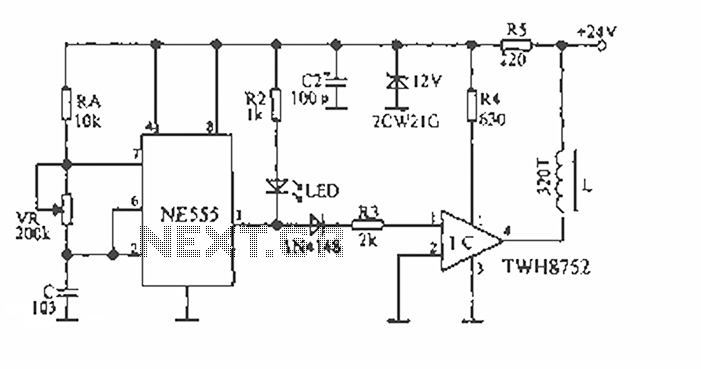
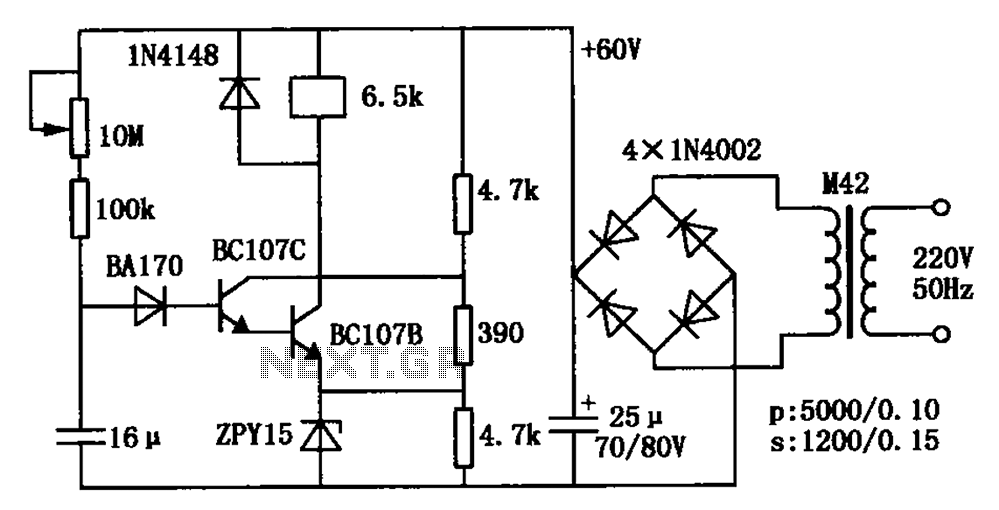
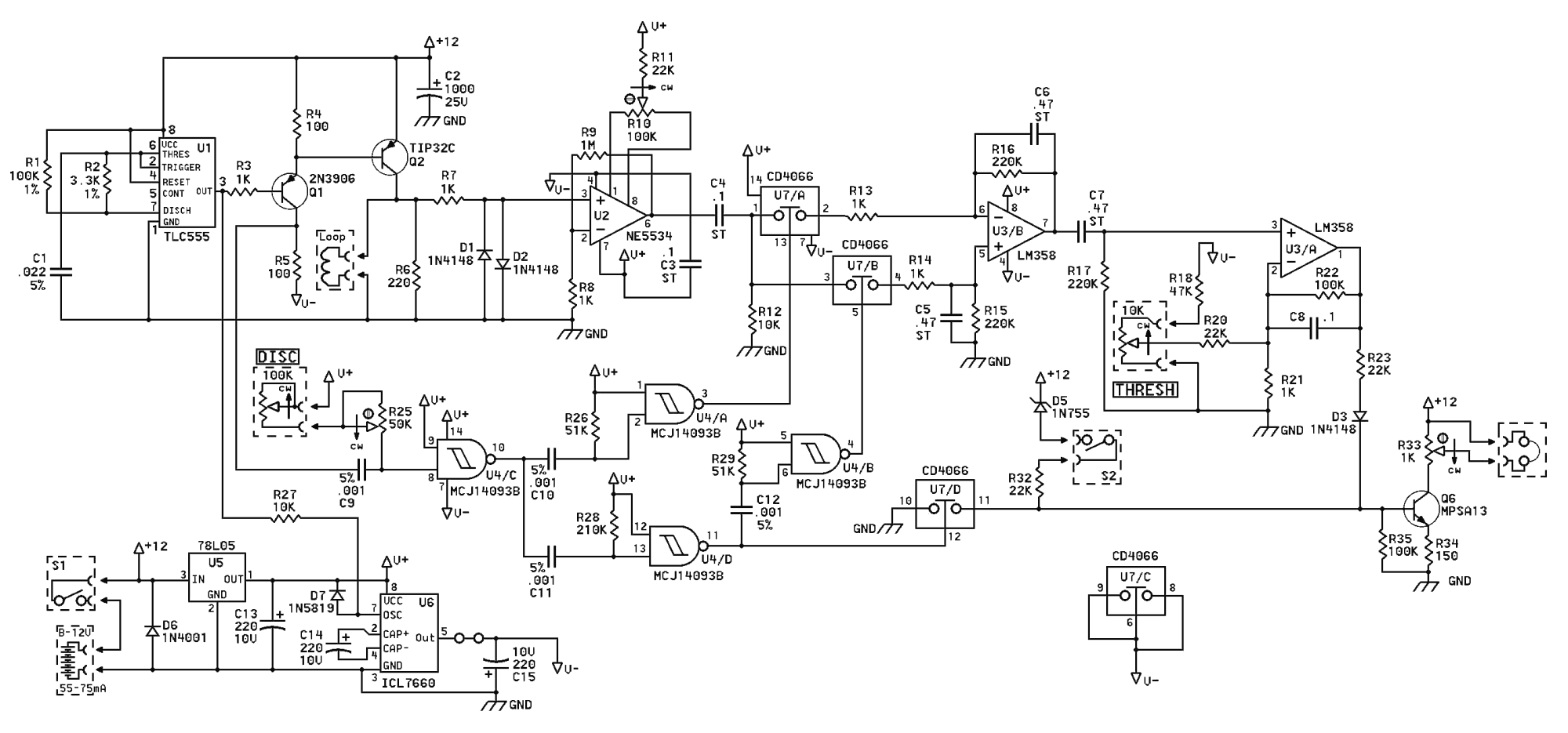
Surfmaster PI Metal Detector Schematic Diagram
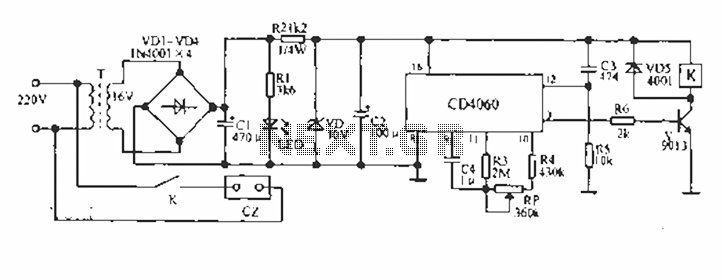
If the TIP32C (Q2) transistor becomes excessively hot, consider replacing it with an IRF9640 MOSFET. It is advisable to experiment with different resistor values for R6 to determine the optimal resistance (a 390-ohm resistor is recommended). A trim potentiometer (470 ohms or 1k ohms) can be temporarily used in place of R6 to identify the best dumping resistor for the coil.
The circuit utilizes a TIP32C transistor as a switching element, which may exhibit overheating under certain conditions, indicating potential inefficiencies or excessive load. The IRF9640 MOSFET serves as a suitable alternative due to its higher efficiency and thermal performance, particularly in applications requiring rapid switching and low on-resistance.
In the circuit, R6 plays a critical role in controlling the timing and damping characteristics of the coil. The selection of this resistor is pivotal for optimizing the performance of the circuit. A standard 390-ohm resistor may suffice for many applications; however, variations in the load or operating conditions may necessitate adjustments to this value.
To facilitate precise tuning, employing a trim potentiometer in the range of 470 to 1k ohms allows for fine adjustments. This flexibility enables the user to empirically determine the most effective dumping resistor value. The optimal resistance can significantly influence the transient response of the system, enhancing stability and performance.
Additionally, careful attention should be paid to the thermal management of the components in the circuit. Adequate heat sinking or thermal dissipation methods may be required, especially when using the TIP32C, to prevent thermal runaway and ensure reliable operation. The transition to the IRF9640 MOSFET may alleviate some of these thermal concerns due to its enhanced heat dissipation capabilities.
Ultimately, the choice of components and their respective values should be guided by the specific application requirements, load characteristics, and desired performance metrics of the circuit.If TIP32C (Q2) gets excessively hot, use an IRF9640 MOSFET instead. Experiment with different values for R6 to find the optimal value (I use a 390 ohm resistor). Temporarily substitute R6 for a trim potentiometer (470 or 1k) to find the optimal dumping resistor for your coil. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a TIP32C transistor as a switching element, which may exhibit overheating under certain conditions, indicating potential inefficiencies or excessive load. The IRF9640 MOSFET serves as a suitable alternative due to its higher efficiency and thermal performance, particularly in applications requiring rapid switching and low on-resistance.
In the circuit, R6 plays a critical role in controlling the timing and damping characteristics of the coil. The selection of this resistor is pivotal for optimizing the performance of the circuit. A standard 390-ohm resistor may suffice for many applications; however, variations in the load or operating conditions may necessitate adjustments to this value.
To facilitate precise tuning, employing a trim potentiometer in the range of 470 to 1k ohms allows for fine adjustments. This flexibility enables the user to empirically determine the most effective dumping resistor value. The optimal resistance can significantly influence the transient response of the system, enhancing stability and performance.
Additionally, careful attention should be paid to the thermal management of the components in the circuit. Adequate heat sinking or thermal dissipation methods may be required, especially when using the TIP32C, to prevent thermal runaway and ensure reliable operation. The transition to the IRF9640 MOSFET may alleviate some of these thermal concerns due to its enhanced heat dissipation capabilities.
Ultimately, the choice of components and their respective values should be guided by the specific application requirements, load characteristics, and desired performance metrics of the circuit.If TIP32C (Q2) gets excessively hot, use an IRF9640 MOSFET instead. Experiment with different values for R6 to find the optimal value (I use a 390 ohm resistor). Temporarily substitute R6 for a trim potentiometer (470 or 1k) to find the optimal dumping resistor for your coil. 🔗 External reference