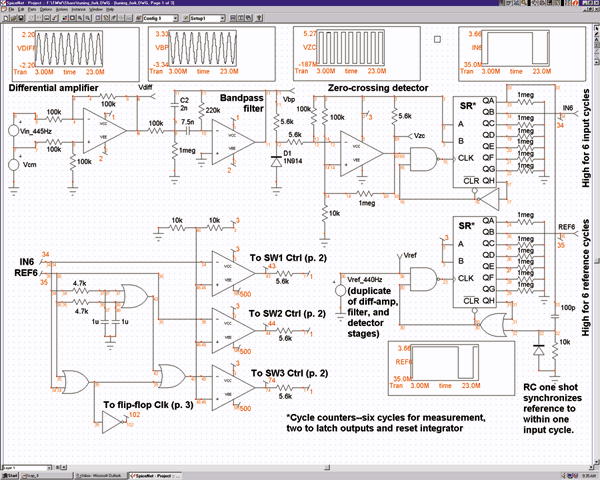
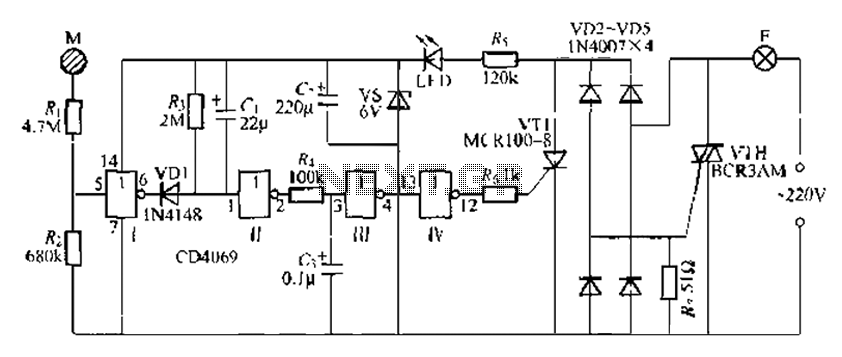
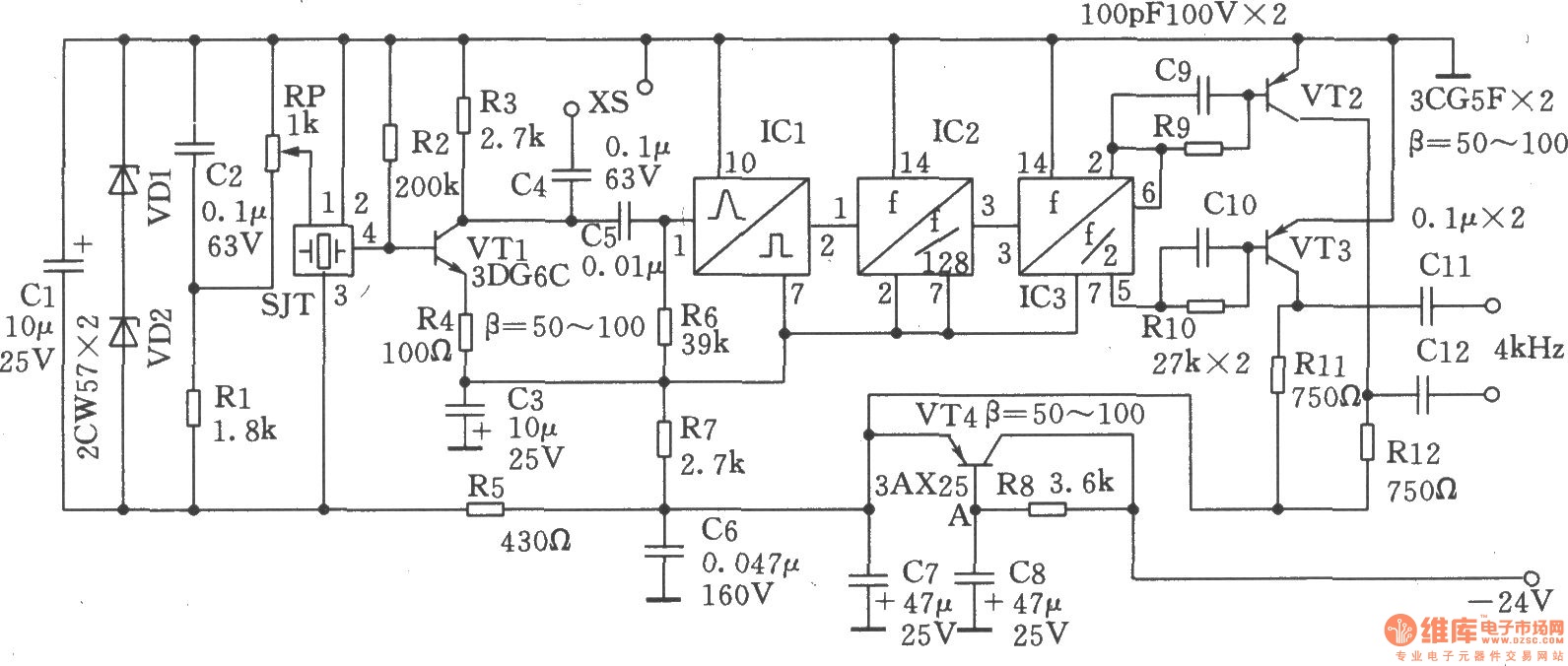
Temperature Relay Circuit
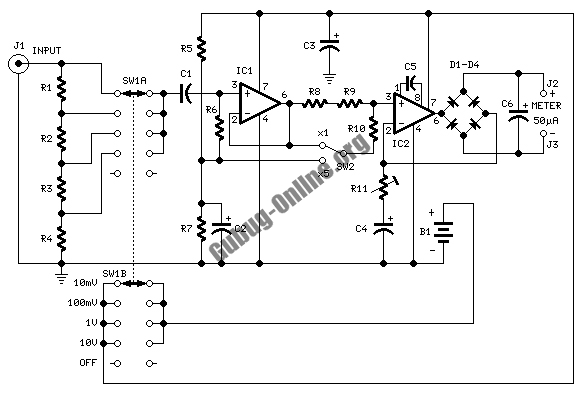
This is a circuit design for a temperature relay that can be used to signal a fire or monitor temperature set points. The adjustment of P1 is necessary to ensure that the base voltage of T1 is 0.5V lower than the emitter voltage at a slightly elevated temperature.
The temperature relay circuit typically consists of a temperature sensor, a transistor, and a relay. The temperature sensor can be a thermistor or an integrated circuit temperature sensor, which provides an output voltage that varies with temperature. This output is fed into the base of the transistor (T1), which acts as a switch to control the relay.
In this design, the potentiometer (P1) is used to fine-tune the base voltage of the transistor. By adjusting P1, the voltage at the base of T1 can be set to be 0.5V less than the emitter voltage, ensuring that the transistor operates correctly within its active region. This precise adjustment is crucial for accurate temperature detection and relay operation.
When the temperature exceeds the predetermined threshold, the voltage from the temperature sensor will rise, causing the base-emitter junction of T1 to become forward-biased. This will allow current to flow through the collector-emitter path of the transistor, energizing the relay coil. The relay can then activate an alarm system or a fire suppression mechanism.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors to limit current, capacitors for stability, and diodes for flyback protection across the relay coil to prevent voltage spikes when the relay is de-energized. Proper layout and component selection are essential to ensure reliable operation and to minimize false triggering due to noise or transient signals.This is a design circuit for temperature relay that can be used to signal a fire or set point for temperature monitoring function. You need to adjust P1 so that T1?s base voltage is 0.5V smaller than the emitter voltage at a temperature a little bit..
🔗 External reference
The temperature relay circuit typically consists of a temperature sensor, a transistor, and a relay. The temperature sensor can be a thermistor or an integrated circuit temperature sensor, which provides an output voltage that varies with temperature. This output is fed into the base of the transistor (T1), which acts as a switch to control the relay.
In this design, the potentiometer (P1) is used to fine-tune the base voltage of the transistor. By adjusting P1, the voltage at the base of T1 can be set to be 0.5V less than the emitter voltage, ensuring that the transistor operates correctly within its active region. This precise adjustment is crucial for accurate temperature detection and relay operation.
When the temperature exceeds the predetermined threshold, the voltage from the temperature sensor will rise, causing the base-emitter junction of T1 to become forward-biased. This will allow current to flow through the collector-emitter path of the transistor, energizing the relay coil. The relay can then activate an alarm system or a fire suppression mechanism.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors to limit current, capacitors for stability, and diodes for flyback protection across the relay coil to prevent voltage spikes when the relay is de-energized. Proper layout and component selection are essential to ensure reliable operation and to minimize false triggering due to noise or transient signals.This is a design circuit for temperature relay that can be used to signal a fire or set point for temperature monitoring function. You need to adjust P1 so that T1?s base voltage is 0.5V smaller than the emitter voltage at a temperature a little bit..
🔗 External reference