400mA Micropower Synchronous Step-Up DC/DC Converter with Output Disconnect
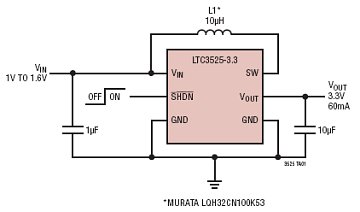
The LTC3525-3/LTC3525-3.3/LTC3525-5 are high-efficiency synchronous step-up DC/DC converters with output disconnect capability that can operate with an input voltage as low as 1V. These converters provide a compact and efficient alternative to charge pumps for single-cell or dual-cell alkaline or Li-Ion applications, requiring only three small external components. The LTC3525 is available in fixed output voltages of 3V, 3.3V, or 5V. The device features a 0.5Ω N-channel MOSFET switch and a 0.8Ω P-channel synchronous rectifier. The peak switch current ranges from 150mA to 400mA, depending on the load, which enhances efficiency. The quiescent current is an ultra-low 7µA, maximizing battery life in portable applications.
The LTC3525 series of DC/DC converters is designed to efficiently boost low input voltages, making them well-suited for applications where power sources are limited, such as in portable devices powered by single or dual-cell batteries. The synchronous step-up architecture allows for a reduction in the number of external components required, simplifying the design process and minimizing the board space needed for implementation.
The device's output disconnect feature enables the output voltage to be isolated from the input when the converter is not in operation, which is critical for battery-powered applications where minimizing leakage current is essential. The selection of fixed output voltages (3V, 3.3V, or 5V) allows designers to choose the most suitable option for their specific application requirements, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of electronic components.
The integration of a 0.5Ω N-channel MOSFET switch along with a 0.8Ω P-channel synchronous rectifier contributes to the overall efficiency of the converter by minimizing conduction losses during operation. The peak switch current capability of 150mA to 400mA enables the converter to handle varying load conditions effectively, ensuring stable output voltage even under dynamic load changes.
The extremely low quiescent current of 7µA is particularly advantageous for battery-operated devices, as it significantly extends battery life when the device is in standby mode. This feature is crucial for applications that require long periods of operation without frequent battery replacement or recharging.
Overall, the LTC3525 series provides a reliable and efficient solution for boosting low input voltages in a compact package, making it an ideal choice for a variety of portable electronic applications.The LTC ®3525-3/LTC3525-3. 3/LTC3525-5 are high efficiency synchronous step-up DC/DC converters with output disconnect that can start up with an input as low as 1V. They offer a compact, high efficiency alternative to charge pumps in single cell or dual cell alkaline or Li-Ion applications.
Only three small external components are required. The LTC 3525 is offered in fixed output voltages of 3V, 3. 3V or 5V. The device includes a 0. 5 © N-channel MOSFET switch and a 0. 8 © P-channel synchronous rectifier. Peak switch current ranges from 150mA to 400mA, depending on load, providing enhanced efficiency. Quiescent current is an ultralow 7 A, maximizing battery life in portable applications. 🔗 External reference
The LTC3525 series of DC/DC converters is designed to efficiently boost low input voltages, making them well-suited for applications where power sources are limited, such as in portable devices powered by single or dual-cell batteries. The synchronous step-up architecture allows for a reduction in the number of external components required, simplifying the design process and minimizing the board space needed for implementation.
The device's output disconnect feature enables the output voltage to be isolated from the input when the converter is not in operation, which is critical for battery-powered applications where minimizing leakage current is essential. The selection of fixed output voltages (3V, 3.3V, or 5V) allows designers to choose the most suitable option for their specific application requirements, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of electronic components.
The integration of a 0.5Ω N-channel MOSFET switch along with a 0.8Ω P-channel synchronous rectifier contributes to the overall efficiency of the converter by minimizing conduction losses during operation. The peak switch current capability of 150mA to 400mA enables the converter to handle varying load conditions effectively, ensuring stable output voltage even under dynamic load changes.
The extremely low quiescent current of 7µA is particularly advantageous for battery-operated devices, as it significantly extends battery life when the device is in standby mode. This feature is crucial for applications that require long periods of operation without frequent battery replacement or recharging.
Overall, the LTC3525 series provides a reliable and efficient solution for boosting low input voltages in a compact package, making it an ideal choice for a variety of portable electronic applications.The LTC ®3525-3/LTC3525-3. 3/LTC3525-5 are high efficiency synchronous step-up DC/DC converters with output disconnect that can start up with an input as low as 1V. They offer a compact, high efficiency alternative to charge pumps in single cell or dual cell alkaline or Li-Ion applications.
Only three small external components are required. The LTC 3525 is offered in fixed output voltages of 3V, 3. 3V or 5V. The device includes a 0. 5 © N-channel MOSFET switch and a 0. 8 © P-channel synchronous rectifier. Peak switch current ranges from 150mA to 400mA, depending on load, providing enhanced efficiency. Quiescent current is an ultralow 7 A, maximizing battery life in portable applications. 🔗 External reference