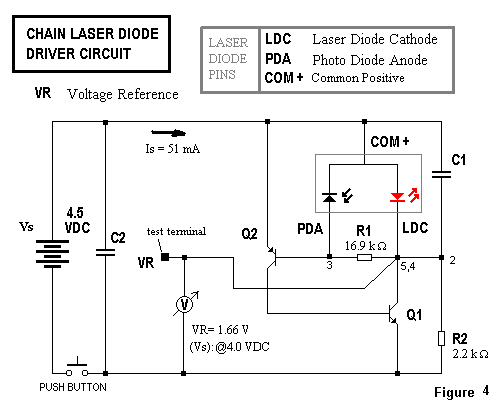
Thermoelectric Heat Pump for Laser Diodes Stabilization
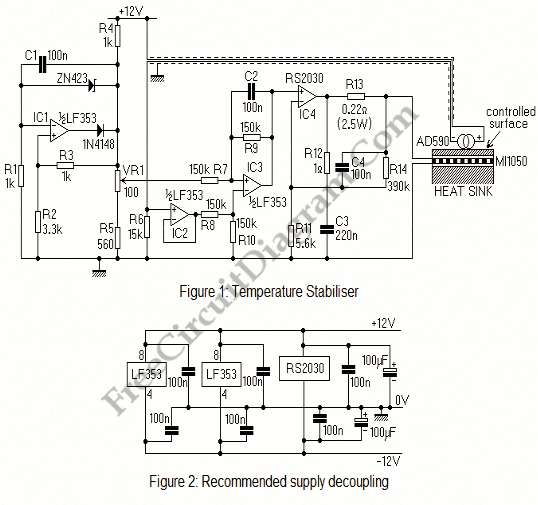
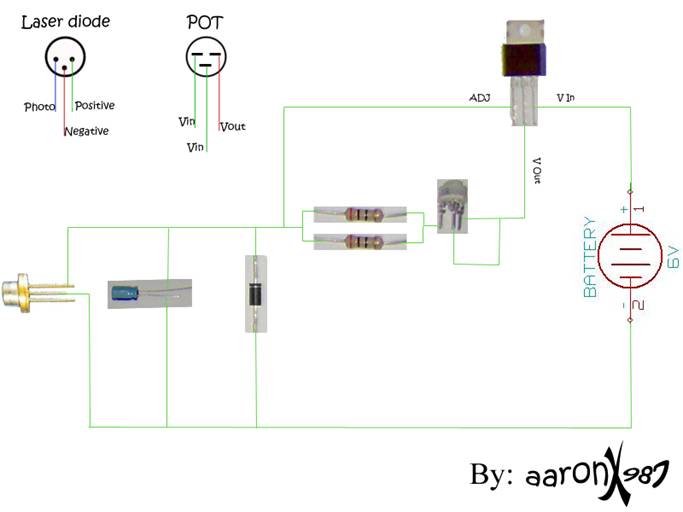
Semiconductor laser diodes are typically driven by current sources. However, the output power is significantly influenced by the temperature of the device.
Semiconductor laser diodes are essential components in various applications, including optical communication, laser printing, and medical devices. These diodes operate based on the principle of electroluminescence, where electrons recombine with holes within the semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons. The output power of a semiconductor laser diode is primarily controlled by the current supplied to it; however, it is crucial to recognize that the performance is also heavily influenced by the operating temperature.
As the temperature of the semiconductor laser diode increases, several factors contribute to a decrease in output power. The bandgap energy of the semiconductor material decreases with rising temperature, which affects the efficiency of the electron-hole recombination process. Additionally, increased temperature can lead to a higher rate of non-radiative recombination processes, further reducing the number of photons emitted. Consequently, maintaining an optimal operating temperature is vital for achieving consistent and reliable performance from semiconductor laser diodes.
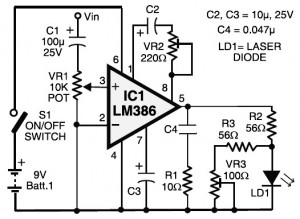
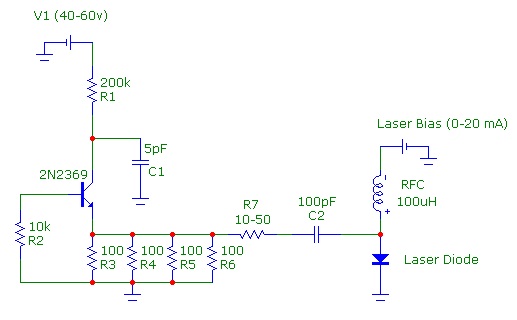
To mitigate the effects of temperature on output power, various thermal management techniques can be employed. These include the use of heat sinks, thermoelectric coolers, and active temperature control circuits. Implementing these methods ensures that the laser diode operates within its specified temperature range, thereby enhancing its efficiency and longevity. Furthermore, feedback mechanisms can be integrated into the circuit design to monitor temperature and adjust the driving current accordingly, ensuring stable output power across varying environmental conditions.Usually, semiconductor laser diodes are operated from current drives. Unfortunately, The output power is strongly dependent on the device temperature ? a. 🔗 External reference
Semiconductor laser diodes are essential components in various applications, including optical communication, laser printing, and medical devices. These diodes operate based on the principle of electroluminescence, where electrons recombine with holes within the semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons. The output power of a semiconductor laser diode is primarily controlled by the current supplied to it; however, it is crucial to recognize that the performance is also heavily influenced by the operating temperature.
As the temperature of the semiconductor laser diode increases, several factors contribute to a decrease in output power. The bandgap energy of the semiconductor material decreases with rising temperature, which affects the efficiency of the electron-hole recombination process. Additionally, increased temperature can lead to a higher rate of non-radiative recombination processes, further reducing the number of photons emitted. Consequently, maintaining an optimal operating temperature is vital for achieving consistent and reliable performance from semiconductor laser diodes.
To mitigate the effects of temperature on output power, various thermal management techniques can be employed. These include the use of heat sinks, thermoelectric coolers, and active temperature control circuits. Implementing these methods ensures that the laser diode operates within its specified temperature range, thereby enhancing its efficiency and longevity. Furthermore, feedback mechanisms can be integrated into the circuit design to monitor temperature and adjust the driving current accordingly, ensuring stable output power across varying environmental conditions.Usually, semiconductor laser diodes are operated from current drives. Unfortunately, The output power is strongly dependent on the device temperature ? a. 🔗 External reference