supernode dependent voltage source
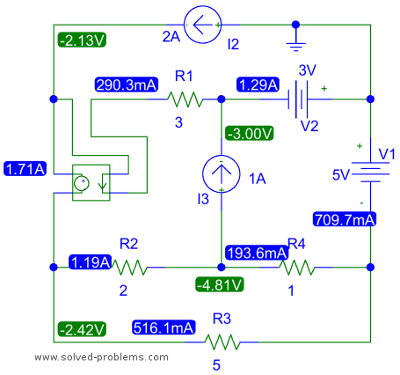
The top right node is connected to two voltage sources and contains three elements. All other nodes also have three elements. The selection of the top right node is significant because it allows for the determination of the node voltages of two additional nodes, specifically those connected to the reference node via voltage sources. Consequently, all node voltages can be established. The power of the voltage sources can then be calculated using the established node voltages. To compute the power for each source, it is necessary to determine both the voltage across the source and the current flowing through it. According to the passive sign convention, the current must enter from the positive terminal of the defined voltage source.
The described circuit involves a network of nodes and voltage sources, where the top right node serves as a critical point for voltage determination. The connection of two voltage sources to this node suggests that it plays a pivotal role in the overall voltage distribution within the circuit. Each node in the circuit contains three elements, which may include resistors, capacitors, or inductors, contributing to the overall functionality and behavior of the circuit.
By selecting the top right node, the voltages at adjacent nodes can be inferred, enabling a systematic approach to analyzing the circuit. The reference node, typically grounded, establishes a common potential against which all other node voltages are measured. This method simplifies the analysis by reducing the number of unknowns and allowing for the application of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) to the circuit.
Once the node voltages are calculated, the next step involves assessing the power associated with each voltage source. The power (P) delivered by a voltage source can be computed using the formula P = V * I, where V is the voltage across the source and I is the current flowing through it. It is essential to adhere to the passive sign convention when determining the direction of current flow, ensuring that it enters through the positive terminal of the voltage source. This convention is crucial for accurate power calculations, as it dictates the sign of the power value, indicating whether the source is supplying or absorbing power.
In summary, the circuit analysis begins with the identification of a pivotal node connected to voltage sources, leading to the determination of node voltages. Following this, the power calculations for the voltage sources are conducted, adhering to the passive sign convention to ensure accurate results. This structured approach provides a clear pathway for understanding the behavior of the circuit and the interactions between its components.The right top node is connected to two voltage sources and has three elements. All other nodes also have three elements. Hence, we select the right top node because by this selection, we already know the node voltages of two other nodes, i. e. the ones that the reference node is connected to them by voltage sources. All node voltages are determined . Now, the power of voltage sources can be calculated from the node voltages. For each source, we need to find the voltage across the source as well as the current flowing through it to compute the power. . However, the comply with the passive voltage convention, the current should be entering from the positive terminal of the defined voltage as shown below.
Therefore, 🔗 External reference
The described circuit involves a network of nodes and voltage sources, where the top right node serves as a critical point for voltage determination. The connection of two voltage sources to this node suggests that it plays a pivotal role in the overall voltage distribution within the circuit. Each node in the circuit contains three elements, which may include resistors, capacitors, or inductors, contributing to the overall functionality and behavior of the circuit.
By selecting the top right node, the voltages at adjacent nodes can be inferred, enabling a systematic approach to analyzing the circuit. The reference node, typically grounded, establishes a common potential against which all other node voltages are measured. This method simplifies the analysis by reducing the number of unknowns and allowing for the application of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) to the circuit.
Once the node voltages are calculated, the next step involves assessing the power associated with each voltage source. The power (P) delivered by a voltage source can be computed using the formula P = V * I, where V is the voltage across the source and I is the current flowing through it. It is essential to adhere to the passive sign convention when determining the direction of current flow, ensuring that it enters through the positive terminal of the voltage source. This convention is crucial for accurate power calculations, as it dictates the sign of the power value, indicating whether the source is supplying or absorbing power.
In summary, the circuit analysis begins with the identification of a pivotal node connected to voltage sources, leading to the determination of node voltages. Following this, the power calculations for the voltage sources are conducted, adhering to the passive sign convention to ensure accurate results. This structured approach provides a clear pathway for understanding the behavior of the circuit and the interactions between its components.The right top node is connected to two voltage sources and has three elements. All other nodes also have three elements. Hence, we select the right top node because by this selection, we already know the node voltages of two other nodes, i. e. the ones that the reference node is connected to them by voltage sources. All node voltages are determined . Now, the power of voltage sources can be calculated from the node voltages. For each source, we need to find the voltage across the source as well as the current flowing through it to compute the power. . However, the comply with the passive voltage convention, the current should be entering from the positive terminal of the defined voltage as shown below.
Therefore, 🔗 External reference