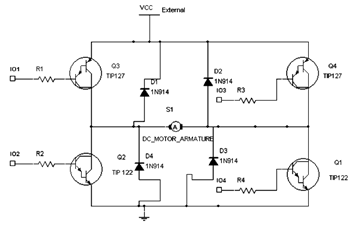
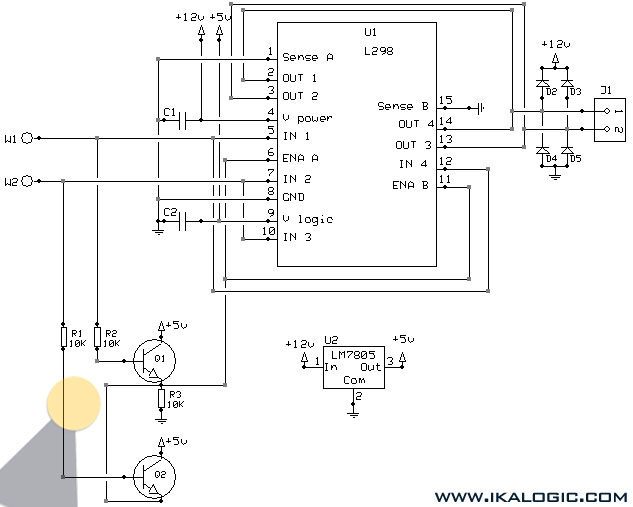
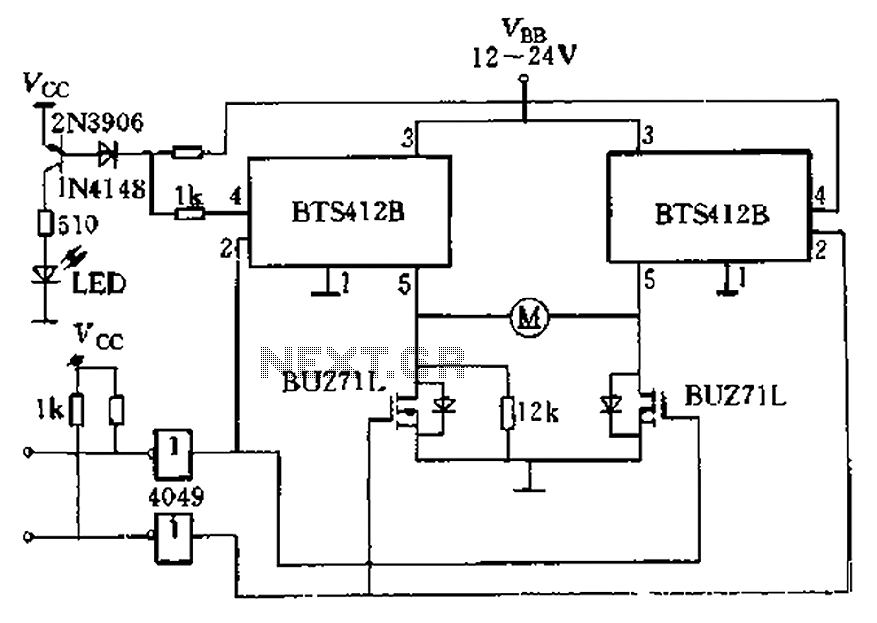
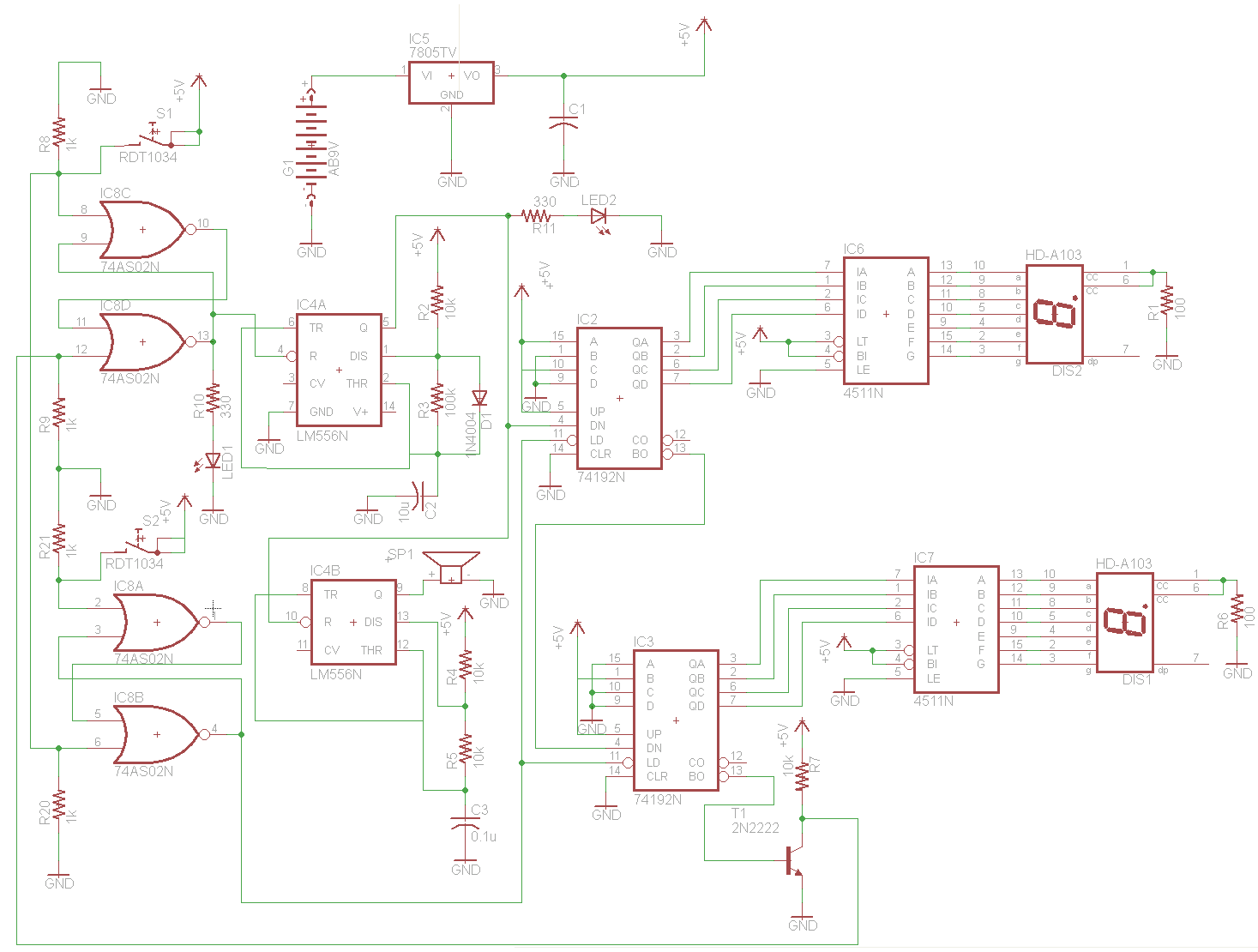
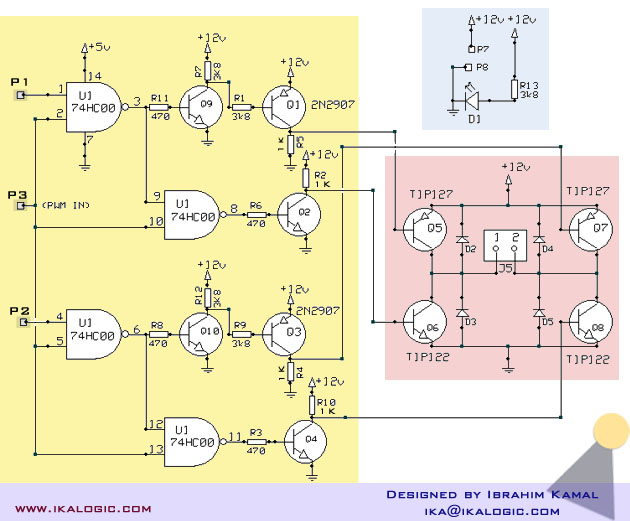
The H-Bridge
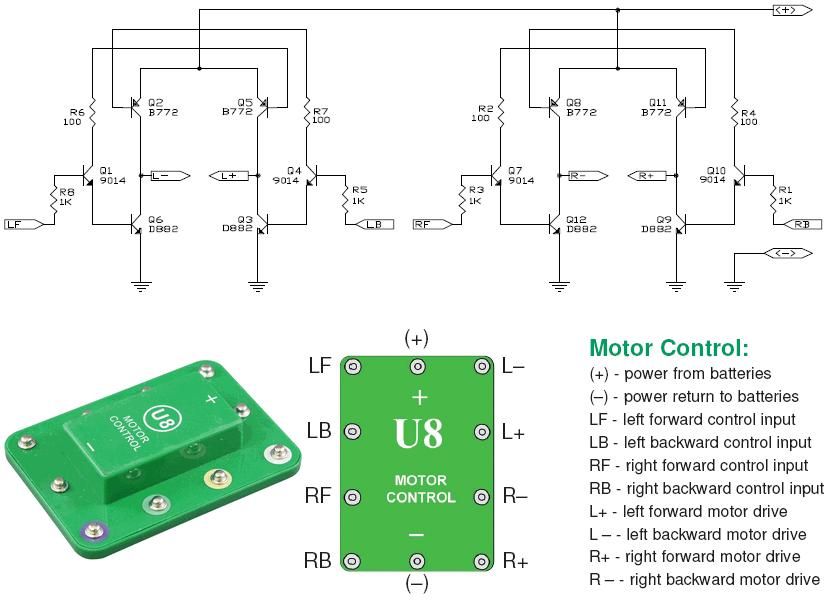
This is the Snap Circuits Motor Control IC, also known as an H-bridge. The electronic schematic of the Motor Control block is illustrated at the top of the figure.
The Snap Circuits Motor Control IC is designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors using an H-bridge configuration. An H-bridge consists of four switches that can be transistors, MOSFETs, or relays, which allow the voltage to be applied across the motor in either direction, thus enabling forward and reverse motion.
In the schematic, the inputs to the H-bridge are typically connected to a microcontroller or a control circuit that generates the necessary signals to switch the transistors on and off. The control signals determine the operation of the motor by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals, which in turn controls the speed of the motor.
The H-bridge may include additional features such as current sensing, thermal protection, and over-voltage protection to ensure safe operation. Often, diodes are included in the design to protect against back EMF generated by the motor when it is turned off or when it changes direction.
The layout of the circuit should ensure that the traces carrying high current are sufficiently wide to handle the load without overheating, and the ground connections should be robust to minimize noise and ensure stable operation. Proper decoupling capacitors may also be placed near the power supply pins to filter out any voltage spikes.
Overall, the Snap Circuits Motor Control IC is a versatile component for educational projects and prototyping, allowing users to easily integrate motor control functionality into their designs.This is the Snap Circuits Motor Control IC, or H-bridge. At the top of the figure you can see the electronic schematic of the Motor Control block. On.. 🔗 External reference
The Snap Circuits Motor Control IC is designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors using an H-bridge configuration. An H-bridge consists of four switches that can be transistors, MOSFETs, or relays, which allow the voltage to be applied across the motor in either direction, thus enabling forward and reverse motion.
In the schematic, the inputs to the H-bridge are typically connected to a microcontroller or a control circuit that generates the necessary signals to switch the transistors on and off. The control signals determine the operation of the motor by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals, which in turn controls the speed of the motor.
The H-bridge may include additional features such as current sensing, thermal protection, and over-voltage protection to ensure safe operation. Often, diodes are included in the design to protect against back EMF generated by the motor when it is turned off or when it changes direction.
The layout of the circuit should ensure that the traces carrying high current are sufficiently wide to handle the load without overheating, and the ground connections should be robust to minimize noise and ensure stable operation. Proper decoupling capacitors may also be placed near the power supply pins to filter out any voltage spikes.
Overall, the Snap Circuits Motor Control IC is a versatile component for educational projects and prototyping, allowing users to easily integrate motor control functionality into their designs.This is the Snap Circuits Motor Control IC, or H-bridge. At the top of the figure you can see the electronic schematic of the Motor Control block. On.. 🔗 External reference