Temperature Sensor Current Loop Transmitter
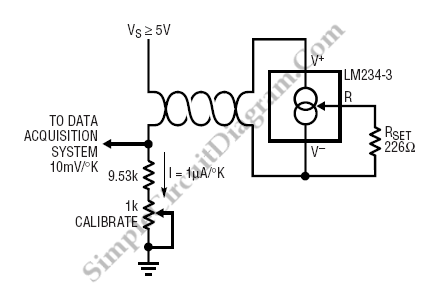
The LM134 is an effective temperature sensor due to its highly linear output characteristic. As a current output device, it remains unaffected by certain environmental factors.
The LM134 is a three-terminal device that operates as a current source, providing a linear output proportional to temperature changes. This characteristic makes it suitable for precise temperature measurement applications. The output current can be calibrated to represent temperature in various units, such as degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the configuration of the circuit.
To utilize the LM134 as a temperature sensor, it is essential to connect it in a circuit that can convert the current output into a measurable voltage. This is typically achieved by incorporating a resistor in series with the output. The value of this resistor can be selected based on the desired output voltage range. For instance, using a resistor of 1 kΩ will yield an output voltage of 1 mV per degree Celsius change in temperature, assuming a linear relationship.
In addition to the series resistor, it may be beneficial to include a buffer amplifier to isolate the LM134 from the load, ensuring that the output current remains stable. This buffer can be implemented using an operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower. This approach minimizes the loading effect on the LM134 and preserves the accuracy of the temperature readings.
Furthermore, the LM134 can be integrated into a more complex system that includes temperature compensation and signal conditioning circuitry. This may involve additional components such as thermistors or RTDs for enhanced accuracy in specific temperature ranges. The overall design should also consider the power supply requirements and ensure that the LM134 operates within its specified voltage limits to maintain linearity and reliability.
In summary, the LM134 is a versatile and reliable temperature sensor that leverages its linear output characteristic for accurate temperature measurement. Proper circuit design and component selection are crucial to optimize its performance in various applications.LM134 makes a good temperature sensor because it has a highly linear output characteristic. Because it is a current output device and is therefore not affected.. 🔗 External reference
The LM134 is a three-terminal device that operates as a current source, providing a linear output proportional to temperature changes. This characteristic makes it suitable for precise temperature measurement applications. The output current can be calibrated to represent temperature in various units, such as degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the configuration of the circuit.
To utilize the LM134 as a temperature sensor, it is essential to connect it in a circuit that can convert the current output into a measurable voltage. This is typically achieved by incorporating a resistor in series with the output. The value of this resistor can be selected based on the desired output voltage range. For instance, using a resistor of 1 kΩ will yield an output voltage of 1 mV per degree Celsius change in temperature, assuming a linear relationship.
In addition to the series resistor, it may be beneficial to include a buffer amplifier to isolate the LM134 from the load, ensuring that the output current remains stable. This buffer can be implemented using an operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower. This approach minimizes the loading effect on the LM134 and preserves the accuracy of the temperature readings.
Furthermore, the LM134 can be integrated into a more complex system that includes temperature compensation and signal conditioning circuitry. This may involve additional components such as thermistors or RTDs for enhanced accuracy in specific temperature ranges. The overall design should also consider the power supply requirements and ensure that the LM134 operates within its specified voltage limits to maintain linearity and reliability.
In summary, the LM134 is a versatile and reliable temperature sensor that leverages its linear output characteristic for accurate temperature measurement. Proper circuit design and component selection are crucial to optimize its performance in various applications.LM134 makes a good temperature sensor because it has a highly linear output characteristic. Because it is a current output device and is therefore not affected.. 🔗 External reference