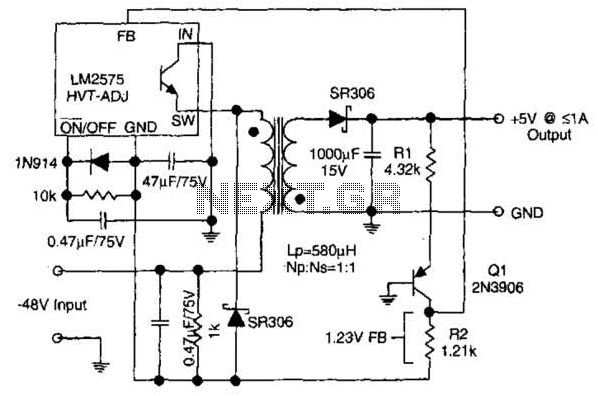
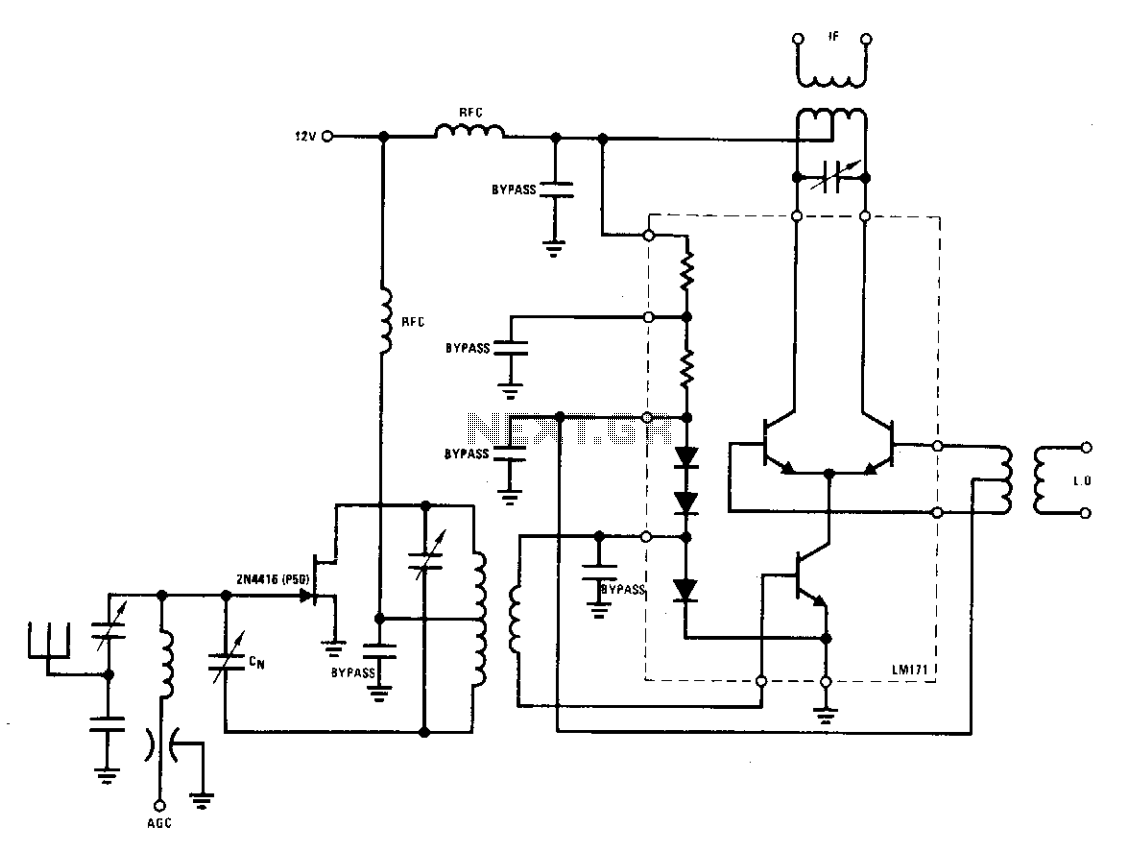
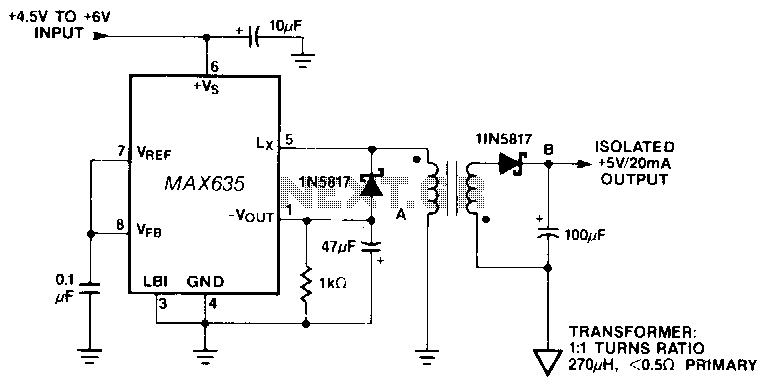
The Output Adjustable Flyback Converter
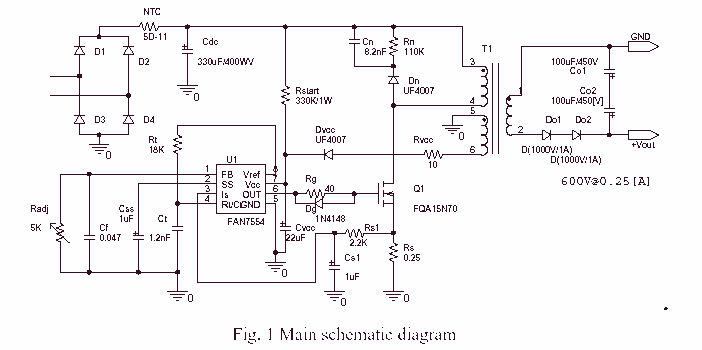
A high voltage step-up DC power supply using adjustable flyback conversion.
The described circuit is a high voltage step-up DC power supply that employs an adjustable flyback converter topology. Flyback converters are widely used in applications requiring electrical isolation and voltage transformation. The circuit operates by storing energy in a magnetic field within a transformer during the switch-on period and then releasing that energy to the output during the switch-off period.
Key components of the circuit include a power switch (typically a MOSFET), a flyback transformer, a diode for rectification, and output filtering capacitors. The power switch is controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which adjusts the duty cycle to regulate the output voltage. The flyback transformer not only steps up the voltage but also provides isolation between the input and output.
The adjustable feature of the converter can be achieved through feedback mechanisms that monitor the output voltage and adjust the PWM signal accordingly. This is often implemented using an operational amplifier (op-amp) in conjunction with a voltage divider from the output. The feedback loop ensures that variations in load or input voltage do not affect the output voltage significantly.
The output stage typically includes a rectifier diode to convert the high-frequency AC output from the transformer into a DC voltage, followed by smoothing capacitors to filter out voltage ripples. The choice of the flyback transformer is critical, as it must be designed to handle the required voltage and current levels while maintaining efficiency.
Safety considerations are paramount in high voltage applications. Proper insulation, component ratings, and protective circuitry, such as over-voltage and over-current protection, must be incorporated to prevent damage and ensure safe operation.
Overall, this high voltage step-up DC power supply design is suitable for applications requiring isolated high voltage outputs, such as in testing environments, medical devices, and high voltage laboratory equipment.A high voltage step-up DC power supply using adjustable flyback conversion. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a high voltage step-up DC power supply that employs an adjustable flyback converter topology. Flyback converters are widely used in applications requiring electrical isolation and voltage transformation. The circuit operates by storing energy in a magnetic field within a transformer during the switch-on period and then releasing that energy to the output during the switch-off period.
Key components of the circuit include a power switch (typically a MOSFET), a flyback transformer, a diode for rectification, and output filtering capacitors. The power switch is controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which adjusts the duty cycle to regulate the output voltage. The flyback transformer not only steps up the voltage but also provides isolation between the input and output.
The adjustable feature of the converter can be achieved through feedback mechanisms that monitor the output voltage and adjust the PWM signal accordingly. This is often implemented using an operational amplifier (op-amp) in conjunction with a voltage divider from the output. The feedback loop ensures that variations in load or input voltage do not affect the output voltage significantly.
The output stage typically includes a rectifier diode to convert the high-frequency AC output from the transformer into a DC voltage, followed by smoothing capacitors to filter out voltage ripples. The choice of the flyback transformer is critical, as it must be designed to handle the required voltage and current levels while maintaining efficiency.
Safety considerations are paramount in high voltage applications. Proper insulation, component ratings, and protective circuitry, such as over-voltage and over-current protection, must be incorporated to prevent damage and ensure safe operation.
Overall, this high voltage step-up DC power supply design is suitable for applications requiring isolated high voltage outputs, such as in testing environments, medical devices, and high voltage laboratory equipment.A high voltage step-up DC power supply using adjustable flyback conversion. 🔗 External reference