SYNCHRONOUS FILTER FOR ADF
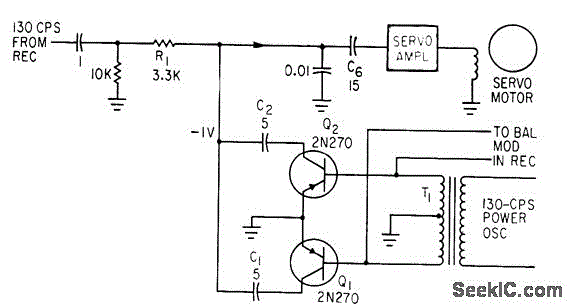
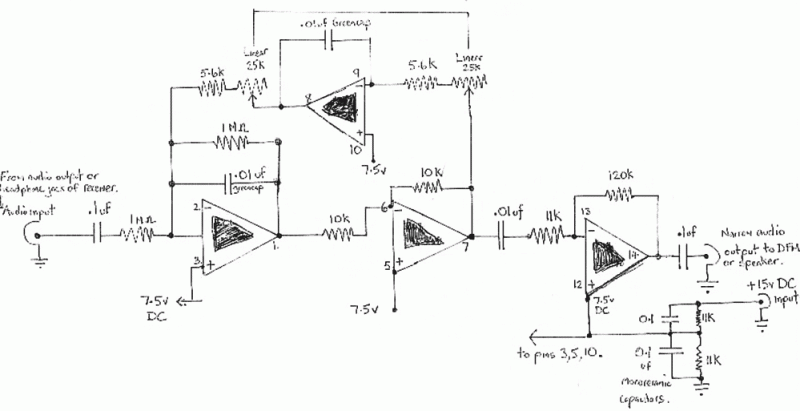
Separates 130-cps motor drive voltage from voice frequencies in the output of an ADF receiver. P. V. Sparks, Servo Filter and Gain Control Improve Automatic Direction Finder, Electronics, 34:23, p 110-113.
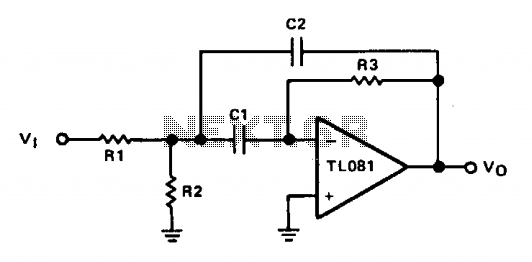
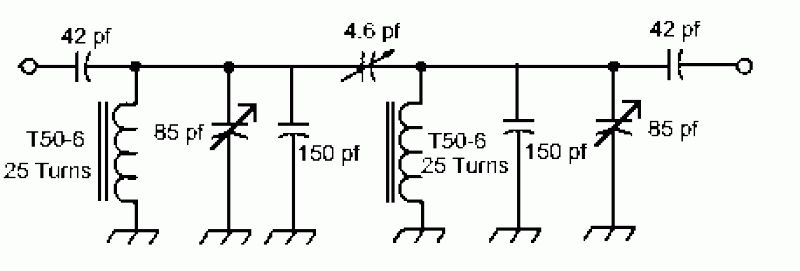
The circuit described functions as a filter that effectively separates the 130-cps motor drive voltage from voice frequency signals present in the output of an Automatic Direction Finder (ADF) receiver. This separation is crucial for ensuring that the motor control signals do not interfere with the audio signals being processed, thereby maintaining clarity and functionality in the system.
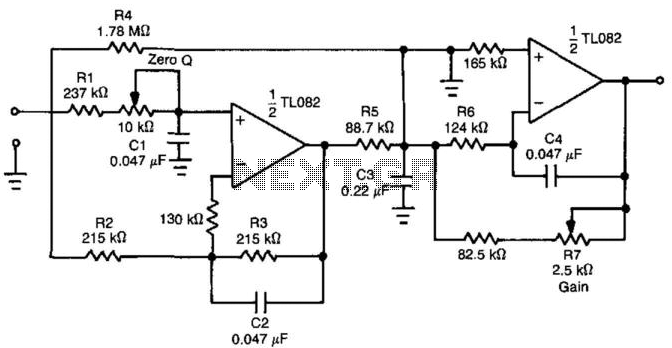
The design likely employs a combination of passive and active filtering techniques. A low-pass filter may be utilized to allow voice frequencies to pass while attenuating higher frequency components, such as the motor drive voltage. The filter might consist of resistors, capacitors, and possibly operational amplifiers to enhance the gain and control of the output signal.
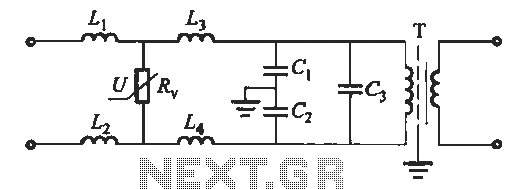
The inclusion of a servo filter suggests that feedback mechanisms are in place to stabilize the output, ensuring that variations in the motor drive do not adversely affect the voice frequency output. Gain control circuitry may also be integrated to adjust the amplitude of the filtered signal, providing flexibility in the output level according to the requirements of the subsequent stages in the ADF system.
Overall, the circuit plays a vital role in improving the performance and reliability of the ADF receiver by isolating critical signals and maintaining the integrity of voice communications.Separates 130-cps motor drive voltage from voice frequencies in output of adf receiver-P. V. Sparks, Servo Filter and Gain Control Improve Automatic Direction Finder, Electronics, 34:23, p 110-113.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described functions as a filter that effectively separates the 130-cps motor drive voltage from voice frequency signals present in the output of an Automatic Direction Finder (ADF) receiver. This separation is crucial for ensuring that the motor control signals do not interfere with the audio signals being processed, thereby maintaining clarity and functionality in the system.
The design likely employs a combination of passive and active filtering techniques. A low-pass filter may be utilized to allow voice frequencies to pass while attenuating higher frequency components, such as the motor drive voltage. The filter might consist of resistors, capacitors, and possibly operational amplifiers to enhance the gain and control of the output signal.
The inclusion of a servo filter suggests that feedback mechanisms are in place to stabilize the output, ensuring that variations in the motor drive do not adversely affect the voice frequency output. Gain control circuitry may also be integrated to adjust the amplitude of the filtered signal, providing flexibility in the output level according to the requirements of the subsequent stages in the ADF system.
Overall, the circuit plays a vital role in improving the performance and reliability of the ADF receiver by isolating critical signals and maintaining the integrity of voice communications.Separates 130-cps motor drive voltage from voice frequencies in output of adf receiver-P. V. Sparks, Servo Filter and Gain Control Improve Automatic Direction Finder, Electronics, 34:23, p 110-113.. 🔗 External reference