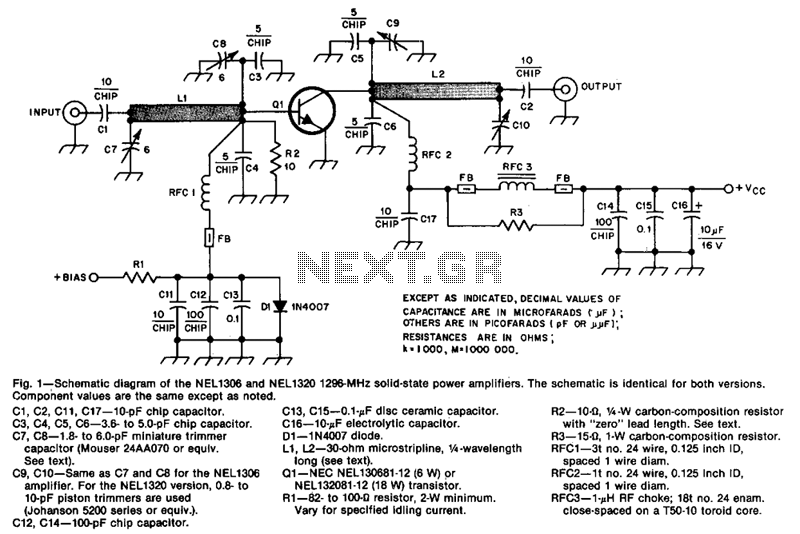
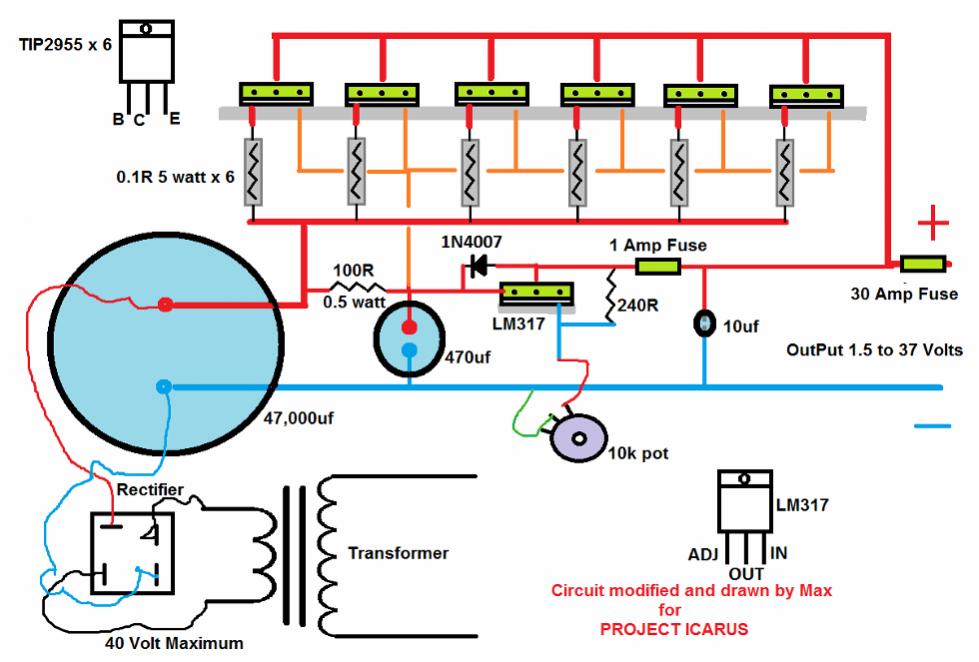
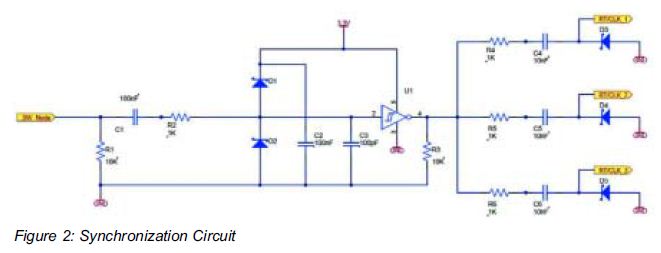
Synchronization of SMPS Power Modules
A Practical Application for Cyclone V FPGA Power Requirements The integration of multiple power modules on a single power board allows for specific load requirements to be met efficiently.
The Cyclone V FPGA requires careful consideration of its power supply architecture to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The integration of multiple power modules on a single power board is a practical solution to meet the specific load requirements of the FPGA. This approach allows for the distribution of power across various voltage levels, which is essential for the different operational blocks within the FPGA.
Typically, the power board would incorporate several DC-DC converters, each tailored to supply different voltage rails as dictated by the FPGA's specifications. Common voltage levels required by Cyclone V FPGAs include 1.2V for the core, 2.5V for I/O, and 3.3V for auxiliary functions. The use of synchronous buck converters is recommended for their efficiency in converting higher input voltages down to the required levels with minimal heat generation.
The power management system should also include features such as power sequencing and monitoring to ensure that all voltage rails are stable before the FPGA begins operation. This can be achieved through the use of power management ICs (PMICs) that can coordinate the startup and shutdown sequences of the power modules.
Thermal management must also be considered, as the concentration of multiple power modules can lead to increased heat generation. Adequate heat sinking and airflow must be designed into the PCB layout to maintain operational temperatures within specified limits.
In summary, the effective integration of multiple power modules on a single power board is crucial for meeting the diverse power requirements of Cyclone V FPGAs. This design approach enhances efficiency, reliability, and performance, ensuring that the FPGA operates within its specified parameters.A Practical Application for Cyclone V FPGA Power Requirements The integration of multiple power modules on a single power board allows for specific load requirements to be.. 🔗 External reference
The Cyclone V FPGA requires careful consideration of its power supply architecture to ensure optimal performance and reliability. The integration of multiple power modules on a single power board is a practical solution to meet the specific load requirements of the FPGA. This approach allows for the distribution of power across various voltage levels, which is essential for the different operational blocks within the FPGA.
Typically, the power board would incorporate several DC-DC converters, each tailored to supply different voltage rails as dictated by the FPGA's specifications. Common voltage levels required by Cyclone V FPGAs include 1.2V for the core, 2.5V for I/O, and 3.3V for auxiliary functions. The use of synchronous buck converters is recommended for their efficiency in converting higher input voltages down to the required levels with minimal heat generation.
The power management system should also include features such as power sequencing and monitoring to ensure that all voltage rails are stable before the FPGA begins operation. This can be achieved through the use of power management ICs (PMICs) that can coordinate the startup and shutdown sequences of the power modules.
Thermal management must also be considered, as the concentration of multiple power modules can lead to increased heat generation. Adequate heat sinking and airflow must be designed into the PCB layout to maintain operational temperatures within specified limits.
In summary, the effective integration of multiple power modules on a single power board is crucial for meeting the diverse power requirements of Cyclone V FPGAs. This design approach enhances efficiency, reliability, and performance, ensuring that the FPGA operates within its specified parameters.A Practical Application for Cyclone V FPGA Power Requirements The integration of multiple power modules on a single power board allows for specific load requirements to be.. 🔗 External reference