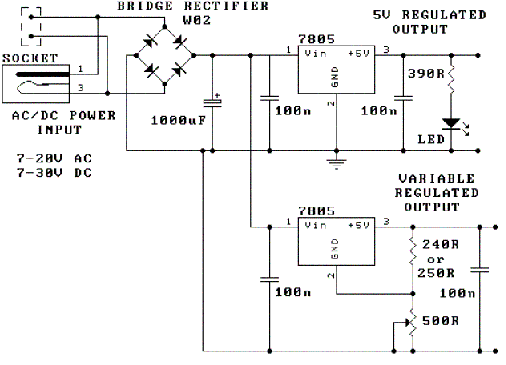
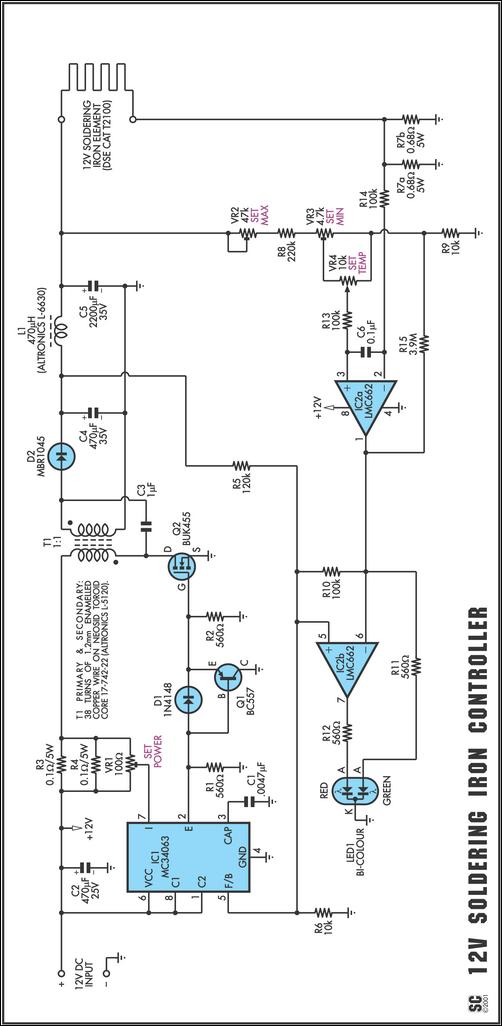
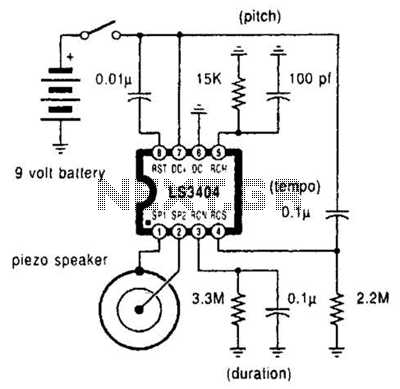
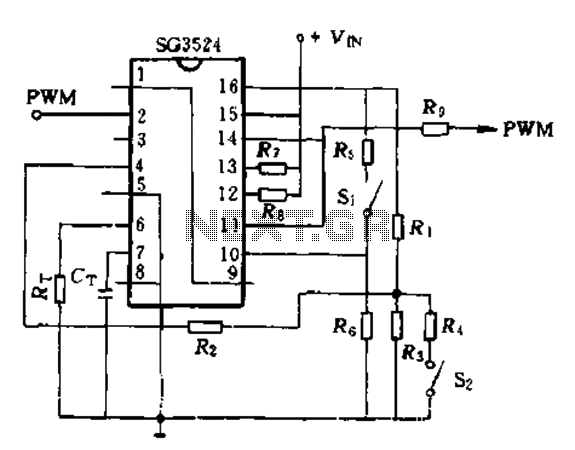
Thyristor cascade speed control circuit
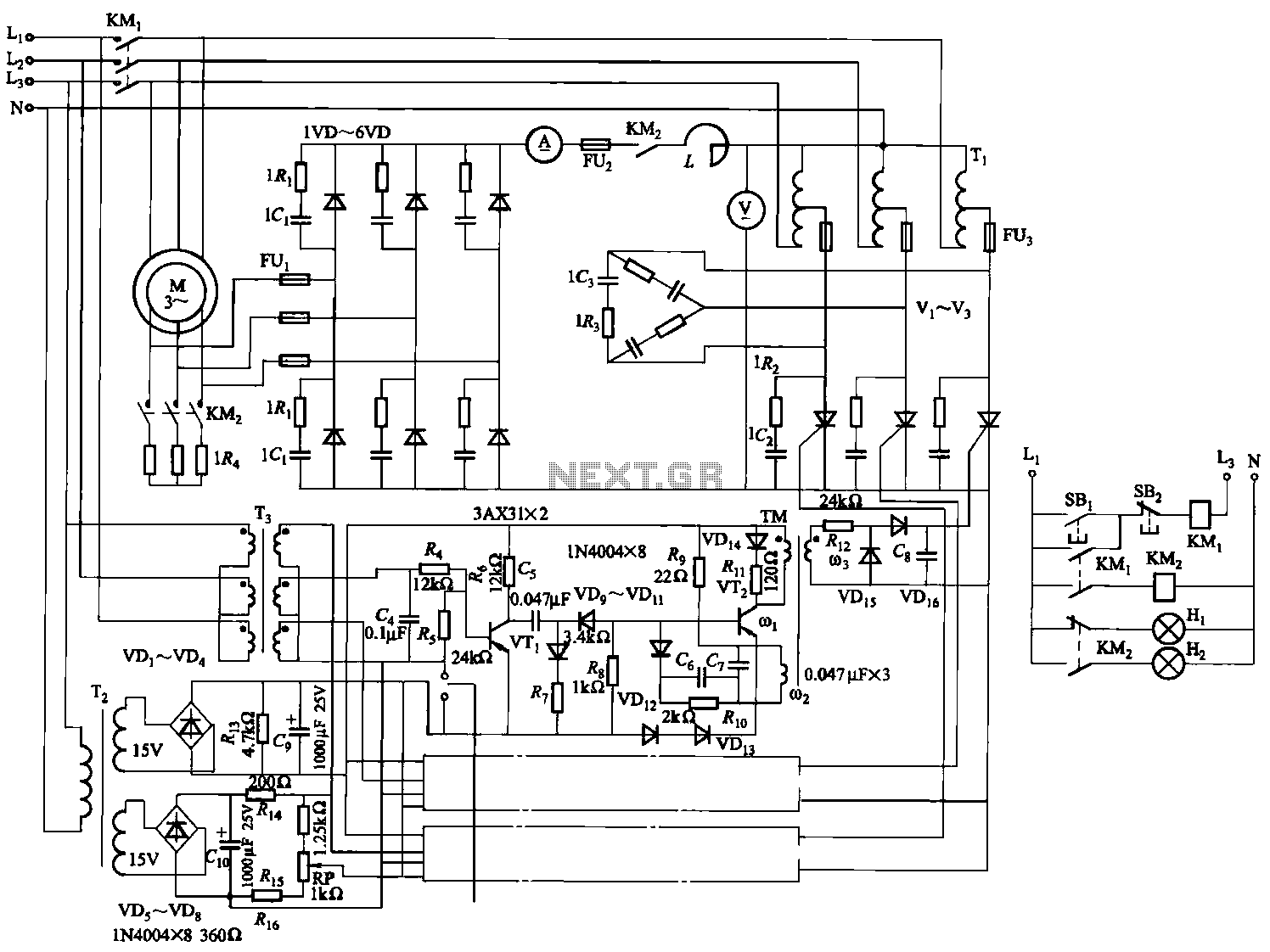
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-170 illustrates a wound rotor induction motor operating at various speeds, with a voltage (turn difference frequency EMF) U induced in the rotor. The rotor open circuit voltage is represented as Uo (Us0). A three-phase voltage is converted into a DC voltage (UD) through a bridge rectifier. Subsequently, this DC voltage is transformed back into AC voltage by an inverter, which incorporates a feedback network from the inverter transformer. The inverter voltage (Up) can be seen as an addition to the rotor circuit EMF. By adjusting the inverter control variable angle (Lu), the magnitude of Up can be modified to facilitate speed control.
The circuit operates on the principle of a wound rotor induction motor, which allows for variable speed operation by manipulating the rotor's electrical characteristics. The induction motor generates an electromotive force (EMF) in the rotor due to the interaction between the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator and the rotor's windings. The induced voltage U reflects the difference in frequency between the stator and rotor, which is essential for determining the motor's operational speed.
The bridge rectifier plays a critical role in converting the three-phase AC voltage to a stable DC voltage (UD), which is necessary for the inverter's operation. This inverter is responsible for converting the DC voltage back to AC voltage, enabling the motor to operate under different frequency conditions. The feedback network from the inverter transformer is crucial for maintaining stability and efficiency in the system, as it allows for real-time adjustments based on the motor's performance.
The inverter voltage (Up) is added to the rotor circuit EMF, enhancing the overall voltage available to the rotor. By controlling the inverter angle (Lu), the system can effectively adjust the magnitude of Up, thereby allowing for precise speed control of the motor. This method of speed regulation is particularly advantageous in applications requiring variable speed operation, as it provides flexibility and efficiency in motor control. The overall design emphasizes the integration of power electronics with traditional motor systems, showcasing advancements in control strategies for induction motors.Circuit shown in Figure 3-170. Wound rotor induction electric motive at different speeds induced in the rotor voltage (turn difference frequency EMF) U. A s U, o (Us0 is sl when the rotor open circuit voltage). The three-phase voltage through a bridge rectifier into a DC voltage UD, UD and then by the inverter to AC inverter power, the inverter transformer feedback network. Then the inverter voltage Up can be viewed as added in the rotor circuit EMF. Inverse control variable inverter angle Lu, you can change the size of Up in order to achieve speed control.
The circuit operates on the principle of a wound rotor induction motor, which allows for variable speed operation by manipulating the rotor's electrical characteristics. The induction motor generates an electromotive force (EMF) in the rotor due to the interaction between the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator and the rotor's windings. The induced voltage U reflects the difference in frequency between the stator and rotor, which is essential for determining the motor's operational speed.
The bridge rectifier plays a critical role in converting the three-phase AC voltage to a stable DC voltage (UD), which is necessary for the inverter's operation. This inverter is responsible for converting the DC voltage back to AC voltage, enabling the motor to operate under different frequency conditions. The feedback network from the inverter transformer is crucial for maintaining stability and efficiency in the system, as it allows for real-time adjustments based on the motor's performance.
The inverter voltage (Up) is added to the rotor circuit EMF, enhancing the overall voltage available to the rotor. By controlling the inverter angle (Lu), the system can effectively adjust the magnitude of Up, thereby allowing for precise speed control of the motor. This method of speed regulation is particularly advantageous in applications requiring variable speed operation, as it provides flexibility and efficiency in motor control. The overall design emphasizes the integration of power electronics with traditional motor systems, showcasing advancements in control strategies for induction motors.Circuit shown in Figure 3-170. Wound rotor induction electric motive at different speeds induced in the rotor voltage (turn difference frequency EMF) U. A s U, o (Us0 is sl when the rotor open circuit voltage). The three-phase voltage through a bridge rectifier into a DC voltage UD, UD and then by the inverter to AC inverter power, the inverter transformer feedback network. Then the inverter voltage Up can be viewed as added in the rotor circuit EMF. Inverse control variable inverter angle Lu, you can change the size of Up in order to achieve speed control.