Super Cheap 1.5V Joule Thief circuit
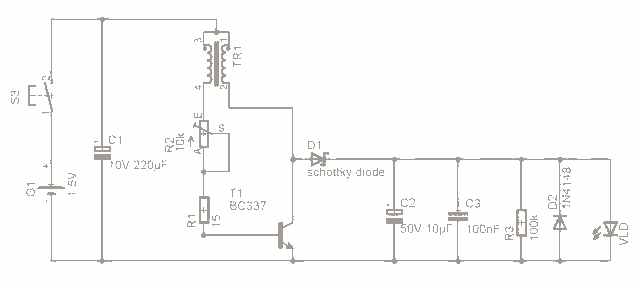
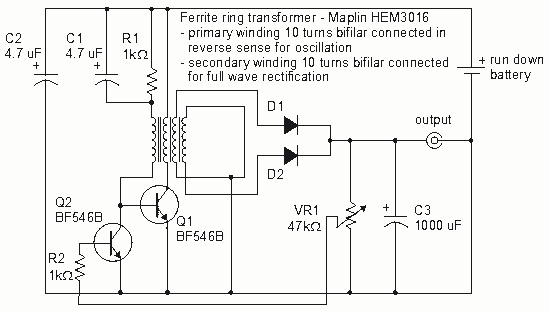
For the past few days, research has been conducted on an intriguing boost circuit known as the Joule Thief. The original schematic can be found through online resources.
The Joule Thief is a simple yet effective boost converter circuit designed to extract energy from low-voltage power sources, such as depleted batteries. It operates on the principle of oscillation, utilizing a transistor to switch current through an inductor, which stores energy in its magnetic field. When the transistor turns off, this stored energy is released and stepped up to a higher voltage, allowing it to power devices that require more voltage than the source can provide.
The basic components of a Joule Thief circuit include a NPN transistor, a toroidal inductor or a ferrite core inductor, a resistor, and a diode. The transistor serves as the main switching element, while the inductor is crucial for energy storage and voltage boosting. The resistor is typically connected to the base of the transistor to limit the current and ensure proper operation. The diode is used to rectify the output voltage, allowing the energy to flow to the load.
When constructing a Joule Thief, the inductor is often wound with a specific number of turns, typically around 10 to 20 turns, depending on the desired output voltage and current. The choice of the transistor is also important; commonly used transistors include the 2N3904 or BC547. The circuit can operate efficiently with input voltages as low as 0.5V, making it ideal for scavenging energy from nearly depleted batteries.
The output voltage can vary depending on the load and the input voltage, but it can often exceed the input voltage by a factor of two or more, making it suitable for powering low-voltage LEDs or small electronic devices. The simplicity of the Joule Thief circuit, combined with its ability to utilize otherwise wasted energy, makes it a popular choice among hobbyists and engineers interested in low-power applications.For the past few days Ive been researching in this very interesting boost circuit called the joule thief (google it) and done allot of. The original schematic from google 🔗 External reference
The Joule Thief is a simple yet effective boost converter circuit designed to extract energy from low-voltage power sources, such as depleted batteries. It operates on the principle of oscillation, utilizing a transistor to switch current through an inductor, which stores energy in its magnetic field. When the transistor turns off, this stored energy is released and stepped up to a higher voltage, allowing it to power devices that require more voltage than the source can provide.
The basic components of a Joule Thief circuit include a NPN transistor, a toroidal inductor or a ferrite core inductor, a resistor, and a diode. The transistor serves as the main switching element, while the inductor is crucial for energy storage and voltage boosting. The resistor is typically connected to the base of the transistor to limit the current and ensure proper operation. The diode is used to rectify the output voltage, allowing the energy to flow to the load.
When constructing a Joule Thief, the inductor is often wound with a specific number of turns, typically around 10 to 20 turns, depending on the desired output voltage and current. The choice of the transistor is also important; commonly used transistors include the 2N3904 or BC547. The circuit can operate efficiently with input voltages as low as 0.5V, making it ideal for scavenging energy from nearly depleted batteries.
The output voltage can vary depending on the load and the input voltage, but it can often exceed the input voltage by a factor of two or more, making it suitable for powering low-voltage LEDs or small electronic devices. The simplicity of the Joule Thief circuit, combined with its ability to utilize otherwise wasted energy, makes it a popular choice among hobbyists and engineers interested in low-power applications.For the past few days Ive been researching in this very interesting boost circuit called the joule thief (google it) and done allot of. The original schematic from google 🔗 External reference