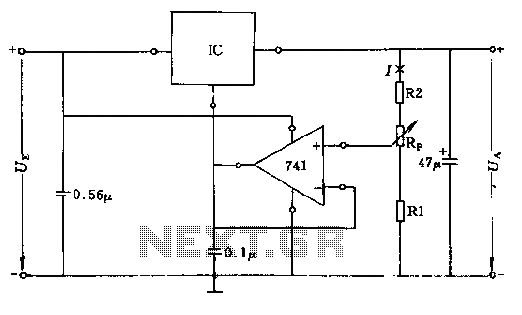
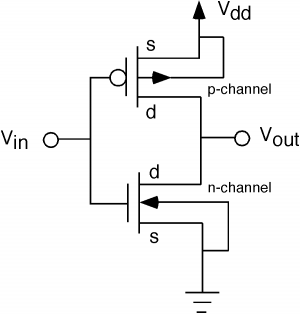
The basic form of frequency equalization circuit
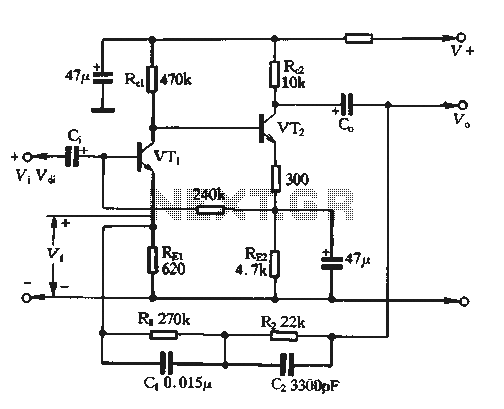
The feedback voltage (Vf) is derived from the output voltage (Vo) through an EQ network. The input voltage (Vf) is related to the subtraction process, yielding a pure input voltage for the circuit, which is associated with the tandem type negative voltage feedback coefficient. The relationship is expressed as B = Vf / Vo = REI / Zm + REIo, where ZEQ represents the total frequency characteristic impedance of the balanced network. In the absence of negative feedback, Vf equals 0V, and the input voltage (vi) is at a specified level. At this point, the voltage magnification is defined as V = Vo / Vdi.
The circuit described involves a feedback mechanism that utilizes the EQ network to stabilize the output voltage by adjusting the input voltage. The feedback voltage (Vf) is critical in controlling the gain of the system, which is represented by the coefficient B. This coefficient is a ratio of the feedback voltage to the output voltage, indicating the effectiveness of the feedback loop in maintaining desired performance characteristics.
The equation B = Vf / Vo illustrates the relationship between the output voltage and the feedback voltage, where REI denotes the resistance in the feedback path, Zm represents a load impedance, and REIo is an additional resistance that contributes to the feedback loop. The total frequency characteristic impedance (ZEQ) of the balanced network plays a significant role in determining the frequency response of the circuit, impacting how the circuit behaves under varying signal conditions.
When the circuit operates without negative feedback, the feedback voltage (Vf) is zero, indicating that the circuit is in an open-loop configuration. In this state, the input voltage (vi) is maintained at a specific level, which allows for an assessment of the circuit's natural gain. The voltage magnification, expressed as V = Vo / Vdi, provides insights into the amplification capabilities of the circuit, highlighting the importance of feedback in achieving stable and predictable performance.
In summary, the circuit's feedback mechanism, characterized by the EQ network and the associated equations, is essential for optimizing voltage control and enhancing the overall functionality of the electronic system. The interplay between the feedback voltage, output voltage, and various resistances defines the operational dynamics of the circuit, ensuring effective performance across different conditions.The figure for the feedback voltage Vf, it is taken from the output voltage Vo by EQ network. Input voltage Vf i and subtraction to give pure input voltage of the circuit belongs Vdjo tandem type negative voltage feedback coefficient B Vf / Vo = REI / Zm + REIo where ZEQ total frequency characteristic impedance balanced network. When the circuit without negative feedback, Vf = OV, V & vi = 'At this point the voltage magnification V- Vo / Vdi.
The circuit described involves a feedback mechanism that utilizes the EQ network to stabilize the output voltage by adjusting the input voltage. The feedback voltage (Vf) is critical in controlling the gain of the system, which is represented by the coefficient B. This coefficient is a ratio of the feedback voltage to the output voltage, indicating the effectiveness of the feedback loop in maintaining desired performance characteristics.
The equation B = Vf / Vo illustrates the relationship between the output voltage and the feedback voltage, where REI denotes the resistance in the feedback path, Zm represents a load impedance, and REIo is an additional resistance that contributes to the feedback loop. The total frequency characteristic impedance (ZEQ) of the balanced network plays a significant role in determining the frequency response of the circuit, impacting how the circuit behaves under varying signal conditions.
When the circuit operates without negative feedback, the feedback voltage (Vf) is zero, indicating that the circuit is in an open-loop configuration. In this state, the input voltage (vi) is maintained at a specific level, which allows for an assessment of the circuit's natural gain. The voltage magnification, expressed as V = Vo / Vdi, provides insights into the amplification capabilities of the circuit, highlighting the importance of feedback in achieving stable and predictable performance.
In summary, the circuit's feedback mechanism, characterized by the EQ network and the associated equations, is essential for optimizing voltage control and enhancing the overall functionality of the electronic system. The interplay between the feedback voltage, output voltage, and various resistances defines the operational dynamics of the circuit, ensuring effective performance across different conditions.The figure for the feedback voltage Vf, it is taken from the output voltage Vo by EQ network. Input voltage Vf i and subtraction to give pure input voltage of the circuit belongs Vdjo tandem type negative voltage feedback coefficient B Vf / Vo = REI / Zm + REIo where ZEQ total frequency characteristic impedance balanced network. When the circuit without negative feedback, Vf = OV, V & vi = 'At this point the voltage magnification V- Vo / Vdi.