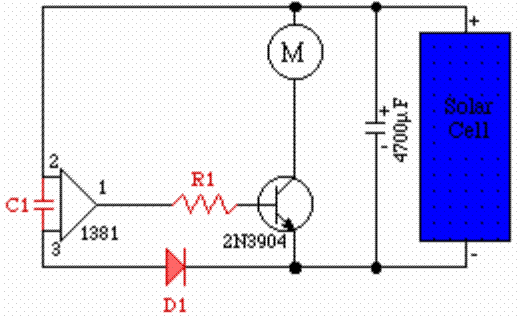
The electric motor, under 🔗 External reference
A switching power supply circuit typically consists of several key components: an input filter, a rectifier, a high-frequency inverter, a transformer, and an output stage. The input filter serves to eliminate high-frequency noise and protect the power supply from voltage spikes. The rectifier converts the incoming AC voltage to DC, utilizing diodes arranged in a bridge configuration for single-phase systems or more complex arrangements for three-phase systems.
The inverter is a critical component that transforms the rectified DC voltage into high-frequency AC. This is achieved using switching devices such as MOSFETs or IGBTs, which rapidly turn on and off to create a pulse-width modulated (PWM) output. The frequency of the output can be adjusted to optimize performance and efficiency.
Following the inverter, a high-frequency transformer steps down the voltage to the desired level. The transformer is designed to operate at high frequencies, significantly reducing its size and weight compared to traditional transformers.
The output stage includes rectification and filtering to convert the high-frequency AC back into a stable DC voltage suitable for powering electronic devices. Capacitors and inductors are used in this stage to smooth out the output voltage and minimize ripple.
In summary, a switching power supply is an efficient and compact solution for providing DC power to electronic devices, utilizing advanced circuitry and components to achieve high performance and reliability while ensuring electromagnetic compatibility and protection against various electrical faults.Daily switching power supply, mainly offer the direct current power supply for electronic device and supply power. The required direct-current volts of the electronic device, ranges are generally all between several volts and more than ten volts, and the voltage of exchanging Piower supply of city power is 220V 110V, The frequency is 50Hz 60Hz.
T he function of switching power supply is to vary the mains frequency alternating current of a high voltage class into the direct current of a low voltage class. The alternating current of mains frequency is commutated directly, save bulky mains frequency with big weight and commutate the voltage transformer after entering the switching power supply.
The rectifier is outputted for very high direct current of voltage, the voltage after commutating passes the capacitor filtering, the mean value of the voltage is 300V 310V. The direct current of the high voltage class is sent to the input end of the inverter, vary by the inverter, turn into upper voltage, high-frequency alternating current.
The variety operating frequency of the inverter of the switching power supply is in dozens of to several hundred KHz ranges at present. The exchange electric energy that the inverter exported, connect the primary side of the high-frequency step-down transformer, exchange the mains frequency of the electric frequency ratio much higher because of the high frequency that is produced by the inverter, so the volume of the high-frequency voltage transformer is much smaller than with the mains frequency voltage transformer of the capacity, have reduced volume and weight of the whole power fundamentally.
The high-frequency alternating current that the inverter produce, after the high-frequency voltage transformer steps down, links such as commutating, voltage regulation, etc. , can vary the undervoltage direct current which accords with the load requirement out, supply load. The rectifying circuit of mains frequency is generally uncontrolled rectifying circuit, according to the magnitude of the power capacity, can single-phase commutate, generally choose the structure of single-phase bridge, the high-capacity switching power supply can use the three-phase a.
c. voltage supply. The switching power supply is in inputting the interference-free characteristic, because the characteristic multistep connects in series of its one`s own circuit structure, It is passed that general input interference such as surge voltage is very difficult, have the advantage of being greater compared with linear power in outputting voltage stability this technical indicator, it outputs reachable 0. 5% to 1% of voltage stability. The switch power module is as a kind of electric and electronic integrated device, should pay attention to the following several points in application.
Because the operating efficiency of the switching power supply is high, can generally be more than 80%, so on the choice of its output current, should measure or calculate and use the maximum absorption current of the electrical equipment accurately, in order to make the switching power supply that is chosen have high performance-cost ratio, Switching power supply will produce more interference than linear power, responsive to spend the electrical equipment to common-mode interference, should take and earth and shield the measure, so there are EMC electromagnetic compatibility electric-wave filters in the switching power supply. The switching power supply must have excessive load, excessive heating, short out etc. to protect the function in the design, so should first choose to protect the switch power module with complete function during design, and the technical parameter of its protective circuit answers and uses the operating characteristic of the electrical equipment to be assorted, in order to avoid damaging and using the electrical equipment or switching power supply.
The electric motor, under 🔗 External reference